* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Polycystic ovary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
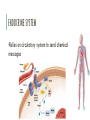
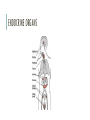
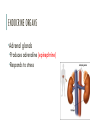
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pages 1031-1042 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM •Communication system that controls metabolism, growth and development with hormones •Maintains homeostasis •Hormones: chemical messengers that act on target cells •Glands: organs that secrete hormones ENDOCRINE SYSTEM •Relies on circulatory system to send chemical messages ENDOCRINE ORGANS ENDOCRINE ORGANS •Pituitary Gland •Produces hormones that affect other glands (thyroid, gonads, adrenal glands) •Controls growth, metabolism, sexual development, and reproduction •Known as “master gland” ENDOCRINE ORGANS Growth hormone or GH - GH stimulates growth in childhood and is important for maintaining a healthy body composition. In adults it is also important for maintaining muscle mass and bone mass. It can affect fat distribution in the body. Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH - ACTH stimulates production of cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cortisol, a so-called "stress hormone," is vital to survival. It helps maintain blood pressure and blood glucose levels. Thyroid-stimulating hormone or TSH - TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to make thyroid hormones, which, in turn, control (regulate) the body's metabolism, energy, growth and development, and nervous system activity. Luteinizing hormone or LH - LH regulates testosterone in men and estrogen in women. (gonadotropin) Follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH - FSH promotes sperm production in men and stimulates the ovaries to release eggs (ovulate) in women. LH and FSH work together to allow normal function of the ovaries or testes. (gonadotropin) Oxytocin - Oxytocin causes milk letdown in nursing mothers and contractions during childbirth. Antidiuretic hormone or ADH - ADH, also called vasopressin, is stored in the back part of the pituitary gland and regulates water balance. If this hormone is not secreted properly, this can lead to problems of sodium (salt) and water balance, and could also affect the kidneys so that they do not work as well. ENDOCRINE ORGANS •Thyroid •Regulates metabolism, growth, and development ENDOCRINE ORGANS •Adrenal glands •Produces adrenaline (epinephrine) •Responds to stress ENDOCRINE ORGANS •Pancreas •Produces insulin and glucagon •Regulates blood sugar levels ENDOCRINE ORGANS •Thymus •Stimulate formation of T-cells (immune cells) ENDOCRINE ORGANS •Gonads (ovaries and testes) •Produce sex hormones NERVOUS SYSTEM VS ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Nervous System Endocrine System Nerve impulses (electrical) Hormones (chemicals) Mode of Transmitted by transmission/transport neurons Transported by blood Speed Fast Slow Connectedness Highly connected Disconnected Signals