* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.03 Remember Structures of the endocrine system What are the
Polycystic ovary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
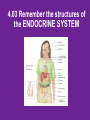
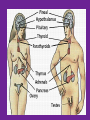
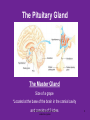
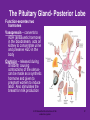
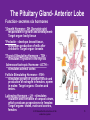
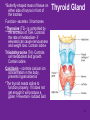
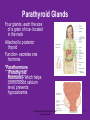
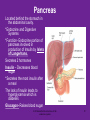
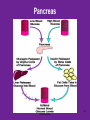
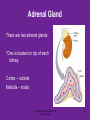
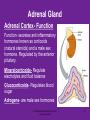
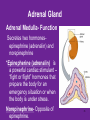
4.03 Remember the structures of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 1 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 2 Activity Day 1 Have students go to media center and get a 6ft piece of paper. Students will trace someone in each group on the paper. Using the textbook, students are to draw the endocrine glands- do not label these or write the names on these. Do this later in the unit. Finish vocabulary. Textbook pgs 324-341 Processing Day 1 Endocrine System Crash Course- Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WVrlHH14q 3o The Endocrine Systemhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S_vQZDH9hY&list=PL5A39C879B19478E5 Warm up Day 2 In groups brainstorm what you know about the endocrine system on the large piece of paper on table. Share with the class. 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system *ENDOCRINE GLANDS *Their function is to secrete hormones directly into bloodstream Ductless -only act on target cells 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 6 Hormonal Control- 2 Types Negative Feedback Drop in hormone level triggers a chain reaction to increase secretion, for example Blood level of hormone falls Brain gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland Gland stimulates more hormone When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop Nervous Control In some cases, sympathetic nervous system causes direct release of hormone from gland (for example, when stress causes the adrenal medulla to secrete adrenalin) Hypothalamus Located in the brain and is •Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone- Increases the release of also part of the Nervous growth hormone from the pituitary. System. Function- Controls much •Growth Hormone Inhibiting of the bodies function and Hormone- Decreases the release of secretes 5 hormones that GH from the pituitary. control the Pituitary Gland •Corticotropin- Increases the release of Adrenocorticotropic Hormone– ACTH from the pituitary. •Gonadotropin Releasing HormoneIncreases the release of LH and FSH by the pituitary. •Thyrotropin Releasing HormoneIncreases the release of TSH from the pituitary. Pineal Gland Located deep in the brain between the right and left hemispheres of the brain. Function- secretes Melatonin- Regulates sleep cycle. The Pituitary Gland The Master Gland Size of a grape *Located at the base of the brain in the cranial cavity 4.03consists Remember the structures of the and of 2 lobes endocrine system 11 The Pituitary Gland- Posterior Lobe Function-secretes two hormones Vasopressin – converts to ADH (antidiuretic hormone) in the bloodstream, acts on kidney to concentrate urine and preserve H2O in the body Oxytocin – released during childbirth causing contractions of the uteruscan be made as a synthetic hormone and given to pregnant women to induce labor. Also stimulates the breast for milk production 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 12 The Pituitary Gland- Anterior Lobe Function- secretes six hormones *Growth Hormone - GH (Somatotropin) responsible for growth and developmentTarget organ- body tissue *Prolactin – develops breast tissue, stimulates production of milk after childbirth- Target organ- breasts *Thyroid Stimulating Hormone – TSH stimulates Thyroxine in the thyroid Adrenocorticotropic Hormone– ACTH – stimulates adrenal cortex Follicle Stimulating Hormone – FSH stimulates growth of graafian follicle and production of estrogen in females, sperm in males- Target organs- Ovaries and testes. Lutinezing Hormone – LH – stimulates ovulation and formation of corpus luteum, which produces progesterone in femalesTarget organs- testes, male and ovaries , females 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 13 *Butterfly-shaped mass of tissue on either side of larynx in front of the trachea Function- secretes 3 hormones *Thyroxine (T3)– is controlled by the secretion of TSH. Controls the rate of metabolism- if elevated can cause nervousness and weight loss. Contain iodine Triiodothyronine (T4)- Controls cell metabolism and growth. Contain iodine Calcitonin – controls calcium ion concentration in the body, prevents hypercalcemia *The thyroid needs iodine to function properly. If it does not get enough it will produce a goiter. Prevention- Iodized Salt. Thyroid Gland 14 Parathyroid Glands Four glands, each the size of a grain of rice- located in the neck Attached to posterior thyroid Function- secretes one hormone *Parathormone (Parathyroid Hormone)- which helps control blood calcium level, prevents hypocalcemia 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 15 Processing • Take paper from yesterday and label the endocrine glands you learned about today. Add which hormones each one secretes • Identify Endocrine Glands Labeling Warm up Endocrine System Videohttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S_vQZDH9hY Thymus Gland Serves both the endocrine system and the lymphatic system Function- Secretes ThymosinT-lymphocyte production Located under the sternum Large during childhood but atrophy with age. 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 18 Pancreas Located behind the stomach in the abdominal cavity. *Endocrine and Digestive Systems *Function- Endocrine portion of pancreas involved in production of Insulin by Islets of Langerhans. Secretes 2 hormones Insulin – Decreases blood sugar *Secretes the most insulin after a meal The lack of insulin leads to hyperglycemia which is diabetes Glucagon- Raises blood sugar 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 19 Pancreas 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 20 Adrenal Gland There are two adrenal glands. *One is located on top of each kidney. Cortex – outside Medulla – inside 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 21 Adrenal Gland Adrenal Cortex- Function Function- secretes anti inflammatory hormones known as corticoids (natural steroids) and a male sex hormone. Regulated by the anterior pituitary. Mineralcorticoids- Regulate electrolytes and fluid balance Glucocorticoids- Regulates blood sugar Adrogens- are male sex hormones 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 22 Adrenal Gland Adrenal Medulla- Function Secretes two hormonesepinephrine (adrenalin) and norepinephrine *Epinepherine (adrenalin) is a powerful cardiac stimulant – “fight or flight” hormones that prepare the body for an emergency situation or when the body is under stress. Norepinephrine- Opposite of epinephrine. 23 Sex glands Gonads Testes (male) Function- secretes one hormone *Testosterone – male reproductive organs and secondary sex characteristics *If a male does not produce this during puberty, he will not develop a deep voice, body hair or increased muscle mass. 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 24 Gonads Sex glands: *Ovaries (female)- located in the pelvic cavity Function- secretes 2 hormones *Estrogen – development of female reproductive organs, secondary sex characteristics*If not produced during the teenage years, breasts will be undeveloped and the menstrual cycle will not begin. Progesterone – plays a part in the menstrual cycle and maintaining pregnancy 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 25 Processing • Hormone Functions Crossword • Who Am I? • Endocrine System Matching • Processing I Questions Processing I What is the chemical that is secreted by the endocrine glands? TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) is secreted by the pituitary and acts on what gland? Which gland is divided into anterior and posterior lobes? Which gland is butterfly shaped and is located in the neck? Which endocrine gland is located in the cranial cavity at the base of the brain? The pancreas is also an organ in what body system? Which gland is divided into a cortex and medulla? What is the structure called that produces hormones? Which hormone stimulates milk production? Which hormone causes the “fight or flight” response and what gland secretes this? Parathormone increases what substance in the blood? Which endocrine gland is located in the pelvic cavity? Which gland contains the Islet of Langerhans? Which hormone if elevated would cause nervousness and weight loss? When will the pancreas secrete the most insulin? 4.03 Remember Structures of the endocrine system What are the structures of the endocrine system? 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system 28