ENDOCTRINOLOGY REFERRAL
... Is there associated ophthalmopathy? Cardiac rhythm, evidence of cardiac failure? ...
... Is there associated ophthalmopathy? Cardiac rhythm, evidence of cardiac failure? ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 19 Martini Lecture Outine
... 2. Triggers release of TRH from the 3. TRH targets the adenohypophysis 4. Causes the release of TSH 5. TSH targets the thyroid gland 6. Triggers release of T3 and T4 7. Normal levels of T3 and T4 are restored ...
... 2. Triggers release of TRH from the 3. TRH targets the adenohypophysis 4. Causes the release of TSH 5. TSH targets the thyroid gland 6. Triggers release of T3 and T4 7. Normal levels of T3 and T4 are restored ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 19 Martini Lecture Outine
... 2. Triggers release of TRH from the 3. TRH targets the adenohypophysis 4. Causes the release of TSH 5. TSH targets the thyroid gland 6. Triggers release of T3 and T4 7. Normal levels of T3 and T4 are restored ...
... 2. Triggers release of TRH from the 3. TRH targets the adenohypophysis 4. Causes the release of TSH 5. TSH targets the thyroid gland 6. Triggers release of T3 and T4 7. Normal levels of T3 and T4 are restored ...
Endocrine System
... certain tissues called target tissue/cell • Target cell (tissue)— cell that can only can be signaled by a certain hormone – They get to the tissue by traveling thru blood ...
... certain tissues called target tissue/cell • Target cell (tissue)— cell that can only can be signaled by a certain hormone – They get to the tissue by traveling thru blood ...
Chapter 10 Endocrine System
... and low blood glucose levels – effects: ¹ increased heart rate, ² vasodilation of the vessels that supply blood to the muscles, ³ vasoconstriction (shunting) of blood vessels that supply the skin and internal organs, 4 increased break down of glycogen to glucose and release of fatty acids to increas ...
... and low blood glucose levels – effects: ¹ increased heart rate, ² vasodilation of the vessels that supply blood to the muscles, ³ vasoconstriction (shunting) of blood vessels that supply the skin and internal organs, 4 increased break down of glycogen to glucose and release of fatty acids to increas ...
hashimoto`s thyroiditis: surgical treatment
... HASHIMOTO'S THYROIDITIS: SURGICAL TREATMENT Summary. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) is an organ-specific autoimmune disease characterized by production of antibodies such as anti-thyroperoxidase, which leads to destruction of the thyroid gland and a decrease in normal thyroid function. Thyroidectomy i ...
... HASHIMOTO'S THYROIDITIS: SURGICAL TREATMENT Summary. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) is an organ-specific autoimmune disease characterized by production of antibodies such as anti-thyroperoxidase, which leads to destruction of the thyroid gland and a decrease in normal thyroid function. Thyroidectomy i ...
Notes on the Endocrine System
... The thyroid regulates development and metabolism The thyroid produces two amine hormones. Thyroxin is often called T4 because it contains four iodine atoms; the other, triiodothyronine, is called T3 because it contains three iodine atoms. They have crucial roles in development a maturation. For exa ...
... The thyroid regulates development and metabolism The thyroid produces two amine hormones. Thyroxin is often called T4 because it contains four iodine atoms; the other, triiodothyronine, is called T3 because it contains three iodine atoms. They have crucial roles in development a maturation. For exa ...
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System
... The thyroid gland is located in the neck, just under the larynx (voice box). The thyroid gland produces two similar hormones - thyroxine (T4).甲狀腺素 - triiodothyronine (T3).三碘甲狀腺素 The maturation of a tadpole (below) These hormones regulate many aspects of into an adult frog (above), as regulated b ...
... The thyroid gland is located in the neck, just under the larynx (voice box). The thyroid gland produces two similar hormones - thyroxine (T4).甲狀腺素 - triiodothyronine (T3).三碘甲狀腺素 The maturation of a tadpole (below) These hormones regulate many aspects of into an adult frog (above), as regulated b ...
End of Chapter 13 Questions
... (CRH) from the hypothalamus in response to low levels of adrenal cortical hormones. Stress increases secretion of ACTH by stimulating CRH production. 20. List the major gonadotropins, and explain the general functions of each. The major gonadotropins are: Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)—FSH is re ...
... (CRH) from the hypothalamus in response to low levels of adrenal cortical hormones. Stress increases secretion of ACTH by stimulating CRH production. 20. List the major gonadotropins, and explain the general functions of each. The major gonadotropins are: Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)—FSH is re ...
PTA/OTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 2
... the short arm (the "p" end) of chromosome 3 at a specific location of 3p11. Other studies have found changes on the short arm of chromosome 7. • Or tumors: • Most commonly craniopharyngioma (a tumor near the pituitary gland), children and adolescents. • Symptoms: headaches, vomiting, problems with v ...
