Laboratory Exercise 18: Experiments in Hormonal Action
... Insulin is secreted by the pancreas into the blood. It circulates to the muscles, adipose and other connective tissues where it increases the rate of glucose uptake across the cell membranes of these cells. Insulin in excess causes too rapid drop in the blood glucose level, resulting in hypoglycemia ...
... Insulin is secreted by the pancreas into the blood. It circulates to the muscles, adipose and other connective tissues where it increases the rate of glucose uptake across the cell membranes of these cells. Insulin in excess causes too rapid drop in the blood glucose level, resulting in hypoglycemia ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... Menarche, pregnancy, menopause for which the female hormones are one of the main responsible factors. The thyroid hormones influence the heart, brain, kidney, along with reproductive system development and overall body metabolism. In women diseases of the thyroid gland are among the most prevalent d ...
... Menarche, pregnancy, menopause for which the female hormones are one of the main responsible factors. The thyroid hormones influence the heart, brain, kidney, along with reproductive system development and overall body metabolism. In women diseases of the thyroid gland are among the most prevalent d ...
Hormonal Mechanisms as Potential Constraints on Evolution
... FIG. 2. Effect of [0.37 u.M] 17|3 estradiol (E2) on vitellogenin mRNA expression in reproductively mature Xenopus laevis (A), pre-metamorphic tadpoles (B), and post-metamorphic sexually immature juveniles (C). Estradiol was administered directly into water in all cases. Expression was analyzed using ...
... FIG. 2. Effect of [0.37 u.M] 17|3 estradiol (E2) on vitellogenin mRNA expression in reproductively mature Xenopus laevis (A), pre-metamorphic tadpoles (B), and post-metamorphic sexually immature juveniles (C). Estradiol was administered directly into water in all cases. Expression was analyzed using ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... PTH secretion occurs when there is a decrease in calcium ion concentration in the body. Calcium ions are needed for many body activities, such as activity at nerve synapses, muscle contraction, etc. Insufficient PTH secretion may result in ...
... PTH secretion occurs when there is a decrease in calcium ion concentration in the body. Calcium ions are needed for many body activities, such as activity at nerve synapses, muscle contraction, etc. Insufficient PTH secretion may result in ...
Chapter 1 A Perspective on Human Genetics
... – Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) secreted from anterior pituitary stimulates thyroid hormone secretion by thyroid gland • Also maintains structural integrity of thyroid gland ...
... – Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) secreted from anterior pituitary stimulates thyroid hormone secretion by thyroid gland • Also maintains structural integrity of thyroid gland ...
Teratogenic action of the thyroid stimulating hormone
... experiments although the sample specifications furnished by Nutritional Biochemicals report only a trace of organic iodide and ash. The major effect of release of thyroxin by the thyroid gland is described as a generalized increase in metabolism with a fall in liver glycogen, increased excretion of ...
... experiments although the sample specifications furnished by Nutritional Biochemicals report only a trace of organic iodide and ash. The major effect of release of thyroxin by the thyroid gland is described as a generalized increase in metabolism with a fall in liver glycogen, increased excretion of ...
Chapter 45.
... The Anterior Pituitary The hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary are partially controlled by the very hormones whose secretion they stimulate -This is termed negative feedback or feedback inhibition Positive feedback is uncommon because it causes deviations from homeostasis -One example is the co ...
... The Anterior Pituitary The hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary are partially controlled by the very hormones whose secretion they stimulate -This is termed negative feedback or feedback inhibition Positive feedback is uncommon because it causes deviations from homeostasis -One example is the co ...
The SNM Practice Guideline for Therapy of Thyroid Disease with
... guidelines will be reviewed for revision or renewal, as appropriate, on their fifth anniversary or sooner, if indicated. Each practice guideline, representing a policy statement by the SNM, has undergone a thorough consensus process in which it has been subjected to extensive review, requiring the a ...
... guidelines will be reviewed for revision or renewal, as appropriate, on their fifth anniversary or sooner, if indicated. Each practice guideline, representing a policy statement by the SNM, has undergone a thorough consensus process in which it has been subjected to extensive review, requiring the a ...
