Nutrition and Metabolism
... CCK stimulates secretion of pancreatic juices and enzymes in response to fat. It causes contraction of the gallbladder (i.e., causes the gallbladder to squirt bile into the small intestine) and slows stomach emptying. 14. What causes the release of secretin? Secretin is secreted into the blood by S- ...
... CCK stimulates secretion of pancreatic juices and enzymes in response to fat. It causes contraction of the gallbladder (i.e., causes the gallbladder to squirt bile into the small intestine) and slows stomach emptying. 14. What causes the release of secretin? Secretin is secreted into the blood by S- ...
Digestive system
... •The first portion of the small intestine is the duodenum where acidic chyme from the stomach mixes with bile from the liver & gallbladder and digestive juices from the pancreas & intestine itself. Small Intestine: Chemical Digestion: The pancreas and gland cells of the small intestine secrete diges ...
... •The first portion of the small intestine is the duodenum where acidic chyme from the stomach mixes with bile from the liver & gallbladder and digestive juices from the pancreas & intestine itself. Small Intestine: Chemical Digestion: The pancreas and gland cells of the small intestine secrete diges ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... production. Cite two reasons that bovine growth hormone might not stimulate growth in people drinking the milk. Bovine growth hormone would probably not interact with receptors on target cells in humans, because bovine growth hormone probably has a slightly different shape than human growth hormone. ...
... production. Cite two reasons that bovine growth hormone might not stimulate growth in people drinking the milk. Bovine growth hormone would probably not interact with receptors on target cells in humans, because bovine growth hormone probably has a slightly different shape than human growth hormone. ...
Lecture Presentation Outline
... Over one hundred different enzymes participate in the digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and fat. Digestion in the mouth a. Chewing causes glands under the tongue to release saliva. b. Saliva lubricates food so that it can be swallowed. c. Saliva also contains salivary amylase and lipase. 1. Amyl ...
... Over one hundred different enzymes participate in the digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and fat. Digestion in the mouth a. Chewing causes glands under the tongue to release saliva. b. Saliva lubricates food so that it can be swallowed. c. Saliva also contains salivary amylase and lipase. 1. Amyl ...
MEN1 - NET Patient Foundation
... focus on the pituitary gland. This is quite painless, and is usually given for 5 days a week over 5 weeks, giving 25 treatments altogether. Each treatment is usually over in half an hour, and most patients can carry on their normal life throughout although they may tire more easily than usual. ...
... focus on the pituitary gland. This is quite painless, and is usually given for 5 days a week over 5 weeks, giving 25 treatments altogether. Each treatment is usually over in half an hour, and most patients can carry on their normal life throughout although they may tire more easily than usual. ...
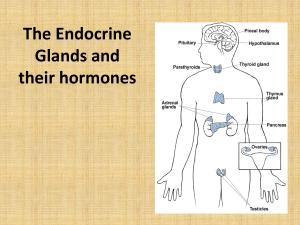
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... by a midline isthmus which lies anterior to the trachea. Although not shown on this torso model, attached to its posterior surface are four parathyroid glands. From Figure 17.10 in your Saladin text you should understand where these are located. In the abdomen of the torso model, identify the pancre ...
... by a midline isthmus which lies anterior to the trachea. Although not shown on this torso model, attached to its posterior surface are four parathyroid glands. From Figure 17.10 in your Saladin text you should understand where these are located. In the abdomen of the torso model, identify the pancre ...
endocrine system
... • Located in the neck, is the target gland of thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH) • When the thyroid is stimulated by TSH it releases the hormones Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4), which regulates the metabolic rate of your body tissues ...
... • Located in the neck, is the target gland of thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH) • When the thyroid is stimulated by TSH it releases the hormones Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4), which regulates the metabolic rate of your body tissues ...
How Gastric Bypass Rapidly Reverses Diabetes Symptoms
... A report in the September Cell Metabolism, a publication of Cell Press, offers new evidence to explain why those who undergo gastric bypass surgery often show greater control of their diabetes symptoms within days. It also helps to explain why lap-band surgery doesn't offer the same instant gratific ...
... A report in the September Cell Metabolism, a publication of Cell Press, offers new evidence to explain why those who undergo gastric bypass surgery often show greater control of their diabetes symptoms within days. It also helps to explain why lap-band surgery doesn't offer the same instant gratific ...
