D502 – Endocrine System
... The pars nervosa contains the non-myelinated axons (why not-myelinated?) and nerve terminals of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract (as opposed to the portal system). The cells bodies of these fibers lie in the supraoptic (SO) and paraventricular (PV) nuclei of the hypothalamus. The nerve terminals of ...
... The pars nervosa contains the non-myelinated axons (why not-myelinated?) and nerve terminals of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract (as opposed to the portal system). The cells bodies of these fibers lie in the supraoptic (SO) and paraventricular (PV) nuclei of the hypothalamus. The nerve terminals of ...
1 GI,ENDO Release of which of the following peptides leads to an
... gastrin also causes the pyloric sphincter to contract. It also may contribute to the increase in ileal and colonic motility as part of the gastroileal and gastrocolic reflexes, respectively. Gastrin-releasing peptide (choice C) mediates the neural release of gastrin. Antral enteric neurons that are ...
... gastrin also causes the pyloric sphincter to contract. It also may contribute to the increase in ileal and colonic motility as part of the gastroileal and gastrocolic reflexes, respectively. Gastrin-releasing peptide (choice C) mediates the neural release of gastrin. Antral enteric neurons that are ...
hormones
... 2. Skeletal muscle cells and liver cells: With glucagon’s help, glycogen is broken down into glucose. Muscle cells retain all the glucose they derive from this process, using it to power their own activities. Liver cells, meanwhile, move much of the glucose they liberate into general circulation. ...
... 2. Skeletal muscle cells and liver cells: With glucagon’s help, glycogen is broken down into glucose. Muscle cells retain all the glucose they derive from this process, using it to power their own activities. Liver cells, meanwhile, move much of the glucose they liberate into general circulation. ...
There are two types of glands: Endocrine Glands Hormones
... blood pressure and send a message to the brain. The brain will cause the heart to beat slower and thus decrease the blood pressure. Decreasing heart rate has a negative effect on blood pressure. ...
... blood pressure and send a message to the brain. The brain will cause the heart to beat slower and thus decrease the blood pressure. Decreasing heart rate has a negative effect on blood pressure. ...
Gastro17-GITractPt1
... Clinical Vignette: If a patient has a gall bladder stone and it gets inflamed and perforates posteriorly, the stones can get inside the duodenum. If the stone is large enough, it can obstruct the duodenum. It also stains the anterior surface of the duodenum postmortem Neck of the pancreas is l ...
... Clinical Vignette: If a patient has a gall bladder stone and it gets inflamed and perforates posteriorly, the stones can get inside the duodenum. If the stone is large enough, it can obstruct the duodenum. It also stains the anterior surface of the duodenum postmortem Neck of the pancreas is l ...
The Endocrine System
... Aldosterone is the major form Stimulates Na+ reabsorption from urine to blood Stimulates excretion of K + into urine Part of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone pathway – Decreased BP release of renin from kidney – Renin causes angiotensinogen angiotensin I – In lungs Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE ...
... Aldosterone is the major form Stimulates Na+ reabsorption from urine to blood Stimulates excretion of K + into urine Part of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone pathway – Decreased BP release of renin from kidney – Renin causes angiotensinogen angiotensin I – In lungs Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE ...
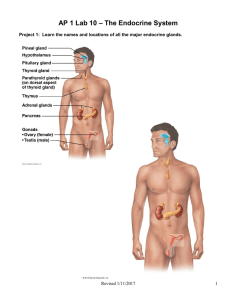
AP 1 Lab 10 – The Endocrine System
... Is called the "Master Gland" because it releases more Hs than any other and affects many other glands. _____________ Organ found adjacent to first part of the small intestine containing endocrine glands for control of blood sugar levels. _____________ This type of diabetes is caused by target tissue ...
... Is called the "Master Gland" because it releases more Hs than any other and affects many other glands. _____________ Organ found adjacent to first part of the small intestine containing endocrine glands for control of blood sugar levels. _____________ This type of diabetes is caused by target tissue ...