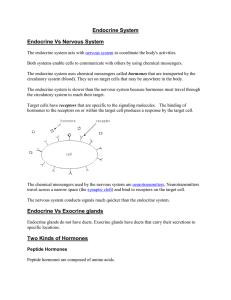
Endocrine System
... ii. Relative number of receptors on target cell iii. Affinity of receptors for the hormone b. Up-regulation: Target cells form more receptors in response to the hormone c. Down-regulation: Target cells lose receptors in response to the hormone 8. Types of Hormone Interaction a. Permissiveness: One ...
... ii. Relative number of receptors on target cell iii. Affinity of receptors for the hormone b. Up-regulation: Target cells form more receptors in response to the hormone c. Down-regulation: Target cells lose receptors in response to the hormone 8. Types of Hormone Interaction a. Permissiveness: One ...
Thyro-Tabs® Canine
... 12 hours. The dose may then be adjusted by monitoring the serum total thyroxine (TT4) concentrations 4 to 6 hours post-tablet administration, along with clinical response, of the dog every 4 to 8 weeks until an adequate maintenance dose is established. Due to potential differences in bioavailability ...
... 12 hours. The dose may then be adjusted by monitoring the serum total thyroxine (TT4) concentrations 4 to 6 hours post-tablet administration, along with clinical response, of the dog every 4 to 8 weeks until an adequate maintenance dose is established. Due to potential differences in bioavailability ...
NVCC Bio 212 - gserianne.com
... • stimulates increase in size and metabolic rate of body cells • anabolic (tissue building) and diabetogenic ( [glucose]) • Circadian (24-hour) pattern of secretion - highest during sleep • action via insulin-like growth factors (somatomedins) • enhances movement of amino acids through membranes • ...
... • stimulates increase in size and metabolic rate of body cells • anabolic (tissue building) and diabetogenic ( [glucose]) • Circadian (24-hour) pattern of secretion - highest during sleep • action via insulin-like growth factors (somatomedins) • enhances movement of amino acids through membranes • ...
Clinical THYROIDOLOGY FOR PATIENTS
... This was a study using the medical charts of women in the national birth, hospital, and prescription registries in Denmark from 1996-2008. Of over 450,000 mothers, almost 20% smoked cigarettes during their first pregnancy. After delivery, women who had smoked were more likely to develop hyperthyroid ...
... This was a study using the medical charts of women in the national birth, hospital, and prescription registries in Denmark from 1996-2008. Of over 450,000 mothers, almost 20% smoked cigarettes during their first pregnancy. After delivery, women who had smoked were more likely to develop hyperthyroid ...
is dental fluorosis caused by thyroid hormone disturbances?
... Perhaps the most obvious indication that DF is a condition caused by disordered thyroid hormone signaling during the time of enamel development is the long-standing observation of delayed eruption of teeth in fluoridated areas.9 DF is invariably associated with dental age and eruption of teeth, a pr ...
... Perhaps the most obvious indication that DF is a condition caused by disordered thyroid hormone signaling during the time of enamel development is the long-standing observation of delayed eruption of teeth in fluoridated areas.9 DF is invariably associated with dental age and eruption of teeth, a pr ...
Hormone review
... hormone called atrial natriuretic factor (ANF). This hormone inhibits the release of ADH by the posterior pituitary causing the kidneys to excrete excess water. Alcohol inhibits the release of ADH, causing the kidneys to produce dilute urine. Control of the Anterior Pituitary The hypothalamus produc ...
... hormone called atrial natriuretic factor (ANF). This hormone inhibits the release of ADH by the posterior pituitary causing the kidneys to excrete excess water. Alcohol inhibits the release of ADH, causing the kidneys to produce dilute urine. Control of the Anterior Pituitary The hypothalamus produc ...
The Endocrine System
... Hormones produced by hypothalamus Stores antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin Released in response to nerve impulses ...
... Hormones produced by hypothalamus Stores antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin Released in response to nerve impulses ...
It`s All About Balance - Women`s International Pharmacy
... leaving less available to work on the cells. When women take supplementary estrogen at menopause, they actually tie up a little more of the testosterone that’s left. This can cause symptoms of testosterone deficiency. Testosterone supplementation has sometimes been feared by women because they’ve he ...
