growth hormone (GH)
... a disease caused by low level of adrenal cortex hormones resulting in the loss of sodium and low blood pressure; this disease can be fatal. adrenal glands there are two adrenal glands located one on top of each kidney. Each of these glands are divided into two endocrine glands the inner adrenal medu ...
... a disease caused by low level of adrenal cortex hormones resulting in the loss of sodium and low blood pressure; this disease can be fatal. adrenal glands there are two adrenal glands located one on top of each kidney. Each of these glands are divided into two endocrine glands the inner adrenal medu ...
Lecture Outline ()
... • head trauma affects pituitary gland’s ability to secrete ADH – diabetes insipidus = chronic polyuria ...
... • head trauma affects pituitary gland’s ability to secrete ADH – diabetes insipidus = chronic polyuria ...
cells - LPS.org
... Depresses the immune system Promotes changes in cardiovascular, neural, and gastrointestinal function ...
... Depresses the immune system Promotes changes in cardiovascular, neural, and gastrointestinal function ...
Chapter 13 Endocrine System
... of sugars. When there is not enough insulin being produced you develop a condition called diabetes mellitus. ...
... of sugars. When there is not enough insulin being produced you develop a condition called diabetes mellitus. ...
Endocrine System Endocrine Vs Nervous System
... hormone called atrial natriuretic factor (ANF). This hormone inhibits the release of ADH by the posterior pituitary causing the kidneys to excrete excess water. Alcohol inhibits the release of ADH, causing the kidneys to produce dilute urine. ...
... hormone called atrial natriuretic factor (ANF). This hormone inhibits the release of ADH by the posterior pituitary causing the kidneys to excrete excess water. Alcohol inhibits the release of ADH, causing the kidneys to produce dilute urine. ...
USMLE Step 1 Web Prep — Mechanism of Hormone Action 152675
... be bound, reduces free fraction transiently, and more hormones will be secreted. Estrogen increases the circulating level of bound hormones. It won’t affect the free form (it’s regulated by feedback). Total hormones- mainly measure bound fractionnot good index to activity. Lutheal phase and pregnan ...
... be bound, reduces free fraction transiently, and more hormones will be secreted. Estrogen increases the circulating level of bound hormones. It won’t affect the free form (it’s regulated by feedback). Total hormones- mainly measure bound fractionnot good index to activity. Lutheal phase and pregnan ...
The endocrine system (overview) The endocrine system (overview)
... The endocrine system: a system of endocrine (ductless) glands or specialised cells which can secrete hormones directly into local capillaries for distribution around the body. ...
... The endocrine system: a system of endocrine (ductless) glands or specialised cells which can secrete hormones directly into local capillaries for distribution around the body. ...
hypothalamus,pituitary
... • Because posterior pituitary hormones are synthesized in the hypothalamus rather than the pituitary, hypophysectomy (pituitary removal) does not necessarily permanently disrupt synthesis and secretion of these hormones. • Immediately after hypophysectomy, secretion of the hormones decreases. • Howe ...
... • Because posterior pituitary hormones are synthesized in the hypothalamus rather than the pituitary, hypophysectomy (pituitary removal) does not necessarily permanently disrupt synthesis and secretion of these hormones. • Immediately after hypophysectomy, secretion of the hormones decreases. • Howe ...
The Endocrine System
... _________________ hormone _________________ Thyroid hormone Major _____________________ hormone Composed of two active _____________-containing hormones ____________________ (T4)—secreted by thyroid follicles Triiodothyronine (_____)—conversion of T4 at target tissues Thyroid hormone ...
... _________________ hormone _________________ Thyroid hormone Major _____________________ hormone Composed of two active _____________-containing hormones ____________________ (T4)—secreted by thyroid follicles Triiodothyronine (_____)—conversion of T4 at target tissues Thyroid hormone ...
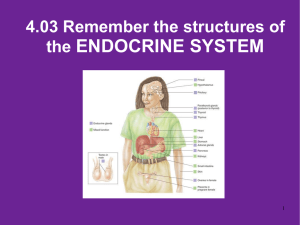
4.03 Remember Structures of the endocrine system What are the
... Function- secretes 3 hormones *Thyroxine (T3)– is controlled by the secretion of TSH. Controls the rate of metabolism- if elevated can cause nervousness and weight loss. Contain iodine Triiodothyronine (T4)- Controls cell metabolism and growth. Contain iodine Calcitonin – controls calcium ion concen ...
