Three basic patterns of changes in serum thyroid hormone levels in
... and 7 hyperthyroid), 2 (9%) minimum change (one euthyroid and one hyperthyroid) and 2 (9%) increased (one euthyroid and one hyperthyroid) cases. As a total, there were 54 (77%) decreased, 8 (11.5%) minimum change and 8 (11.5%) increased cases. There were no statistically significant differences in ...
... and 7 hyperthyroid), 2 (9%) minimum change (one euthyroid and one hyperthyroid) and 2 (9%) increased (one euthyroid and one hyperthyroid) cases. As a total, there were 54 (77%) decreased, 8 (11.5%) minimum change and 8 (11.5%) increased cases. There were no statistically significant differences in ...
The endocrine system
... Disorders of Thyroid Function and Regulation • Hypothyroidism, too little thyroid function, can produce symptoms such as – Weight gain, lethargy, cold intolerance ...
... Disorders of Thyroid Function and Regulation • Hypothyroidism, too little thyroid function, can produce symptoms such as – Weight gain, lethargy, cold intolerance ...
Endocrine System
... 2 . Secreted hormones are transported by the blood to specific sites called ______________________ ______________________, where they perform precise functions. 3 . Another name for the pituitary gland is the ______________________. 4 . The pancreas and gonads are classified as _____________________ ...
... 2 . Secreted hormones are transported by the blood to specific sites called ______________________ ______________________, where they perform precise functions. 3 . Another name for the pituitary gland is the ______________________. 4 . The pancreas and gonads are classified as _____________________ ...
The SNMMI Practice Guideline for Therapy of Thyroid Disease with I 3.0* 131
... with oral levothyroxine. The goal of therapy for a large nontoxic nodular goiter is the reduction of thyroid volume to relieve symptoms caused by compression of the goiter on structures in the neck. ...
... with oral levothyroxine. The goal of therapy for a large nontoxic nodular goiter is the reduction of thyroid volume to relieve symptoms caused by compression of the goiter on structures in the neck. ...
hGH - ISpatula
... • Hypothalamus is a major link between nervous and endocrine system • Pituitary is attached to hypothalamus by infundibulum and divided in to: • Anterior pituitary or adenohypophysis • Posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • The anterior pituitary receives signalling molecules from the hypothalamu ...
... • Hypothalamus is a major link between nervous and endocrine system • Pituitary is attached to hypothalamus by infundibulum and divided in to: • Anterior pituitary or adenohypophysis • Posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • The anterior pituitary receives signalling molecules from the hypothalamu ...
Endocrine System
... • Oxytocin secretion from posterior pituitary regulated by neurotransmitter release ...
... • Oxytocin secretion from posterior pituitary regulated by neurotransmitter release ...
Supplementary Figure 1 - PowerPoint (70 KB )
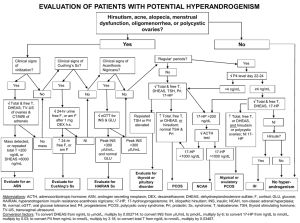
... EVALUATION OF PATIENTS WITH POTENTIAL HYPERANDROGENISM Hirsutism, acne, alopecia, menstrual dysfunction, oligomenorrhea, or polycystic ovaries? Yes Clinical signs of virilization? ...
... EVALUATION OF PATIENTS WITH POTENTIAL HYPERANDROGENISM Hirsutism, acne, alopecia, menstrual dysfunction, oligomenorrhea, or polycystic ovaries? Yes Clinical signs of virilization? ...
Lect 08 Endocrine 1 - intro (KKD)
... hi hormones h regulate l t secretion ti other hormones (either releasing or inhibitory) • example l – thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) – secreted from anterior pituitary – stimulates thyroid hormone secretion from thyroid gland – maintains structural integrity of thyroid gland ...
... hi hormones h regulate l t secretion ti other hormones (either releasing or inhibitory) • example l – thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) – secreted from anterior pituitary – stimulates thyroid hormone secretion from thyroid gland – maintains structural integrity of thyroid gland ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 22
... Thyroxine maintains the basal metabolic rate of the body and regulates the carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism. Water and electrolyte balance is also maintained by thyroid hormones. Thyrocalcitonin or calcitonin lowers calcium level in blood plasma. It plays a significant role in calcium level ...
