* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13 Endocrine System
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
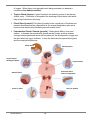
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Chapter Objectives Upon completion of this chapter the participant will be able to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Define hormones. Define homeostasis. List the glands of the endocrine system. Define what is meant by the “master gland”. Discuss the function of each of the endocrine glands. Label a diagram of the endocrine glands. Analyze, pronounce and define the terms related to the endocrine system. Successfully complete the exercises at the end of the chapter. The endocrine system is a series of glands that secrete chemicals called hormones directly into the blood. The blood then carries the hormone to the particular part of the body where it will have its action. One of the prime functions of the endocrine system is the maintenance of the body in a state of homeostasis. Homeostasis is a state of balance that the body must attain if all systems are to function to their optimum. Structures of the Endocrine System Pituitary Gland (pituit/o): The master gland that is located at the base of the brain. It consists of two lobes, the anterior and the posterior. This gland is referred to as the master gland because it secretes hormones that affect how the other endocrine glands function. Thyroid Gland (thyr/o, thyroid/o): Butterfly shaped gland found on either side of the larynx in the neck. It secretes thyroxine and calcitonin which affect metabolism in the body and the regulation of calcium levels in the blood. Parathyroid Glands: There are four parathyroid glands, each of which is about the size of a grain of rice. These glands are located on the posterior side of the thyroid gland (para-: near, upon). The function of the hormone released from this gland is to work with calcitonin to control the blood levels of calcium. Adrenal Gland (adren/o, adrenal/o): Two small glands which sit like a hat on the top of each kidney. Each adrenal gland has two parts; a cortex (cortic/o) which is the outer portion and a medulla (medull/o) which is the inner portion. This gland releases a number of hormones that are responsible for: regulating water levels in the body, affecting the body’s response to inflammation, nutrient absorption and development of male sex characteristics. Pancreas (pancreat/o): Located behind the stomach this gland is involved with digestion and only part of the gland has an endocrine function. Part of the gland is the islets of langerhans which secrete insulin that is involved with the breakdown Revised 2005-09-13 -143- of sugars. When there is not enough insulin being produced you develop a condition called diabetes mellitus. Thymus Gland (thym/o): A gland located in the anterior portion of the thoracic (chest) cavity. It functions to bring about the maturing of white blood cells which help to fight infections in the body. Pineal Gland (pineal/o) This gland is located in the central part of the brain and secretes hormones that are responsible for the normal sleep/wake cycle and a hormone that assists with stimulating smooth muscle action. Reproductive Glands: Gonads (gonad/o): These glands differ in men and women. In females the reproductive glands are the ovaries and they release estrogen and progesterone which are necessary for the development of eggs and the fetus when the egg is fertilized. In men the testes are the reproductive gland and they secrete testosterone. Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Parathyroid Gland Thymus Gland Pancreasl Gland Islets of Langerhans Adrenal Gland Ovary in females Testes in males Revised 2005-09-13 -144- Endocrine Glands contained in the body and their function … Gland Anterior Pituitary Posterior Pituitary Thyroid Revised 2005-09-13 Hormone Function somatotrophin (growth hormone) Stimulates growth of body cells. thyrotrophin (thyroid stimulating hormone TSH) Stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4 corticotrophin (adrenocorticotrophic hormone ACTH) Stimulates the adrenal cortex to release cortisol and aldosterone. gonadotrophin (follicle stimulating hormone FSH) Development of the ovaries and testes: promotes monthly growth of the egg in females and sperm production in males. gonadotrophin (luteinizing hormone LH) Triggers ovulation in women and regulates the secretion of sex hormone in men. prolactin Stimulates production of milk by the mammary gland melanocytestimulating hormone (MSH) produces melanin for skin pigmentation antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Regulates the retention of water in the body. oxytocin Regulates the flow of milk in mammary glands and stimulates uterine contraction during childbirth. thyroxine (T4) & triiodothyronine (T3) Increase metabolic rate and stimulates growth calcitonin Regulates blood calcium levels -145- Gland Hormone Function Parathyroid parathyroid hormone (PTH) Contributes to the regulation of blood calcium and phosphorus levels. Adrenal Cortex glucocorticoid hormone Production of antibodies, involved in the body’s stress response and the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates and proteins. mineralocorticoid hormones (aldosterone) Regulates sodium and potassium levels sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone) Development of the secondary sex characteristics in males and females. Adrenal Medulla epinephrine and norepinephrine Helps the body respond to stress Pineal Gland melatonin Involved in the sleep/wake cycle. Pancreas