Dear Notetaker:
... internalized, receptor is no longer on cell surface, cannot respond to any more hormone Desensitizing cell to specific hormone o Hormone permissiveness When a hormone binds its receptor, it will have an effect on target cell, but it does not a full effect Requires action of another hormone – o ...
... internalized, receptor is no longer on cell surface, cannot respond to any more hormone Desensitizing cell to specific hormone o Hormone permissiveness When a hormone binds its receptor, it will have an effect on target cell, but it does not a full effect Requires action of another hormone – o ...
Chapter 17 Endocrine System
... – low metabolic rate, sluggishness, sleepiness, weight gain, constipation, dry skin and hair, cold sensitivity, blood pressure and tissue swelling ...
... – low metabolic rate, sluggishness, sleepiness, weight gain, constipation, dry skin and hair, cold sensitivity, blood pressure and tissue swelling ...
File
... (against), which tells the kidneys to slow down the removal of water, and you fell thirsty. When you have too much, your cells are dilute with water, less antidiuretic hormone is released, and the kidneys remove more water. ...
... (against), which tells the kidneys to slow down the removal of water, and you fell thirsty. When you have too much, your cells are dilute with water, less antidiuretic hormone is released, and the kidneys remove more water. ...
Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Anti
... and hyperlipidemia in euthyroid subjects with naturally occurring thyroid hormones, T3 and T4 , is not viable because of deleterious cardiac effects, including tachycardia, arrhythmias and heart failure (8,12), and excessive increases in metabolic rate (8,12). Indeed, the lack of selectivity of thes ...
... and hyperlipidemia in euthyroid subjects with naturally occurring thyroid hormones, T3 and T4 , is not viable because of deleterious cardiac effects, including tachycardia, arrhythmias and heart failure (8,12), and excessive increases in metabolic rate (8,12). Indeed, the lack of selectivity of thes ...
TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma
... been described in the management of patients with acromegaly, with some centres using somatostatin analogue therapy as primary treatment, some for a period of three to 6 months pre-operatively and some only if there is no biochemical cure following surgery. A reduction of tumour size has also been d ...
... been described in the management of patients with acromegaly, with some centres using somatostatin analogue therapy as primary treatment, some for a period of three to 6 months pre-operatively and some only if there is no biochemical cure following surgery. A reduction of tumour size has also been d ...
Endocrine Physiology - e-safe
... as neurotransmitters, prostaglandins and growth factors but their physiological relevance remains to be demonstrated. Iodide supply is monitored through its effects on the plasma level of thyroid hormone and in the thyroid itself, where it depresses the response of the thyroid cells to TSH. Large do ...
... as neurotransmitters, prostaglandins and growth factors but their physiological relevance remains to be demonstrated. Iodide supply is monitored through its effects on the plasma level of thyroid hormone and in the thyroid itself, where it depresses the response of the thyroid cells to TSH. Large do ...
Endocrine System and Stress
... Q: are hypothalamic cells neurons are endocrine cells? Q: are the chemicals released neurotransmitters or hormones? Q: could one detect levels of the releasing-hormones in the blood? 4. Posterior pituitary Fig. 16.4 contains the axons of cells in the hypothalamus these cells release the hormones ...
... Q: are hypothalamic cells neurons are endocrine cells? Q: are the chemicals released neurotransmitters or hormones? Q: could one detect levels of the releasing-hormones in the blood? 4. Posterior pituitary Fig. 16.4 contains the axons of cells in the hypothalamus these cells release the hormones ...
Increases blood calcium levels Parathyroid Hormone
... What do we call two hormones that play opposite functions in order to maintain homeostasis ...
... What do we call two hormones that play opposite functions in order to maintain homeostasis ...
Endocrine_System__part_1__Feb_28__studen
... feedback pathway • Can occur at any point in the axis – Hypothalamus – Pituitary gland – Adrenal gland ...
... feedback pathway • Can occur at any point in the axis – Hypothalamus – Pituitary gland – Adrenal gland ...
Chapter 11- Parathyroid Hormone2 _1
... Symptoms of parathyroid disease do NOT correlate with the level of calcium in the blood. Many patients with only slightly elevated calcium and parathyroid hormone will have BAD symptoms and develop severe osteoporosis. ...
... Symptoms of parathyroid disease do NOT correlate with the level of calcium in the blood. Many patients with only slightly elevated calcium and parathyroid hormone will have BAD symptoms and develop severe osteoporosis. ...
Ectopic Thyroid at the Base of the Tongue of a Young Patient
... Lingual thyroid is defined as an ectopic thyroid gland tissue located in the midline of the tongue base and it is uncommonly observed in clinical practice and is rare in children. This paper describes the surgical treatment of ectopic thyroid at the base of the tongue in a child. The chief complaint ...
... Lingual thyroid is defined as an ectopic thyroid gland tissue located in the midline of the tongue base and it is uncommonly observed in clinical practice and is rare in children. This paper describes the surgical treatment of ectopic thyroid at the base of the tongue in a child. The chief complaint ...
The Endocrine System - KCPE-KCSE
... III.Control of Endocrine Function A. Positive B. or Negative Feedback mechanisms ...
