Nature-Throid® (Thyroid USP) Tablets CLICK HERE TO VISIT
... Geriatric use: Clinical studies of Thyroid Tablets, USP did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger ...
... Geriatric use: Clinical studies of Thyroid Tablets, USP did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger ...
Beneficial Bacteria Stimulate Youthful Thyroid Gland Activity
... pituitary gland in response to thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) produced in the hypothalamus. Together these hormones also regulate brain growth and rate of function of many different body systems ...
... pituitary gland in response to thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) produced in the hypothalamus. Together these hormones also regulate brain growth and rate of function of many different body systems ...
BCLT-R2ppt DRAFT 3
... transient hypothyroidism during the recovery phase of subacute thyroiditis. This category includes cretinism, myxedema, and ordinary hypothyroidism in patients of any age (children, adults, the elderly), or state (including pregnancy); primary hypothyroidism resulting from functional deficiency, pri ...
... transient hypothyroidism during the recovery phase of subacute thyroiditis. This category includes cretinism, myxedema, and ordinary hypothyroidism in patients of any age (children, adults, the elderly), or state (including pregnancy); primary hypothyroidism resulting from functional deficiency, pri ...
clinical disorders of pituitary
... Is a syndrome due to excess cortisol from pituitary, adrenal or other sources (exogenous glucocorticoids, ectopic ACTH, etc.) ...
... Is a syndrome due to excess cortisol from pituitary, adrenal or other sources (exogenous glucocorticoids, ectopic ACTH, etc.) ...
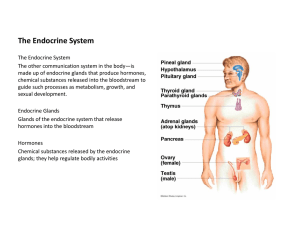
Endocrine System
... thyroid. By activating genes which produce enzymes important in cell metabolism they facilitate the demand for energy by the cells and also raise the BMR slightly. The increase in thyroid hormones T4 and T3 feeds back to the hypothalamus to control the process. ...
... thyroid. By activating genes which produce enzymes important in cell metabolism they facilitate the demand for energy by the cells and also raise the BMR slightly. The increase in thyroid hormones T4 and T3 feeds back to the hypothalamus to control the process. ...
Alterations in Pituitary, Thyroid, Parathyroid, and Adrenal Function
... build, delayed skeletal and sexual maturation, and absence of other causes of decreased growth. Catch-up growth is a term used to describe an abnormally high growth rate that occurs as a child approaches normal height for age. It occurs after the initiation of therapy for GH deficiency and hypothyroi ...
... build, delayed skeletal and sexual maturation, and absence of other causes of decreased growth. Catch-up growth is a term used to describe an abnormally high growth rate that occurs as a child approaches normal height for age. It occurs after the initiation of therapy for GH deficiency and hypothyroi ...
The Endocrine System
... thyroid. By activating genes which produce enzymes important in cell metabolism they facilitate the demand for energy by the cells and also raise the BMR slightly. The increase in thyroid hormones T4 and T3 feeds back to the hypothalamus to control the process. ...
... thyroid. By activating genes which produce enzymes important in cell metabolism they facilitate the demand for energy by the cells and also raise the BMR slightly. The increase in thyroid hormones T4 and T3 feeds back to the hypothalamus to control the process. ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... 26.5 The thyroid regulates development and metabolism • Two hormones from the thyroid gland, T4 and T3 – T4 = thyroxine; T3 = triiodothyronine – In target cells, T4 is finally converted to T3. • Both exert same effects on cells – Regulate an animal’s development and metabolism – Maintain normal bloo ...
... 26.5 The thyroid regulates development and metabolism • Two hormones from the thyroid gland, T4 and T3 – T4 = thyroxine; T3 = triiodothyronine – In target cells, T4 is finally converted to T3. • Both exert same effects on cells – Regulate an animal’s development and metabolism – Maintain normal bloo ...
Thyroid function and the development of endothermy
... and including week 11, oxygen consumption after injection changed little or even dropped. From week 12, T4 injection raised oxygen consumption, while the level of control VO2 decreased. Maximum levels of VO2 after ...
... and including week 11, oxygen consumption after injection changed little or even dropped. From week 12, T4 injection raised oxygen consumption, while the level of control VO2 decreased. Maximum levels of VO2 after ...
Structure and Functions of Important Endocrine Glands
... In teleosts it is filled from two major veins called the hepatic ...
... In teleosts it is filled from two major veins called the hepatic ...
Document
... are not stored lipid soluble most of cholesterol comes from plasma, but there is also de novo synthesis consist of three cyclohexyl rings and one cyclopentyl ring combined into a single structure ...
... are not stored lipid soluble most of cholesterol comes from plasma, but there is also de novo synthesis consist of three cyclohexyl rings and one cyclopentyl ring combined into a single structure ...
AP Biology Animal Form and Function
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland is derived from neural tissue and its connection to the hypothalamus is neural. Posterior Pituitary produces 2 hormones: ADH and oxytocin. These are produced by the nerve cell bodies that are located in the hypothalamus, where they are packaged into secretor ...
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland is derived from neural tissue and its connection to the hypothalamus is neural. Posterior Pituitary produces 2 hormones: ADH and oxytocin. These are produced by the nerve cell bodies that are located in the hypothalamus, where they are packaged into secretor ...
Hormones - SITH ITB
... • leads to high blood pressure, loss of weight, overheating, and irritability, and • produces Graves’ disease. ...