... Function- secretes 3 hormones *Thyroxine (T3)– is controlled by the secretion of TSH. Controls the rate of metabolism- if elevated can cause nervousness and weight loss. Contain iodine Triiodothyronine (T4)- Controls cell metabolism and growth. Contain iodine Calcitonin – controls calcium ion concen ...
SO-CALLED ALOPECIA-X AND SEASONAL FLANK ALOPECIA
... Breed Predisposition: Pomeranian, Chow Chow, Miniature Poodle, Keeshond Clinical Features: Bilaterally symmetrical alopecia and hyperpigmentation, affects the neck, perineal and genital region, tail, posterior and medial thighs, ventral abdomen. Excess scaling and dull, dry hair coat. Fuzzy hair coa ...
... Breed Predisposition: Pomeranian, Chow Chow, Miniature Poodle, Keeshond Clinical Features: Bilaterally symmetrical alopecia and hyperpigmentation, affects the neck, perineal and genital region, tail, posterior and medial thighs, ventral abdomen. Excess scaling and dull, dry hair coat. Fuzzy hair coa ...
Presentation
... 6. How does a hormone recognize its target cells from the other cells it comes in contact with? ...
... 6. How does a hormone recognize its target cells from the other cells it comes in contact with? ...
Impact of Lithium on Efficacy of Radioactive Iodine Therapy for
... therapy was considered cured if he or she remained euthyroid during the following 12 months. Hypothyroidism was defined as low serum thyroid hormone and increased TSH concentrations; after the first evidence, hypothyroidism was confirmed in the following 2 months, meaning that a patient who develope ...
... therapy was considered cured if he or she remained euthyroid during the following 12 months. Hypothyroidism was defined as low serum thyroid hormone and increased TSH concentrations; after the first evidence, hypothyroidism was confirmed in the following 2 months, meaning that a patient who develope ...
Thyroid Function and Lyme disease
... Denis Wilson, MD, a GP in rural Florida Developed protocol over several years Of clinical observations and treatment Found lab tests often didn’t match patient’s symptoms. Discovered a method to restore “normal” temperatures, eliminate low thyroid symptoms, and eventually stop taking thyro ...
... Denis Wilson, MD, a GP in rural Florida Developed protocol over several years Of clinical observations and treatment Found lab tests often didn’t match patient’s symptoms. Discovered a method to restore “normal” temperatures, eliminate low thyroid symptoms, and eventually stop taking thyro ...
A Direct Relationship between Thyroid Enlargement and Breast
... Breastcancer.The percent frequency distribution of individual thyroid volumes in the 200 patients with breast cancer compared to that in 200 older controls is shown in Fig. 1. The distribution of individual thyroid volumes in the breast cancer group covered a broad range, varying from 5.2-96.0 mL. I ...
... Breastcancer.The percent frequency distribution of individual thyroid volumes in the 200 patients with breast cancer compared to that in 200 older controls is shown in Fig. 1. The distribution of individual thyroid volumes in the breast cancer group covered a broad range, varying from 5.2-96.0 mL. I ...
Dosimetric predictors of hypothyroidism in oropharyngeal cancer
... yearly unless the patient presented with clinical symptoms. However, clinical follow up and hormone testing was not uniform for all patients. The euthyroid classification was chosen if the patient’s record indicated that TSH (0.4-4.0 mIU/L) and T4 (9–24 pmol/L) levels were within normal limits, ...
... yearly unless the patient presented with clinical symptoms. However, clinical follow up and hormone testing was not uniform for all patients. The euthyroid classification was chosen if the patient’s record indicated that TSH (0.4-4.0 mIU/L) and T4 (9–24 pmol/L) levels were within normal limits, ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... patients with thyroid nodules. The percentage of patients undergoing thyroidectomy has decreased by 25%, and the yield of carcinoma in patients who undergo surgery has increased from 15% to at least 30%. Fine-needle aspiration has decreased the cost of care by 25%. [2] Should fine needle aspiration ...