GI Anatomy Histology Lectures
... Sensory neurons receive information from sensory receptors in the mucosa and muscle. At least five different sensory receptors have been identified in the mucosa, which respond to mechanical, thermal, osmotic and chemical stimuli. Chemoreceptors sensitive to acid, glucose and amino acids have been d ...
... Sensory neurons receive information from sensory receptors in the mucosa and muscle. At least five different sensory receptors have been identified in the mucosa, which respond to mechanical, thermal, osmotic and chemical stimuli. Chemoreceptors sensitive to acid, glucose and amino acids have been d ...
DOC
... 13. The _______ nerve carries electrical signals from the brain to the stomach. 14. The hormone ______ regulates gastric secretion during the gastric phase of digestion. 15. Gastric motility ________ as the stomach begins to receive food. 16. The hormone ______ released by the duodenum cause gastri ...
... 13. The _______ nerve carries electrical signals from the brain to the stomach. 14. The hormone ______ regulates gastric secretion during the gastric phase of digestion. 15. Gastric motility ________ as the stomach begins to receive food. 16. The hormone ______ released by the duodenum cause gastri ...
The Digestive System
... • Because your cells need energy to function • Because your cells need raw materials to keep building your body ...
... • Because your cells need energy to function • Because your cells need raw materials to keep building your body ...
Digestion Secretions
... The Structure and Function of the Large Intestine The large intestine is approximately 1.5 m in length but is two to three times larger in diameter than the small intestine, about 7.6 cm. The large intestine consists of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anus (external opening). The small intestine does ...
... The Structure and Function of the Large Intestine The large intestine is approximately 1.5 m in length but is two to three times larger in diameter than the small intestine, about 7.6 cm. The large intestine consists of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anus (external opening). The small intestine does ...
1 1 CHAPTER 23, part b DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2. Pharynx Food
... Gastric glands in deep gastric pits secrete gastric juices Parietal cells: HCl – hydrochloric acid Chief cells: Pepsinogen that becomes pepsin which starts protein digestion Enteroendocrine glands (gut hormones) chemical messengers to stimulate digestion activities ...
... Gastric glands in deep gastric pits secrete gastric juices Parietal cells: HCl – hydrochloric acid Chief cells: Pepsinogen that becomes pepsin which starts protein digestion Enteroendocrine glands (gut hormones) chemical messengers to stimulate digestion activities ...
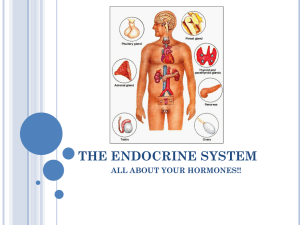
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... carried by blood to thyroid gland which then releases thyroxine which raises metabolism by stimulating sugar utilization by cells high levels of thyroxine cause pathway to be turned off, inhibiting release of TRH thyroxine contains calcitonin hormone acting on bone cells to lower level of calc ...
... carried by blood to thyroid gland which then releases thyroxine which raises metabolism by stimulating sugar utilization by cells high levels of thyroxine cause pathway to be turned off, inhibiting release of TRH thyroxine contains calcitonin hormone acting on bone cells to lower level of calc ...
Digestive apparatus - Portale Docenti
... Pancreas The pancreas rappresents is the sole mixed gland of an organism, composed by an exocrine and an endocrine part. It is closely related to duodenum and generally consists of a body and two lobules. ...
... Pancreas The pancreas rappresents is the sole mixed gland of an organism, composed by an exocrine and an endocrine part. It is closely related to duodenum and generally consists of a body and two lobules. ...
Endo Part 3 - Missouri State University
... • Stimulates ________synthesis. • Promotes maturation of nervous system. • Stimulates rate of cellular respiration by: – Production of uncoupling proteins. ...
... • Stimulates ________synthesis. • Promotes maturation of nervous system. • Stimulates rate of cellular respiration by: – Production of uncoupling proteins. ...