... • leads to high blood pressure, loss of weight, overheating, and irritability, and • produces Graves’ disease. ...
Thyroid Hormone Disruption by Water
... ng/L), followed by the 50% WAF (8,565 ng/L), and site B leachate (672 ng/L). The PAHs with two benzene rings, such as naphthalene (Na) and dibenzothiophene (DBT), and their alkylated homologues were generally dominant in all three test samples, perhaps because of their greater water solubility. In W ...
... ng/L), followed by the 50% WAF (8,565 ng/L), and site B leachate (672 ng/L). The PAHs with two benzene rings, such as naphthalene (Na) and dibenzothiophene (DBT), and their alkylated homologues were generally dominant in all three test samples, perhaps because of their greater water solubility. In W ...
An Oculist Looks at Endocrine Exophthalmos
... commoner in women: and the pituitary type, characterised by oedema of the orbital tissues, palsy of ocular muscles and risk of damage to the eye through exposure. In this type the sexes are equally represented and the disease tends to occur at a later age than does the first variety. We must remembe ...
... commoner in women: and the pituitary type, characterised by oedema of the orbital tissues, palsy of ocular muscles and risk of damage to the eye through exposure. In this type the sexes are equally represented and the disease tends to occur at a later age than does the first variety. We must remembe ...
What is the Endocrine System
... top of each kidney. The primary catecholamines are dopamine, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine. These hormones are released into the bloodstream in response to physical or emotional stress. They help transmit nerve impulses in the brain, increase glucose and fatty acid release for energy, ...
... top of each kidney. The primary catecholamines are dopamine, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine. These hormones are released into the bloodstream in response to physical or emotional stress. They help transmit nerve impulses in the brain, increase glucose and fatty acid release for energy, ...
Relationship between serum zinc levels, thyroid hormones and
... OBJECTIVE: Zinc is essential for many biochemical processes and also for cell proliferation. Thyroid hormones influence zinc metabolism by affecting zinc absorption and excretion. Additionally, zinc deficiency affects thyroid function. The aim of the present study was to evaluate a possible associat ...
... OBJECTIVE: Zinc is essential for many biochemical processes and also for cell proliferation. Thyroid hormones influence zinc metabolism by affecting zinc absorption and excretion. Additionally, zinc deficiency affects thyroid function. The aim of the present study was to evaluate a possible associat ...
What is Hypothyroidism?
... producing enough of certain important hormones upsetting the normal balance of chemical reactions in your body. This can cause a number of health problems such as obesity, joint pain, infertility and heart disease. ...
... producing enough of certain important hormones upsetting the normal balance of chemical reactions in your body. This can cause a number of health problems such as obesity, joint pain, infertility and heart disease. ...
The effects of iron deficiency anemia on the thyroid functions Demir
... and T4 levels.18 T3 levels also higher in post-treatment than control group. They explain this situation by reduction in T3 and T4 conversion in iron deficiency. Because of T3 and T4 levels have increased by adding iron, this mean that iron has an important role in enzyme structure.18 In our study, ...
... and T4 levels.18 T3 levels also higher in post-treatment than control group. They explain this situation by reduction in T3 and T4 conversion in iron deficiency. Because of T3 and T4 levels have increased by adding iron, this mean that iron has an important role in enzyme structure.18 In our study, ...
Management of primary hypothyroidism
... relationship between symptoms suggestive of thyroid hormone deficiency and the biochemical finding of subclinical hypothyroidism have produced conflicting results.3 It is recognized that up to one-quarter of the healthy normal population may have ‘hypothyroid’ symptoms such as lethargy and weight ga ...
... relationship between symptoms suggestive of thyroid hormone deficiency and the biochemical finding of subclinical hypothyroidism have produced conflicting results.3 It is recognized that up to one-quarter of the healthy normal population may have ‘hypothyroid’ symptoms such as lethargy and weight ga ...
Hormones in Animals
... •Via the autonomic nervous system e.g. via the release of adrenaline by the adrenal medulla •Neurones in the hypothalamus produce releasing hormones into the blood portal system causing the release of hormones by specific cells in the anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis) . These tropic hormone ...
... •Via the autonomic nervous system e.g. via the release of adrenaline by the adrenal medulla •Neurones in the hypothalamus produce releasing hormones into the blood portal system causing the release of hormones by specific cells in the anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis) . These tropic hormone ...
Headache and Fatigue Tips
... Headache and Fatigue Tips 1. Magnesium can help migraines and fatigue. Giving a single magnesium injection can stop a migraine and energize the person almost immediately. Sometimes oral magnesium will work too. 2. Gentle osteopathic manipulation can help stop a migraine. An Osteopathic physician who ...
... Headache and Fatigue Tips 1. Magnesium can help migraines and fatigue. Giving a single magnesium injection can stop a migraine and energize the person almost immediately. Sometimes oral magnesium will work too. 2. Gentle osteopathic manipulation can help stop a migraine. An Osteopathic physician who ...
hormones
... not accelerate glucose entry into liver, kidney, and brain tissue, all of which have easy access to blood glucose regardless of insulin levels.) 2-Inhibition of the breakdown of glycogen to glucose and the conversion of amino acids or fats to glucose; thus, it counters any metabolic activity that wo ...
... not accelerate glucose entry into liver, kidney, and brain tissue, all of which have easy access to blood glucose regardless of insulin levels.) 2-Inhibition of the breakdown of glycogen to glucose and the conversion of amino acids or fats to glucose; thus, it counters any metabolic activity that wo ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.