... the short arm (the "p" end) of chromosome 3 at a specific location of 3p11. Other studies have found changes on the short arm of chromosome 7. • Or tumors: • Most commonly craniopharyngioma (a tumor near the pituitary gland), children and adolescents. • Symptoms: headaches, vomiting, problems with v ...
Hypocalcemia
... Nutritional secondary hyperparathyroidism, caused by diets that have too much phosphorus and/or too little calcium and vitamin D—it is a type of malnutrition Abnormal absorption of calcium from the intestines Low levels of magnesium in the blood (known as “hypomagnesemia”) ...
... Nutritional secondary hyperparathyroidism, caused by diets that have too much phosphorus and/or too little calcium and vitamin D—it is a type of malnutrition Abnormal absorption of calcium from the intestines Low levels of magnesium in the blood (known as “hypomagnesemia”) ...
Suppression of Serum TSH by Graves` Ig: Evidence for a Functional
... Corp., Bedford, MA), and the IgGs were isolated by affinity chromatography as described by Harlow and Lane (12). In short, the samples were passed over a 5-ml protein G-Sepharose column (HiTrap Protein G, Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, NJ) that was equilibrated with 0.1% BSA in run buffer (20 mm sod ...
... Corp., Bedford, MA), and the IgGs were isolated by affinity chromatography as described by Harlow and Lane (12). In short, the samples were passed over a 5-ml protein G-Sepharose column (HiTrap Protein G, Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, NJ) that was equilibrated with 0.1% BSA in run buffer (20 mm sod ...
Hypocalcemia - Milliken Animal Clinic
... Nutritional secondary hyperparathyroidism, caused by diets that have too much phosphorus and/or too little calcium and vitamin D—it is a type of malnutrition Abnormal absorption of calcium from the intestines Low levels of magnesium in the blood (known as “hypomagnesemia”) ...
... Nutritional secondary hyperparathyroidism, caused by diets that have too much phosphorus and/or too little calcium and vitamin D—it is a type of malnutrition Abnormal absorption of calcium from the intestines Low levels of magnesium in the blood (known as “hypomagnesemia”) ...
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction (p. 293) A. The
... Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates and fats. a. Growth hormone-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus increases the amount of GH released, GH release-inhibiting hormone inhibits its release. b. Nutritional status ...
... Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates and fats. a. Growth hormone-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus increases the amount of GH released, GH release-inhibiting hormone inhibits its release. b. Nutritional status ...
Endocrine System
... Is called the “master gland.” The anterior pituitary lobe releases hormones that regulate other glands. The posterior lobe regulates water and salt balance. Regulates stress reactions and disease resistance; secrets growth hormone (cause of dwarfism and gigantism). ...
... Is called the “master gland.” The anterior pituitary lobe releases hormones that regulate other glands. The posterior lobe regulates water and salt balance. Regulates stress reactions and disease resistance; secrets growth hormone (cause of dwarfism and gigantism). ...
12-PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANGEGS OF PREGNANCY
... Abdominal wall there is separation of the recti muscles ...
... Abdominal wall there is separation of the recti muscles ...
SYNTHROID - RxAbbVie
... heartbeat, chest pain, shortness of breath, leg cramps, headache, nervousness, irritability, sleeplessness, tremors, change in appetite, weight gain or loss, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, heat intolerance, fever, changes in menstrual periods, hives or skin rash, or any other unusual medica ...
... heartbeat, chest pain, shortness of breath, leg cramps, headache, nervousness, irritability, sleeplessness, tremors, change in appetite, weight gain or loss, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, heat intolerance, fever, changes in menstrual periods, hives or skin rash, or any other unusual medica ...
Z333 Lecture
... 2) Endocrine Glands: • Release substances within the body via bloodstream • Ductless ...
... 2) Endocrine Glands: • Release substances within the body via bloodstream • Ductless ...
Newborn Screening for Congenital Hypothyroidism
... The National Screening Committee o The UK National Screening Committee advises ministers and the NHS in all 4 countries about all aspects of screening policy. o It assesses the evidence for programmes against defined criteria. These are an extended version of the Wilson and Junger criteria (first d ...
... The National Screening Committee o The UK National Screening Committee advises ministers and the NHS in all 4 countries about all aspects of screening policy. o It assesses the evidence for programmes against defined criteria. These are an extended version of the Wilson and Junger criteria (first d ...
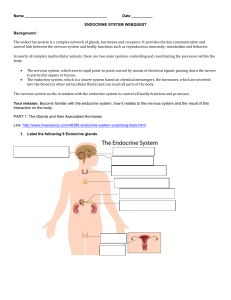
endocrine system webquest
... The endocrine system is a complex network of glands, hormones and receptors. It provides the key communication and control link between the nervous system and bodily functions such as reproduction, immunity, metabolism and behavior. In nearly all complex multicellular animals, there are two main sys ...
... The endocrine system is a complex network of glands, hormones and receptors. It provides the key communication and control link between the nervous system and bodily functions such as reproduction, immunity, metabolism and behavior. In nearly all complex multicellular animals, there are two main sys ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.