insulin, glucagon Insulin converts glucose to glycogen. Glucagon converts glycogen to glucose. Word parts for the Endocrine System Roots acr/o aden/o adren/o, adrenal/o andr/o calc/o, calc/i cortic/o crin/o estr/o gluc/o, glyc/o glycogen/o gonad/o gynec/o home/o insulin/o kal/o ket/o Revised 2005-09-13 extremities gland adrenal gland male calcium outer region secrete female sugar glycogen gonad female same insulin potassium ketones -146- lact/o, lact/i, galact/o lactat/o lute/o medull/o melan/o natr/o pancreat/o parathyroid/o pineal/o pituit/o ren/o, nephr/o somat/o thym/o thyr/o, thyroid/o toxic/o troph/o ure/o milk secrete milk yellow inner section black, dark sodium pancreas parathyroid gland pineal gland pituitary kidney body thymus thyroid gland poison relating to nourishment, development, growth urea Suffixes -assay -crine -dipsia -emia -ism -ma -physis -tropic, -trophy -uria analysis to secrete thirst blood state of tumor to grow pertaining to nourishment urine Prefixes adantieuoxypanparapoly- Revised 2005-09-13 toward against well, good, normal sharp, quick all, entire near many -147- Term Analysis and Definition Word Part Term acr/o acromegaly acr = extremity -megaly = enlargement Enlargement of the extremities aden/o adenoma aden = gland -oma = tumor Tumor of a gland adrenal/o, adren/o adrenalectomy adrenal = adrenal gland -ectomy = surgical removal Surgical removal of the adrenal gland adrenocortical -al = pertaining to cortic = cortex Pertaining to the cortex of the adrenal gland hypercalcemia hyper = excessive calc = calcium emia = blood Excessive calcium in the blood hypocalcemia hypo = deficient Deficiency of calcium in the blood endocrinology endo = within crin = to secrete -logy = study of Study of the diagnosis and treatment of endocrine disorders. endocrinologist -logist Specialist in endocrinology estr/o estrogen estr = female -gen =producing Female producing hormones gluc/o glyc/o glucogenesis gluc = sugar -genesis = production Production of sugar hyperglycemia hyper = excessive glyc = sugar -emia = blood Excessive amounts of sugar in the blood hypoglycemia hypo = deficiency Deficiency of sugar in the blood glycolysis -lysis = Breakdown of sugar calc/o calc/i crin/o Revised 2005-09-13 Analysis -148- Definition Word Part Term Analysis Definition breakdown glycogen/o glycogenolysis glycogen = glycogen -lysis = breakdown Breakdown of glycogen to glucose gonad/o hypergonadism hyper = excessive gonad = sex glands -ism = condition Condition characterized by excessive secretion of sex hormones. hypogonadism hypo = deficiency Condition characterized by deficiency in secretion of sex hormones. gynecomastia gynec = woman mast = breast -ia = condition Abnormal enlargement of the male breast, like that of the female breast gynecology -logy = study of Study of diseases that occur in women home/o homeostasis home = same -stasis = stable, controlling Balanced state insulin/o hyperinsulinism hyper = excessive insulin = insulin -ism = condition Condition where there is an excess in secretion of insulin hypoinsulinism hypo = deficiency Condition where there is a deficiency in secretion of insulin hyperkalemia hyper = excessive kal = potassium -emia = blood Excessive potassium in the blood hypokalemia hypo = deficiency Deficiency of potassium in the blood hypernatremia hyper = excessive natr = sodium Excessive sodium in the blood gynec/o kal/o natr/o Revised 2005-09-13 -149- Word Part Term Analysis Definition -emia = blood hyponatremia hypo = deficiency Deficiency of sodium in the blood parathyroid/o Hyperparathyroidism hyper = excessive parathyroid = parathyroid gland -ism = condition Condition where there is an excess in the secretion of hormones of the parathyroid gland. pituitar/o panhypopituitarism pan = all pituitar = pituitary gland hypo = deficiency -ism = condition Condition where there is a deficiency in all the hormones produced by the pituitary gland. thyr/o, thyroid/o euthyroid eu = normal, good -oid = resembling thyr = thyroid gland Resembling a normal thyroid gland hyperthyroidism hyper = excessive -ism = condition Condition where there is excessive secretion of the hormones produced by the thyroid gland. thyroiditis -itis = inflammation Inflammation of the thyroid gland thyrotomy -tomy = surgical incision Surgical incision into the thyroid gland ure/o antidiuretic hormone anti = against ure = urea -tic = pertaining to Hormone that prevents the loss of excessive amounts of urine -assay radioimmunoass ay radi = radioactive immun = safe -assay = analysis Blood test to identify hormone levels in the blood to identify contents -crine Revised 2005-09-13 endocrine -crine = to secrete endo = within Secretions of endocrine gland hormones directly into the blood. exocrine ex = outside Glands that secrete chemical -150- Word Part Term Analysis Definition into ducts -dipsia polydipsia poly = many dipsia = thirst Excessive thirst -physis adenohypophysis -physis = to grow aden = gland hypo = below, under Another name for the anterior pituitary gland neurohypophysis neuro = nerve Another name for the posterior pituitary gland -trophic, tropic adrenocorticotrophic adreno = adrenal gland cortic = cortex, outer layer -trophic = nourishment Pituitary hormone that stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete its own hormones oxy- oxytocin oxy = sharp, quick -tocin = labor Pituitary hormone that quickens childbirth Abbreviations: ADH antidiuretic hormone BMR basal metabolic rate IDDH insulin dependent diabetes mellitus NIDDM non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus Revised 2005-09-13 -151-