... Thyroxine maintains the basal metabolic rate of the body and regulates the carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism. Water and electrolyte balance is also maintained by thyroid hormones. Thyrocalcitonin or calcitonin lowers calcium level in blood plasma. It plays a significant role in calcium level ...
ANATOMIA FUNCTIONALA/ FIZIOPATOLOGIA HIPOTALAMUSULUI
... can be divided into fat and fat-free or lean body mass with certain characteristics. These techniques are relatively costly, time-consuming and do not give information on the distribution of the fat. Techniques such as bioelectrical impedance rely on the fact that fat is not as good an electrical co ...
... can be divided into fat and fat-free or lean body mass with certain characteristics. These techniques are relatively costly, time-consuming and do not give information on the distribution of the fat. Techniques such as bioelectrical impedance rely on the fact that fat is not as good an electrical co ...
Effect of Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy
... Methods: Eighty subjects were recruited for this study. 40 patients (patient group before treatment G1) were treated with gradually increasing doses of “thyroxine” (50,100 and 150 g/day “doses adjusted by the treating physician”), each for 20 days to achieve a euthyroid state. Then 100-150 µg/day of ...
... Methods: Eighty subjects were recruited for this study. 40 patients (patient group before treatment G1) were treated with gradually increasing doses of “thyroxine” (50,100 and 150 g/day “doses adjusted by the treating physician”), each for 20 days to achieve a euthyroid state. Then 100-150 µg/day of ...
9 Endocrine - bloodhounds Incorporated
... – Nausea, sometimes with vomiting, and diarrhea are common – The muscles are weak and often go into spasm – There are often emotional changes, particularly irritability and depression – Because of salt loss, a craving for salty foods is common – Finally, the increase in ACTH due to the loss of corti ...
... – Nausea, sometimes with vomiting, and diarrhea are common – The muscles are weak and often go into spasm – There are often emotional changes, particularly irritability and depression – Because of salt loss, a craving for salty foods is common – Finally, the increase in ACTH due to the loss of corti ...
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology
... 1. increased cellular uptake of amino acids = increased protein synthesis = growth/maintenance 2. increased lipolysis and gluconeogenesis for energy, leading to hyperglycemia = diabetogenic effect ...
... 1. increased cellular uptake of amino acids = increased protein synthesis = growth/maintenance 2. increased lipolysis and gluconeogenesis for energy, leading to hyperglycemia = diabetogenic effect ...
Essentials of Pathophysiology CHAPTER 31 ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... in receptor numbers by means of a process called _________________ ; this increases the sensitivity of the body to existing hormone levels. ...
... in receptor numbers by means of a process called _________________ ; this increases the sensitivity of the body to existing hormone levels. ...
Endocrine System
... fully functional • Onset of puberty usually occurs between the ages of 9 and 15 & begins about one year earlier in females than in males • Puberty begins when hypothalamus signals pituitary to produce increased levels of ...
... fully functional • Onset of puberty usually occurs between the ages of 9 and 15 & begins about one year earlier in females than in males • Puberty begins when hypothalamus signals pituitary to produce increased levels of ...
The Endocrine System
... Overview of Endocrine System • Endocrine glands secrete into extracellular space, secretion (hormones) diffuses to circulatory system • Includes primary glands - pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, & pineal glands • Accessory structures with glandular function as well as others - hypothalamus, ...
... Overview of Endocrine System • Endocrine glands secrete into extracellular space, secretion (hormones) diffuses to circulatory system • Includes primary glands - pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, & pineal glands • Accessory structures with glandular function as well as others - hypothalamus, ...
The Endocrine System Overview of Endocrine System • Endocrine
... Overview of Endocrine System • Endocrine glands secrete into extracellular space, secretion (hormones) diffuses to circulatory system • Includes primary glands - pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, & pineal glands • Accessory structures with glandular function as well as others - hypothalamus, ...
... Overview of Endocrine System • Endocrine glands secrete into extracellular space, secretion (hormones) diffuses to circulatory system • Includes primary glands - pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, & pineal glands • Accessory structures with glandular function as well as others - hypothalamus, ...