... leaving less available to work on the cells. When women take supplementary estrogen at menopause, they actually tie up a little more of the testosterone that’s left. This can cause symptoms of testosterone deficiency. Testosterone supplementation has sometimes been feared by women because they’ve he ...
Endocrine system I
... enhances the responsiveness of a target organ to the second hormone increases the activity of the second hormone. Estrogen – Expression of progesterone receptors on uterus – progesterone effect on the uterus. Glucocorticoids – effects of catecholamines on ...
... enhances the responsiveness of a target organ to the second hormone increases the activity of the second hormone. Estrogen – Expression of progesterone receptors on uterus – progesterone effect on the uterus. Glucocorticoids – effects of catecholamines on ...
Non – Diabetic Endocrine Emergencies
... Undiagnosed Undertreated (Grave’s disease or Mulitnodular toxic goiter) ...
... Undiagnosed Undertreated (Grave’s disease or Mulitnodular toxic goiter) ...
Isolated Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Deficiency (ACTH
... However, with the early diagnosis and treatment, all symptoms may improve. Digestive problems are the most common symptoms in patients with adrenal insufficiency, however, the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency in such patients is difficult (5). In the literature, the case of IAD in a patient who pr ...
... However, with the early diagnosis and treatment, all symptoms may improve. Digestive problems are the most common symptoms in patients with adrenal insufficiency, however, the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency in such patients is difficult (5). In the literature, the case of IAD in a patient who pr ...
Study of the relationship between calcium ion and thyroid hormones
... Calcium is a body’s abundant divalent cation and more than 99% of the body calcium is concentrated in the skeletal system and approximately 1% is rapidly exchangeable with blood calcium. Small amounts of calcium located outside the bone circulates in the serum partly bound to protein and partly ioni ...
... Calcium is a body’s abundant divalent cation and more than 99% of the body calcium is concentrated in the skeletal system and approximately 1% is rapidly exchangeable with blood calcium. Small amounts of calcium located outside the bone circulates in the serum partly bound to protein and partly ioni ...
Thyroid Hormone Dysfunction and CRP Levels in Neonates With
... acute phase reactant produced in the liver, induced by cytokine IL-6 and its levels are commonly assayed for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Epidemiological studies have shown alterations in thyroid hormones levels in hospitalized patients. These alterations are more commonly observed in those with in ...
... acute phase reactant produced in the liver, induced by cytokine IL-6 and its levels are commonly assayed for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Epidemiological studies have shown alterations in thyroid hormones levels in hospitalized patients. These alterations are more commonly observed in those with in ...
Hormone
... function of the endocrine systems is to regulate metabolic pathways (chemical rxns, electrolyte balance, membrane transport, reproduction, & digestion) by secreting hormones. ...
... function of the endocrine systems is to regulate metabolic pathways (chemical rxns, electrolyte balance, membrane transport, reproduction, & digestion) by secreting hormones. ...
Endocrinology - Zoology, UBC
... The half-life is the time required for the hormone to loose half of its original effectiveness (or drop to half of its original concentration. ...
... The half-life is the time required for the hormone to loose half of its original effectiveness (or drop to half of its original concentration. ...
Key Terms PDF - QuizOver.com
... building and influences nutrient metabolism (also called somatotropin) ...
... building and influences nutrient metabolism (also called somatotropin) ...
ES Note Booklet - Morinville Community High School
... A2. Defining endocrine glands, hormones, and negative feedback A3. Location of endocrine glands Key Concept B: The hypothalamus and pituitary complex controls the secretion of many of the bodyʼs hormones B1. Hormones of the Hypothalamus, posterior and anterior pituitary glands B2. Growth Hormone • g ...
... A2. Defining endocrine glands, hormones, and negative feedback A3. Location of endocrine glands Key Concept B: The hypothalamus and pituitary complex controls the secretion of many of the bodyʼs hormones B1. Hormones of the Hypothalamus, posterior and anterior pituitary glands B2. Growth Hormone • g ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.