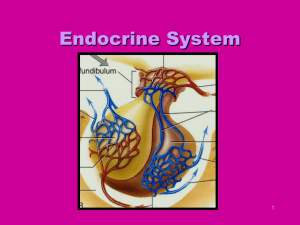
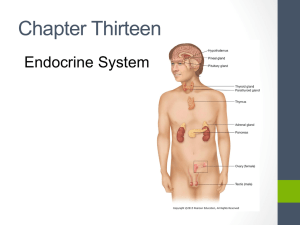
TAKE HOME EXAM –URINARY SYSTEM REPRODUCTIVE
... Fill in the blank-with the correct answer. 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as _______________ ...
... Fill in the blank-with the correct answer. 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as _______________ ...
Endocrine Lesson 2 Monday, March 12
... • Estrogen secondary sex characteristics • Both are involved in the menstrual cycle ...
... • Estrogen secondary sex characteristics • Both are involved in the menstrual cycle ...
Endocrinology - (Chemical signals in animals)
... Indicate whether level is increased, decreased or no change Primary thyroid tumor hypersecreting hypothalamus anterior pituitary thyroid gland ...
... Indicate whether level is increased, decreased or no change Primary thyroid tumor hypersecreting hypothalamus anterior pituitary thyroid gland ...
Endocrine System - Porterville College Home
... ______________________ can result. ________ swells the tissues behind the eyes causing the eye to bulge. IV. Parathyroid Gland _________ glands on the posterior side of the thyroid gland. Chief cells produce __________________________ Oxyphil cells _________________________________________. PTH incr ...
... ______________________ can result. ________ swells the tissues behind the eyes causing the eye to bulge. IV. Parathyroid Gland _________ glands on the posterior side of the thyroid gland. Chief cells produce __________________________ Oxyphil cells _________________________________________. PTH incr ...
Printable - Georgia CTAE | Home
... an abnormal bodily condition that is caused by excess corticosteroids and especially cortisol from adrenal or pituitary hyperfunction ...
... an abnormal bodily condition that is caused by excess corticosteroids and especially cortisol from adrenal or pituitary hyperfunction ...
8Aldosterone 8Na + secretion 8 H 2 O reabsorption9 urine volume
... • Derived from mesoderm • 80% of adrenal gland • Three subdivisions (deep to superficial) – Zona reticularis – Zona fasciculata – Zona glomerulosa ...
... • Derived from mesoderm • 80% of adrenal gland • Three subdivisions (deep to superficial) – Zona reticularis – Zona fasciculata – Zona glomerulosa ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Ductless glands that produce hormones that are released directly into the bloodstream and are transported throughout the body to regulate the metabolic function of other cells in the body. Types of hormones: Paracrine Autocrine ...
... Ductless glands that produce hormones that are released directly into the bloodstream and are transported throughout the body to regulate the metabolic function of other cells in the body. Types of hormones: Paracrine Autocrine ...
The Endocrine System
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
The Endocrine System
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
The Endocrine System
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
The Endocrine System
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
Comparative Vertebrate Physiology
... from ER Ca++ activates channels on plasma membrane or binds to calmodulin which activates metabolism ...
... from ER Ca++ activates channels on plasma membrane or binds to calmodulin which activates metabolism ...
Hormone - Denton ISD
... • Norepinephrine [a.k.a. noradrenaline] is released as a neurotransmitter by the sympathetic nerve endings AND is secreted by the adrenal gland as a hormone • As a neurotransmitter it travels a very short distance across the synaptic cleft and binds to a receptor protein to stimulate the postsynapti ...
... • Norepinephrine [a.k.a. noradrenaline] is released as a neurotransmitter by the sympathetic nerve endings AND is secreted by the adrenal gland as a hormone • As a neurotransmitter it travels a very short distance across the synaptic cleft and binds to a receptor protein to stimulate the postsynapti ...
File
... • With diabetes mellitus, either your body doesn't make enough insulin, it can't use the insulin it does produce, or a combination of both. ...
... • With diabetes mellitus, either your body doesn't make enough insulin, it can't use the insulin it does produce, or a combination of both. ...
2. Thyroid Gland T 4 and T 3
... • located in abdominal cavity against back wall (retroperitoneal), superior to kidney • surrounded by connective tissue capsule • two regions: – cortex - outer region, “glandular”, three zones • zona glomerulosa - outer zone • zona fasciculata - middle zone • zona reticularis - inner zone ...
... • located in abdominal cavity against back wall (retroperitoneal), superior to kidney • surrounded by connective tissue capsule • two regions: – cortex - outer region, “glandular”, three zones • zona glomerulosa - outer zone • zona fasciculata - middle zone • zona reticularis - inner zone ...
Lecture 8 - Endocrine
... Function • Influences growth, metabolism, and homeostasis over prolonged periods • Secretes hormone products into interstitial spaces which are then absorbed into the blood and transported throughout the body • Hormonal control is much slower than nervous control, but the effects of the endocrine sy ...
... Function • Influences growth, metabolism, and homeostasis over prolonged periods • Secretes hormone products into interstitial spaces which are then absorbed into the blood and transported throughout the body • Hormonal control is much slower than nervous control, but the effects of the endocrine sy ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
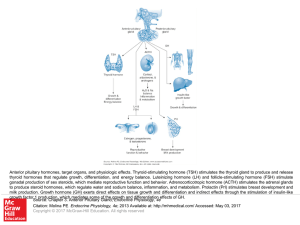
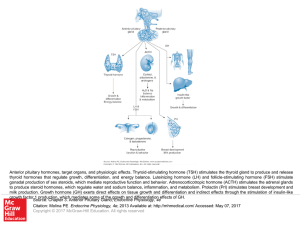
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
Slide ()
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
Hormones
... Endocrine glands that make up the endocrine system1 are not connected, unlike components of other body systems. They secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones have a key role in regulating body processes. For example, they control growth and reproduction. They regulate the composition of body ...
... Endocrine glands that make up the endocrine system1 are not connected, unlike components of other body systems. They secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones have a key role in regulating body processes. For example, they control growth and reproduction. They regulate the composition of body ...
hormones - Cloudfront.net
... • The pancreas is a large gland behind your stomach that helps the body to maintain healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels. Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and ...
... • The pancreas is a large gland behind your stomach that helps the body to maintain healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels. Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and ...
thyroid gland - Uplift Education
... Record stress levels twice a day (once in the morning/afternoon, once at night) for a week On a scale of 1 to 5 where 1 is experiencing no stress and 5 is experiencing extreme stress, rank how stressed you currently feel. ...
... Record stress levels twice a day (once in the morning/afternoon, once at night) for a week On a scale of 1 to 5 where 1 is experiencing no stress and 5 is experiencing extreme stress, rank how stressed you currently feel. ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.