JMJ Name: March 20, 2017 7th Grade Science Miss Dixon Digestive
... 6. _____________________________ is the process by which a substance is released from an organ or gland to assist in digestion. 7. What are the glands called that produce saliva? ...
... 6. _____________________________ is the process by which a substance is released from an organ or gland to assist in digestion. 7. What are the glands called that produce saliva? ...
Unit 1 Lesson 4 The Digestive and Excretory Systems Essential
... •Triangular organ that lies between stomach and first part of small intestine •Role - produces enzymes that flow into the small intestine and help break down carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and nucleic acids •Remember = enzymes do not break down all food substances Ex. Fiber Fiber thickens material ...
... •Triangular organ that lies between stomach and first part of small intestine •Role - produces enzymes that flow into the small intestine and help break down carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and nucleic acids •Remember = enzymes do not break down all food substances Ex. Fiber Fiber thickens material ...
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The
... secretion of gastric juices is a continuous process with the rate increasing when food is eaten. In the horse's stomach food has a tendency to arrange itself in layers. The first food passes into the bottom region of the stomach with subsequent food lying on or around the first food to form layers. ...
... secretion of gastric juices is a continuous process with the rate increasing when food is eaten. In the horse's stomach food has a tendency to arrange itself in layers. The first food passes into the bottom region of the stomach with subsequent food lying on or around the first food to form layers. ...
Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Taste and
... 1. Is there anything else Bobbie can do to boost her fluid intake? 2. Could Bobbie be at risk for digestive problems? Explain why or why not. Classroom Activities ACTIVITY 1: GI TRIVIA TRIVIA QUESTIONS This initial phase begins the digestive process. ANSWER: cephalic phase Starting in the mouth, nam ...
... 1. Is there anything else Bobbie can do to boost her fluid intake? 2. Could Bobbie be at risk for digestive problems? Explain why or why not. Classroom Activities ACTIVITY 1: GI TRIVIA TRIVIA QUESTIONS This initial phase begins the digestive process. ANSWER: cephalic phase Starting in the mouth, nam ...
Frog Anatomy
... Right Atrium, and the Ventricle. • Stomach - Stores food and mixes it with enzymes to begin digestion. ...
... Right Atrium, and the Ventricle. • Stomach - Stores food and mixes it with enzymes to begin digestion. ...
The Digestive System
... either ____stores____ them or lets them through. The liver secretes and sends __bile__ to the small intestine to help with the breakdown of _fats_. Bile's main role is to _____emulsify_ fats which means to break them into _small_ droplets so the body can use them as nutrients. ...
... either ____stores____ them or lets them through. The liver secretes and sends __bile__ to the small intestine to help with the breakdown of _fats_. Bile's main role is to _____emulsify_ fats which means to break them into _small_ droplets so the body can use them as nutrients. ...
NutritionGlossary File
... A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction and is not changed by the reaction ...
... A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction and is not changed by the reaction ...
Large Intestine
... The cecum is that part of the large intestine that lies below the level of the junction of the ileum with the large intestine . It is a blind-ended pouch that is situated in the right iliac fossa. It is about 2.5 in. (6 cm) long and is completely covered with peritoneum. It possesses a considerable ...
... The cecum is that part of the large intestine that lies below the level of the junction of the ileum with the large intestine . It is a blind-ended pouch that is situated in the right iliac fossa. It is about 2.5 in. (6 cm) long and is completely covered with peritoneum. It possesses a considerable ...
DIRECTIONS: Each of the questions or incomplete statements
... (D) It is enhanced in the presence of circulating cholecystokinin (CCK). (E) It likely is mediated by nitric oxide (NO) and/or VIP. 19. All of the following statements about mucus are true EXCEPT: (A) Mucus contains polymeric neutral and acidic glycoproteins. (B) Mucus contains lipids to provide it ...
... (D) It is enhanced in the presence of circulating cholecystokinin (CCK). (E) It likely is mediated by nitric oxide (NO) and/or VIP. 19. All of the following statements about mucus are true EXCEPT: (A) Mucus contains polymeric neutral and acidic glycoproteins. (B) Mucus contains lipids to provide it ...
DMS131 Abdominal Sonography I Multiple
... 4. What do the superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein join together to form? a. celiac axis b. portal vein c. inferior vena cava d. main hepatic vein 5. The celiac axis is _______ to the origin of the superior mesenteric artery. a. cephalad b. caudal c. medial d. lateral 6. Which vessel lies ...
... 4. What do the superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein join together to form? a. celiac axis b. portal vein c. inferior vena cava d. main hepatic vein 5. The celiac axis is _______ to the origin of the superior mesenteric artery. a. cephalad b. caudal c. medial d. lateral 6. Which vessel lies ...
Indezine Template
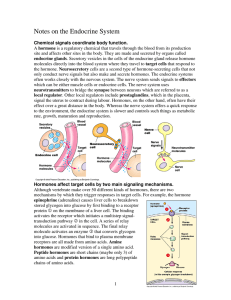
... ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Key role to secrete hormones • Hormones: are natural chemicals that exert their effects on specific tissues known as target tissues. • Endocrine Glands are ductless and must use the blood system to transport secreted hormones to target tissues ...
... ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Key role to secrete hormones • Hormones: are natural chemicals that exert their effects on specific tissues known as target tissues. • Endocrine Glands are ductless and must use the blood system to transport secreted hormones to target tissues ...
Notes on the Endocrine System
... Diabetes mellitus is a serious hormonal disease in which the body cells are unable to absorb glucose from the blood. It affects as many as 5 out of 100 people in the U.S. and Canada. The disease occurs when there is not enough insulin in the blood or when body cells do not respond normally to blood ...
... Diabetes mellitus is a serious hormonal disease in which the body cells are unable to absorb glucose from the blood. It affects as many as 5 out of 100 people in the U.S. and Canada. The disease occurs when there is not enough insulin in the blood or when body cells do not respond normally to blood ...
Digestive System
... – A, B, C, D, E • Cirrhosis – Progressive disease of the liver where scar tissue replaces normal tissue. – Blood flow is decreased causing body shutdown. ...
... – A, B, C, D, E • Cirrhosis – Progressive disease of the liver where scar tissue replaces normal tissue. – Blood flow is decreased causing body shutdown. ...
Endocrine System
... kidneys to resabsorb water • Polydipsia – excessive thirst • Polyphagia – excessive eating ...
... kidneys to resabsorb water • Polydipsia – excessive thirst • Polyphagia – excessive eating ...
Chapter 9: The Endocrine System
... metabolism and help resisting longterm stressors. Can even break down lipids and proteins to create more glucose. (humoral response and ACTH) ...
... metabolism and help resisting longterm stressors. Can even break down lipids and proteins to create more glucose. (humoral response and ACTH) ...
Comparative Digestive Systems
... most of their nutrients are already small enough to be absorbed into the cell • However, some, like the paramecium are able to bring in solid particles as food vacuoles. These use lysosomes (packed with hydrolytic enzymes) to breakdown the contents of the food vacuoles. ...
... most of their nutrients are already small enough to be absorbed into the cell • However, some, like the paramecium are able to bring in solid particles as food vacuoles. These use lysosomes (packed with hydrolytic enzymes) to breakdown the contents of the food vacuoles. ...
branches of the thoracoacromial trunk
... “Rule of 3’s” 3” long 3% of the population Within 3’ of the iliocecal junction 4 Parts of Duodenum “Superman Definitely Has it All” Superior Descending Horizontal Ascending ...
... “Rule of 3’s” 3” long 3% of the population Within 3’ of the iliocecal junction 4 Parts of Duodenum “Superman Definitely Has it All” Superior Descending Horizontal Ascending ...
Lesson 1 - I-Board Allied Schools
... hyperstimulation of the adrenal glands. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Diabetes mellitus is a condition that forms due to a lack of insulin secretion or insulin resistance. ...
... hyperstimulation of the adrenal glands. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Diabetes mellitus is a condition that forms due to a lack of insulin secretion or insulin resistance. ...
Test Review Key - Hartland High School
... 38. What two hormones are produced and released upon food entering the small intestine? Cholecystokinin and secretin 39. Explain the process of deglutition. What is the common name of deglutition? a. The soft palate raises, preventing food from entering the nasal cavity. b. The hyoid bone and the l ...
... 38. What two hormones are produced and released upon food entering the small intestine? Cholecystokinin and secretin 39. Explain the process of deglutition. What is the common name of deglutition? a. The soft palate raises, preventing food from entering the nasal cavity. b. The hyoid bone and the l ...
Digestion is fundamentally a three stage process that begins with
... vessels. These substances will go through scores of biochemical changes before they are eventually used by the cells of the body. These pancreatic enzymes are most effective when the pH is at the proper alkaline level. If the pancreas is unable to produce the necessary bicarbonate level or if it is ...
... vessels. These substances will go through scores of biochemical changes before they are eventually used by the cells of the body. These pancreatic enzymes are most effective when the pH is at the proper alkaline level. If the pancreas is unable to produce the necessary bicarbonate level or if it is ...
Anatomy Pre-Course Quiz
... The thoracic spine is located: Inferior to the lumbar spine and superior to the cervical spine Inferior to the cervical spine and superior to the lumbar spine Inferior to the lumbar spine and superior to the sacrum Inferior to the sacral spine and superior to the lumbar spine ...
... The thoracic spine is located: Inferior to the lumbar spine and superior to the cervical spine Inferior to the cervical spine and superior to the lumbar spine Inferior to the lumbar spine and superior to the sacrum Inferior to the sacral spine and superior to the lumbar spine ...
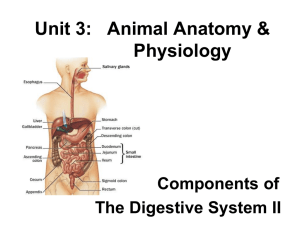
DigesCve System
... Ileum occupy the central and lower parts of the Abdominal cavity. • They are aPached to the posterior abdominal wall by a mesentery which allows considerable mobility of the loops of the small bowel. ...
... Ileum occupy the central and lower parts of the Abdominal cavity. • They are aPached to the posterior abdominal wall by a mesentery which allows considerable mobility of the loops of the small bowel. ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.