* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
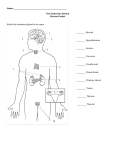
Endocrine System By Samantha Douglass & Ashley Walker Information • Made up of endocrine glands that secrete hormones. • Uses the blood stream to get to the target cells • Is indirect control. And controls tissues regulatory actions and homeostasis. • It’s speed to get places is like mailing a letter • It has more sustained impulses • It is a “duct” less system. It gets secreted then heads directly to the blood stream. Two Types of Hormones • Steroid hormones – made from cholesterol, it is lipid based. Small in size, proteins are synthesized as directed by the hormone. • Non – Steroid hormones – is amino Acid based, big in size. Uses the 2nd messenger system, and activates proteins. Reproductive System -- Ovaries • • • • • • Hormone: Estrogen Gland Source: Ovaries Targets: most bodies cells and female reproductive organs. Action: Develop of 2nd sex characteristics in females. Supports ova maturation. Works with Progesterone on breast development and menstrual cycles. Stimulus for release: Follicle stimulating hormone and Luteinizing hormone. Inhibition: Negative Feedback mechanism • • • • • • Hormone: Progesterone Gland Source: ovaries (corpus Luteum) Targets: uterus and mammary glands (breasts) Action: prepares uterine lining for fertilized egg, causes swelling of the breasts (works with prolactin) Stimulus for release: Luteinizing Hormone Inhibition: Negative Feedback mechanism. Reproductive System -- Testicles • • • • Hormone: Testosterone Gland Sources: Testicles Targets: most body cells and seminiferous tubules Action: stimulates production of sperm, 2nd sex characteristics of males, promotes protein synthesis in skeletal muscles (muscle bulk), repair, and maintenance. • Stimulus for Release: Luteinizing Hormone • Inhibition: Negative Feedback mechanism Pituitary Gland -- Anterior • Hormone: Growth Hormone • Hormone: Follicle (GH) Stimulating Hormone • Targets: all cells in the body (FSH) • Action: Stimulates growth and • Targets: the follicle repair; binds to receptors on surface of liver cells; stimulates cells of the ovary and them to release insulin; like seminiferous tubules Growth-Factor-1 (GF-1) acts in the testis. directly on ends of long bones. • Release of this hormone is controlled by GH releasing hormone and GH release – inhibiting hormone. Pituitary Gland – Anterior (cont.) • Hormone: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) • Target: Thyroid • Action: Stimulates thyroid to secrete it’s own hormone (T3 & T4). • Stimulus for release: The level of thyroid hormones in the blood. • Hormone: Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) • Targets: Adrenals • Stimulates adrenal gland to produce cortisol hormone. • Also produces aldosterone and testosterone. Pituitary Gland – Anterior (cont.) • Hormone: Prolactin (PRL) • Targets: Breasts • Stimulates breasts to produce milk. • Stimulated (prolactin secretion) by TRH/repressed by estrogen and dopamine. • Hormone: Luteinizing Hormone (LH) • Targets: Ovaries(women) and Testes(men). • Controls reproductive functioning/sexual characteristics. • Stimulates ovaries to produce estrogen and testes to produce testosterone and sperm. Pituitary Gland – Anterior (cont.) • Hormone: Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH) Pituitary Gland -- Posterior • Hormone: Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) • Reduces volume of water that kidneys secrete. • Hypothalamus regulates ADH secretions. • Hormone: Oxytocin (OT) • Contracts smooth muscles in uterine wall, causing uterine contractions in later stages of childbirth. Adrenal Gland • Hormone: Aldosterone (zona glomerolus cortex) • Gland source: Adrenal gland (cortex) • Targets: Kidneys • Action: increase sodium levels in blood and increases blood BP and water volume. • Stimulus for release: Renin-Angiotension System. • Hormone: Cortisol (Stress hormone) • Gland Source: Adrenal gland (zona fasciculata) • Targets: adipose tissue and liver. • Action: Gluconeogenesis • Stimulus for release: Stress • Inhibition: Negative feedback mechanism Adrenal Gland • Hormone: Androgens • Gland Source: Adrenal Medulla (zona reticularis) • Targets: Ovaries and Testes. • Action: Increase in cell metabolism, red blood cell production; in adults, plays role in sex drive, and provides female hormones after menopause. • Stimulus: ACTH from pituitary. • Inhibition: Negative Feedback. • Hormone: Epinephrine and Norepinephrine • Gland Source: Adrenal Medulla 80% - 85% Epinepherine 15% - 20% Norepinephrine • Targets: Heart; blood vessels; respiratory system; skeletal muscles; and liver • Action: up blood sugar; up heart rate; up blood pressure; dialaate bronchii; and up blood flow to heart, brain, and muscles • Stimulation for Release: Nerve impulses from sympathetic Nervous system • Inhibition: Nerve impulses end, causes liver and kidneys to absorb the hormones Pancreas Gland • Hormone: Insulin • Gland Source: Pancreas – Islets of Langerhans • Targets: All body cells except liver, kidneys, and brain. • Action: Lowers blood sugar • Stimulus for Response: high blood sugar • Inhibition: Negative feedback mechanism bases on low blood sugar • Hormone: Glucagon • Gland Source: Islet of Langerhans (pancreas) • Targets: Liver and adipose tissue(fat) • Action: “tells” liver to convert glycogen to glucose, increase blood sugar levels, and turn fat into glucose and turn protein into glucose. • Stimulation for Release: low blood sugar • Inhibition: Negative feedback mechanism Parathyroid Gland • • • • Hormone: Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Gland Source: Parathyroid Gland Target: Bones, Kidneys, and Intestine Action: Controls amount of calcium in blood and bones • Stimulus for release: Stimulates osteoclasts to brake down and release calcium. • Inhibition: Negative Feedback mechanism