Endocrine Glands
... • Function: Increase blood calcium • Function: decrease blood levels by releasing the calcium calcium levels and blood from bones and re-absorbing it phosphate levels (by from the kidneys and intestines. helping them get deposited in bone, and by stimulating excretion of Calcium by kidneys) • Contro ...
... • Function: Increase blood calcium • Function: decrease blood levels by releasing the calcium calcium levels and blood from bones and re-absorbing it phosphate levels (by from the kidneys and intestines. helping them get deposited in bone, and by stimulating excretion of Calcium by kidneys) • Contro ...
Digestive System & Aging- Chpt 10
... blocking duct - can be life-threatening - if endocrine cells injured (diabetes mellitus) - exocrine cells--> fat, protein digestion ...
... blocking duct - can be life-threatening - if endocrine cells injured (diabetes mellitus) - exocrine cells--> fat, protein digestion ...
Post-Lab Information Sheet
... 5. The spleen is about the same color as the liver and is attached to the greater curvature of the stomach. It is associated with the circulatory system and functions in the destruction of blood cells and blood storage. A person can live without a spleen, but they're more likely to get sick as it he ...
... 5. The spleen is about the same color as the liver and is attached to the greater curvature of the stomach. It is associated with the circulatory system and functions in the destruction of blood cells and blood storage. A person can live without a spleen, but they're more likely to get sick as it he ...
GLANDS AT A GLANCE
... Location: scrotum/rear of the abdominal cavity not far below the spine. Appearance:egg-shaped/bean-shaped. Structures: seminiferous tubules for producing semen in each testicle, with attached duct (epididymis) to further concentrate and transport semen; follicles mature, erupt to produce one egg (ov ...
... Location: scrotum/rear of the abdominal cavity not far below the spine. Appearance:egg-shaped/bean-shaped. Structures: seminiferous tubules for producing semen in each testicle, with attached duct (epididymis) to further concentrate and transport semen; follicles mature, erupt to produce one egg (ov ...
the digestion of nutrients
... absorption. Sugars pass through the villi in the gut wall, straight into circulation via the venules (small, specifically shaped veins) within the villi. This is referred to as ‘simple passive transport’, which means they can just flow through the gut wall on their own and don’t require any specific ...
... absorption. Sugars pass through the villi in the gut wall, straight into circulation via the venules (small, specifically shaped veins) within the villi. This is referred to as ‘simple passive transport’, which means they can just flow through the gut wall on their own and don’t require any specific ...
Digestion - biologyquest
... - bile is stored in the gallbladder (found under the liver) and goes into the small intestine through a small tube b) Pancreas - small organ that lies below the stomach - pancreatic juice neutralizes the acid in the stomach enzymes - amylase breaks down starch - proteases break down protein - lipa ...
... - bile is stored in the gallbladder (found under the liver) and goes into the small intestine through a small tube b) Pancreas - small organ that lies below the stomach - pancreatic juice neutralizes the acid in the stomach enzymes - amylase breaks down starch - proteases break down protein - lipa ...
Name Period ______ Accelerated Biology The Circulatory and
... 29. Label the following terms on the illustration above; small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. 30. Food passes through many organs. Place the terms in order that shows the passage of nutrients along the alimentary canal; stomach, anus, small intestine, rectum, esophagus, mouth, large intes ...
... 29. Label the following terms on the illustration above; small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. 30. Food passes through many organs. Place the terms in order that shows the passage of nutrients along the alimentary canal; stomach, anus, small intestine, rectum, esophagus, mouth, large intes ...
AH100 – Medical Terminology
... The Endocrine System produces ____________________ that are released directly into the _____________________ ...
... The Endocrine System produces ____________________ that are released directly into the _____________________ ...
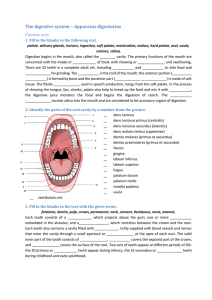
The digestive system – Apparatus digestorius
... The _____________ glands, which secrete into the mouth, are the first accessory organs to act on food. They secrete an enzyme (salivary amylase) that begins the digestion of starch. The remainder of the accessory organs is in the abdomen and secrete into the duodenum. The_________ is a large gland w ...