... III.Control of Endocrine Function A. Positive B. or Negative Feedback mechanisms ...
endocrine system - Doctor Jade Main
... • thyroxine levels fall hypothalamus TRH pituitaryTSH thyroid cells thyroid hormones • 90% is T4-major thytoid hormone • 10% is T3 • T3 is more potent and responsible for effects of thyroid hormone ...
... • thyroxine levels fall hypothalamus TRH pituitaryTSH thyroid cells thyroid hormones • 90% is T4-major thytoid hormone • 10% is T3 • T3 is more potent and responsible for effects of thyroid hormone ...
7 Thyroid Gland
... 0.01 – 0.03 µunits/ml and are particularly helpful in establishing subclinical hyperthyroidism in nodular goiter and athyrotic persons receiving replacement levothyroxine therapy [27, 30]. Subclinical hyperthyroidism in older individuals has been associated with adverse effects on the heart and bone ...
... 0.01 – 0.03 µunits/ml and are particularly helpful in establishing subclinical hyperthyroidism in nodular goiter and athyrotic persons receiving replacement levothyroxine therapy [27, 30]. Subclinical hyperthyroidism in older individuals has been associated with adverse effects on the heart and bone ...
Endocrine System
... Hypoglycemia- lower than normal blood glucose concentration. Too much insulin in the blood Hyperglycemia- higher than normal blood glucose ...
... Hypoglycemia- lower than normal blood glucose concentration. Too much insulin in the blood Hyperglycemia- higher than normal blood glucose ...
Part II Target Cell Specificity Target Cell Specificity
... • Three types of hormone interac@on – Permissiveness – one hormone cannot exert its effects without another hormone being present – Synergism – more than one hormone produces the same effects on a target cell – Antagonism – one or more hormones opposes the ac@on of another hormone – Neuron ...
... • Three types of hormone interac@on – Permissiveness – one hormone cannot exert its effects without another hormone being present – Synergism – more than one hormone produces the same effects on a target cell – Antagonism – one or more hormones opposes the ac@on of another hormone – Neuron ...
Endocrine System
... • It has more sustained impulses • It is a “duct” less system. It gets secreted then heads directly to the blood stream. ...
... • It has more sustained impulses • It is a “duct” less system. It gets secreted then heads directly to the blood stream. ...
Environmental Health Perspectives (EHP) is a monthly journal of
... Consequently, only two groups of structurally similar compounds will be considered. These are the polyhalogenated biphenyls that include the (PCBs) and the family of chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins loosely referred to as dioxins. Both groups of compounds are present in the environment and some PCB con ...
... Consequently, only two groups of structurally similar compounds will be considered. These are the polyhalogenated biphenyls that include the (PCBs) and the family of chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins loosely referred to as dioxins. Both groups of compounds are present in the environment and some PCB con ...
NVCC Bio 212
... • derived from amino acid tyrosine • hormones of ‘fight or flight’ are called catecholamines • release controlled by sympathetic nervous system (neural control of hormone release) • hormone releasing cells are considered equivalent to postganglionic sympathetic neurons • increases heart rate and blo ...
... • derived from amino acid tyrosine • hormones of ‘fight or flight’ are called catecholamines • release controlled by sympathetic nervous system (neural control of hormone release) • hormone releasing cells are considered equivalent to postganglionic sympathetic neurons • increases heart rate and blo ...
Word - Doctor of the Future
... in the brasssica family of vegetables, flax, soy and walnuts can interfere with thyroidal function. These are called goitrogens because they cause the thyroid to over develop (goiter) in an attempt to make up for the block to its function. Specific nutrients can promote normal thyroid function and c ...
... in the brasssica family of vegetables, flax, soy and walnuts can interfere with thyroidal function. These are called goitrogens because they cause the thyroid to over develop (goiter) in an attempt to make up for the block to its function. Specific nutrients can promote normal thyroid function and c ...
Endocrine Ch 16-Fall 2016-StudentRevised
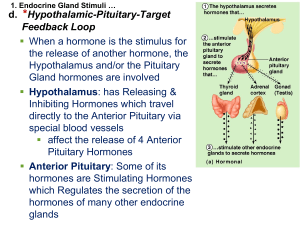
... Feedback Loop When a hormone is the stimulus for the release of another hormone, the Hypothalamus and/or the Pituitary Gland hormones are involved Hypothalamus: has Releasing & Inhibiting Hormones which travel directly to the Anterior Pituitary via special blood vessels affect the release of 4 ...
... Feedback Loop When a hormone is the stimulus for the release of another hormone, the Hypothalamus and/or the Pituitary Gland hormones are involved Hypothalamus: has Releasing & Inhibiting Hormones which travel directly to the Anterior Pituitary via special blood vessels affect the release of 4 ...
Lesson 6. FEEDBACK REGULATION IN THYROID
... µg/liter. Plot both [TH] and [TSH] and determine their "normal" steady state values. Are they consistent with the data? Note how fast the feedback system operates. Compare with different values of n. [Hint: [TH]ss = 80 µg/l; if you don’t get this, check your parameter values carefully. 2. A patient ...
... µg/liter. Plot both [TH] and [TSH] and determine their "normal" steady state values. Are they consistent with the data? Note how fast the feedback system operates. Compare with different values of n. [Hint: [TH]ss = 80 µg/l; if you don’t get this, check your parameter values carefully. 2. A patient ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.