... patients with thyroid nodules. The percentage of patients undergoing thyroidectomy has decreased by 25%, and the yield of carcinoma in patients who undergo surgery has increased from 15% to at least 30%. Fine-needle aspiration has decreased the cost of care by 25%. [2] Should fine needle aspiration ...
Title: The Endocrine System
... b-Only target cells have receptor sites (i.e., TSH only effects the thyroid gland because only the thyroid gland has receptor sites) c- Most target cells have between 200 -100,000 receptors for a particular hormone. When a hormone is present in excess, the target cell becomes less receptive to the h ...
... b-Only target cells have receptor sites (i.e., TSH only effects the thyroid gland because only the thyroid gland has receptor sites) c- Most target cells have between 200 -100,000 receptors for a particular hormone. When a hormone is present in excess, the target cell becomes less receptive to the h ...
The Endocrine System
... and pressure receptors in the cervix are again triggered.... see #2. This positive feedback loop continues until the baby is born. --> When doctors induce labor, the woman receives several doses of a synthetic oxytocin to get the positive feedback loop of labor ...
... and pressure receptors in the cervix are again triggered.... see #2. This positive feedback loop continues until the baby is born. --> When doctors induce labor, the woman receives several doses of a synthetic oxytocin to get the positive feedback loop of labor ...
2608. BW Mod.Medicine 02/1¥1.6
... hormone itself may also play an important role in the cause of hyperprolactinaemia. Davis et al. noticed that 3,5,3’triiodothyronine reduces prolactin messenger RNA levels in rodent pituitary cells.17 Decreased circulating thyroid hormone levels might stimulate prolactin synthesis. The pathophysiolo ...
... hormone itself may also play an important role in the cause of hyperprolactinaemia. Davis et al. noticed that 3,5,3’triiodothyronine reduces prolactin messenger RNA levels in rodent pituitary cells.17 Decreased circulating thyroid hormone levels might stimulate prolactin synthesis. The pathophysiolo ...
the endocrine system
... increasing cellular protein synthesis thereby increasing heat production ...
... increasing cellular protein synthesis thereby increasing heat production ...
Biologic Variation is Important for Interpretation of Thyroid Function
... that T4 and T3 are not normal for the individual even when inside the laboratory reference range. This underlines the importance of TSH in diagnosis and monitoring of thyroid dysfunctions. Also, it implies that subclinical thyroid disease may be defined in purely biochemical terms. Under critical ci ...
... that T4 and T3 are not normal for the individual even when inside the laboratory reference range. This underlines the importance of TSH in diagnosis and monitoring of thyroid dysfunctions. Also, it implies that subclinical thyroid disease may be defined in purely biochemical terms. Under critical ci ...
hormones
... Sometimes the thyroid becomes overactive and produces excess thyroxine, a condition called hyperthyroidism. A hyperthyroid person is nervous, wastes energy, and becomes irritable easily. The disorder is treated with radioisotopes or by surgery (see nuclear energy). On the other hand, lack of thyroid ...
... Sometimes the thyroid becomes overactive and produces excess thyroxine, a condition called hyperthyroidism. A hyperthyroid person is nervous, wastes energy, and becomes irritable easily. The disorder is treated with radioisotopes or by surgery (see nuclear energy). On the other hand, lack of thyroid ...
Control and Coordination
... release thyroid hormone. The thyroid hormone is thus released into the interfollicular connective tissue and further in blood vessels. Role of Calcitonin / TCT Calcitonin / thyrocalcitonin is secreted by the Para follicular cells or C- cells especially when they are stimulated due to hypercalcemia. ...
... release thyroid hormone. The thyroid hormone is thus released into the interfollicular connective tissue and further in blood vessels. Role of Calcitonin / TCT Calcitonin / thyrocalcitonin is secreted by the Para follicular cells or C- cells especially when they are stimulated due to hypercalcemia. ...
The Endocrine System
... Overview of Endocrine System • Endocrine glands secrete into extracellular space, secretion (hormones) diffuses to circulatory system • Includes primary glands - pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, & pineal glands • Accessory structures with glandular function as well as others hypothalamus, ...
... Overview of Endocrine System • Endocrine glands secrete into extracellular space, secretion (hormones) diffuses to circulatory system • Includes primary glands - pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, & pineal glands • Accessory structures with glandular function as well as others hypothalamus, ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.