Exam 2 review - Iowa State University
... A. Fat around the abdominal organs B. Fat stored anywhere but in fat cells C. Fat that has gone outside of its area D. Fat in the liver 46. What are two risks of too much fat in the liver? A. Obesity & high blood pressure B. Loss of sensitivity to insulin & high blood triglycerides C. Visceral fat & ...
... A. Fat around the abdominal organs B. Fat stored anywhere but in fat cells C. Fat that has gone outside of its area D. Fat in the liver 46. What are two risks of too much fat in the liver? A. Obesity & high blood pressure B. Loss of sensitivity to insulin & high blood triglycerides C. Visceral fat & ...
Chapter 20 The Digestive System and Exercise in class
... Mechanical breakdown food and initial digestion of starch and lipids with salivary enzymes. Major site of food digestion and absorption; secretion of hormone and ...
... Mechanical breakdown food and initial digestion of starch and lipids with salivary enzymes. Major site of food digestion and absorption; secretion of hormone and ...
Chapter 10: The Endocrine System
... production, however, diabetes mellitus also results in the presence of sugar in the urine. Diabetes insipidus results from an under production of antidiuretic hormone, whereas diabetes mellitus results from either an under production of insulin or the failure of body cells to respond to insulin. ...
... production, however, diabetes mellitus also results in the presence of sugar in the urine. Diabetes insipidus results from an under production of antidiuretic hormone, whereas diabetes mellitus results from either an under production of insulin or the failure of body cells to respond to insulin. ...
Chapter 10: The Endocrine System
... production, however, diabetes mellitus also results in the presence of sugar in the urine. Diabetes insipidus results from an under production of antidiuretic hormone, whereas diabetes mellitus results from either an under production of insulin or the failure of body cells to respond to insulin. ...
... production, however, diabetes mellitus also results in the presence of sugar in the urine. Diabetes insipidus results from an under production of antidiuretic hormone, whereas diabetes mellitus results from either an under production of insulin or the failure of body cells to respond to insulin. ...
Your Digestive System and How It Works
... near the intestine. These small vessels carry the reformed fat to the veins of the chest, and the blood carries the fat to storage depots in different parts of the body. Vitamins. Another vital part of food that is absorbed through the small intestine are vitamins. The two types of vitamins are clas ...
... near the intestine. These small vessels carry the reformed fat to the veins of the chest, and the blood carries the fat to storage depots in different parts of the body. Vitamins. Another vital part of food that is absorbed through the small intestine are vitamins. The two types of vitamins are clas ...
NAME
... 12. The portion of the peritoneum that descends from the stomach and the transverse colon to form a lacy apron of fat over the intestines is called the _____. 13. The “building blocks” of protein molecules are _____. 14. The small intestine is made up of three sections called _____, _____, and _____ ...
... 12. The portion of the peritoneum that descends from the stomach and the transverse colon to form a lacy apron of fat over the intestines is called the _____. 13. The “building blocks” of protein molecules are _____. 14. The small intestine is made up of three sections called _____, _____, and _____ ...
Chapter 18 Essays
... adenohypophysis, amplification, arachadonic acid, autocrine, bound fraction (of hormone), calmodulin, catecholamine, cholesterol, circulating hormone (endocrine), thyroid follicles and colloid, downregulation, eicosanoid, endocrine, exocrine, free fraction (of hormone), glucocorticoids, gonadocortic ...
... adenohypophysis, amplification, arachadonic acid, autocrine, bound fraction (of hormone), calmodulin, catecholamine, cholesterol, circulating hormone (endocrine), thyroid follicles and colloid, downregulation, eicosanoid, endocrine, exocrine, free fraction (of hormone), glucocorticoids, gonadocortic ...
Enzymes, GI Function, and Autism: What You Should Know
... Only then can polyphenols be conjugated through methylation, sulfation, and glucoronidation in the intestine and liver. This is a detoxification process that limits toxic effects and facilitates elimination through bile or urine ...
... Only then can polyphenols be conjugated through methylation, sulfation, and glucoronidation in the intestine and liver. This is a detoxification process that limits toxic effects and facilitates elimination through bile or urine ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.