... The _____________ glands, which secrete into the mouth, are the first accessory organs to act on food. They secrete an enzyme (salivary amylase) that begins the digestion of starch. The remainder of the accessory organs is in the abdomen and secrete into the duodenum. The_________ is a large gland w ...
Digestive system simulation - UNT's College of Education
... What are the 2 major types of digestion? Where are those 2 types seen in the digestive ...
... What are the 2 major types of digestion? Where are those 2 types seen in the digestive ...
Digestive System
... The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum which is the first segment of the small intestine. The enzymes in the pancreas break down carbohydrates, fats, and, proteins. The pancreas makes insulin, and secretes it directly into the bloodstream. Insulin is the main hormone used f ...
... The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum which is the first segment of the small intestine. The enzymes in the pancreas break down carbohydrates, fats, and, proteins. The pancreas makes insulin, and secretes it directly into the bloodstream. Insulin is the main hormone used f ...
Chapter 17: Digestive System
... 2. Chyme is food substances that have been mixed with gastric juice. 3. Peristaltic waves push chyme toward the pylorus of the stomach. 4. Stomach contractions push chyme a little at a time into the duodenum and backwards into the stomach, mixing it further. 5. The lower esophageal sphincter prevent ...
... 2. Chyme is food substances that have been mixed with gastric juice. 3. Peristaltic waves push chyme toward the pylorus of the stomach. 4. Stomach contractions push chyme a little at a time into the duodenum and backwards into the stomach, mixing it further. 5. The lower esophageal sphincter prevent ...
Endocrine System
... destinations, endocrine glands are ductless. The endocrine glands secrete biologically active chemicals called hormones directly into the blood. Many endocrine glands are discrete organs whose primary functions are the production and secretion of hormones. The pancreas functions as both an exocrine ...
... destinations, endocrine glands are ductless. The endocrine glands secrete biologically active chemicals called hormones directly into the blood. Many endocrine glands are discrete organs whose primary functions are the production and secretion of hormones. The pancreas functions as both an exocrine ...
Endocrine System
... - Amines, thyroxine, peptide, & protein hormones b. Steroids: Gonadal & adrenocortical hormones c. Eicosanoids: Leukotrienes & prostaglandins - Biologically active lipids with local hormone-like activity 4. Mechanisms of Hormone action a. Direct gene activation (e.g. steroid hormones) b. 2nd messeng ...
... - Amines, thyroxine, peptide, & protein hormones b. Steroids: Gonadal & adrenocortical hormones c. Eicosanoids: Leukotrienes & prostaglandins - Biologically active lipids with local hormone-like activity 4. Mechanisms of Hormone action a. Direct gene activation (e.g. steroid hormones) b. 2nd messeng ...
Chapter 1 – Perspectives on Health and Nutrition
... The nutrients that are ready for absorption early are absorbed near the top of the gastrointestinal tract, and those that take longer to be digested are absorbed further down. Although much of the digestion of carbohydrates and proteins begins to take place in the mouth and stomach, respectively, th ...
... The nutrients that are ready for absorption early are absorbed near the top of the gastrointestinal tract, and those that take longer to be digested are absorbed further down. Although much of the digestion of carbohydrates and proteins begins to take place in the mouth and stomach, respectively, th ...
LabStructureListForMidterm
... Anterior Rectus Sheath *Rectus Abdominus Muscle Posterior Rectus Sheath Linea Alba- in center of anterior and posterior rectus sheath, above umbilicus, below umbilicus- only anterior sheath *Tendonis Insertion between each piece of the “6-pack” *Celiac Trunk- looks like a flower. 3 branches *Gastr ...
... Anterior Rectus Sheath *Rectus Abdominus Muscle Posterior Rectus Sheath Linea Alba- in center of anterior and posterior rectus sheath, above umbilicus, below umbilicus- only anterior sheath *Tendonis Insertion between each piece of the “6-pack” *Celiac Trunk- looks like a flower. 3 branches *Gastr ...
Digestion with blanks
... How is food moved along this canal? Draw a labelled diagram of the human digestive system. Identify these parts on a human torso. In which part of the digestive system is most food absorbed into the bloodstream? What is the role of the villi? How does their structure suit their function? What does b ...
... How is food moved along this canal? Draw a labelled diagram of the human digestive system. Identify these parts on a human torso. In which part of the digestive system is most food absorbed into the bloodstream? What is the role of the villi? How does their structure suit their function? What does b ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.