PE1463/C: Dr Henry Lindner Letter of 7 March 2013 (356KB pdf)
... production and inactivates cortisol in the tissues,45,46,47 explaining why women have symptoms of cortisol deficiency when estrogen levels are high in the menstrual cycle (premenstrual syndrome and dysphoric disorder).48,49,50 Cortisol has anti-estrogen effects in the endometrium;51 lower saliva cor ...
... production and inactivates cortisol in the tissues,45,46,47 explaining why women have symptoms of cortisol deficiency when estrogen levels are high in the menstrual cycle (premenstrual syndrome and dysphoric disorder).48,49,50 Cortisol has anti-estrogen effects in the endometrium;51 lower saliva cor ...
File - CAPE BIO UNIT I 2012
... In response to too little calcium in the diet, the parathyroid glands make parathyroid hormone, or PTH, that takes calcium from bones so that it will be available in the blood for nerve conduction and muscle contraction. ...
... In response to too little calcium in the diet, the parathyroid glands make parathyroid hormone, or PTH, that takes calcium from bones so that it will be available in the blood for nerve conduction and muscle contraction. ...
The Endocrine System
... Influences metabolic activities by means of hormones Responses occur more slowly but tend to last longer than those of the nervous system Endocrine glands: pituitary, thyroid, thymus, pancreas, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands ...
... Influences metabolic activities by means of hormones Responses occur more slowly but tend to last longer than those of the nervous system Endocrine glands: pituitary, thyroid, thymus, pancreas, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands ...
Biology 416K Summer 2002
... c. Peptide hormones are stored in intracellular vesicles. d. Peptide hormones are first synthesized as as a longer peptide. e. Peptide hormones interact with receptors on the membrane of their target cell. 17. In a test of hormone therapy, a single large injection of gonadotropin-releasing hormone w ...
... c. Peptide hormones are stored in intracellular vesicles. d. Peptide hormones are first synthesized as as a longer peptide. e. Peptide hormones interact with receptors on the membrane of their target cell. 17. In a test of hormone therapy, a single large injection of gonadotropin-releasing hormone w ...
File
... message is slower. Like bulk mail, the message is more diffuse (reaches a greater area) and affects more than one person or organ. Although the hormone travels through the body via the blood, it can only affect those cells with receptors for that specific hormone. Hormones are a slower method of com ...
... message is slower. Like bulk mail, the message is more diffuse (reaches a greater area) and affects more than one person or organ. Although the hormone travels through the body via the blood, it can only affect those cells with receptors for that specific hormone. Hormones are a slower method of com ...
Endocrine - JCU
... Only the main endocrine glands will be discussed in this chapter. Hormones govern most of the main functions of the body – metabolism, maintenance of blood pressure, maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance, growth, and sexual development and differentiation of the body. When the body is functio ...
... Only the main endocrine glands will be discussed in this chapter. Hormones govern most of the main functions of the body – metabolism, maintenance of blood pressure, maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance, growth, and sexual development and differentiation of the body. When the body is functio ...
Aalborg Universitet Prevention of autoimmune - VBN
... and thyroid function abnormalities. In mild iodine deficiency (median urinary iodine concentration 5099 µg/L6) the consequences observed are less severe, the most common being goitre.5 Normally, the thyroid gland will adapt to the low amount of iodine available in mild iodine deficiency. Iodine auto ...
... and thyroid function abnormalities. In mild iodine deficiency (median urinary iodine concentration 5099 µg/L6) the consequences observed are less severe, the most common being goitre.5 Normally, the thyroid gland will adapt to the low amount of iodine available in mild iodine deficiency. Iodine auto ...
Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology
... homeostasis at the cellular level and is a vital link in proper body operations. Illness and death can result from an endocrine imbalance. Treatment usually requires management of the deviant hormone by either reducing or increasing its production or secretion from its associat ...
... homeostasis at the cellular level and is a vital link in proper body operations. Illness and death can result from an endocrine imbalance. Treatment usually requires management of the deviant hormone by either reducing or increasing its production or secretion from its associat ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.