Chemical Regulation Endocrine System communication
... Releases hormone messengers (do not “do work”) TSH – thyroid stimulating hormone ACTH – stimulates adrenal glands FSH – stimulates the ovaries Oxytocin – labor contractions Calcitonin – Calcium metabolism ...
... Releases hormone messengers (do not “do work”) TSH – thyroid stimulating hormone ACTH – stimulates adrenal glands FSH – stimulates the ovaries Oxytocin – labor contractions Calcitonin – Calcium metabolism ...
www.med.fsu.edu
... 1. Proteins are water soluble and therefore cannot pass through the cell membrane. Therefore nonsteroid hormones affect the activity of the cell via a secondary messenger system (see: lock and key model and cyclic ...
... 1. Proteins are water soluble and therefore cannot pass through the cell membrane. Therefore nonsteroid hormones affect the activity of the cell via a secondary messenger system (see: lock and key model and cyclic ...
Practical 1 Endocrine Tissues Handout
... adrenal cortex produces and secretes steroid hormones including mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids (cortisol in man), and sex hormones (in small amounts). The steroids are produced from cholesterol. Glucocorticoid production and release is regulated mainly by ACTH from the pituitary g ...
... adrenal cortex produces and secretes steroid hormones including mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids (cortisol in man), and sex hormones (in small amounts). The steroids are produced from cholesterol. Glucocorticoid production and release is regulated mainly by ACTH from the pituitary g ...
21-endocrine - life.illinois.edu
... •! intracellular molecule that relays signals from hormonereceptor complex into the cell •! cAMP is most common 2nd messenger ...
... •! intracellular molecule that relays signals from hormonereceptor complex into the cell •! cAMP is most common 2nd messenger ...
chapter 18 study guide
... promotes formation of calcitriol by kidneys which increases GI absorption of Ca2+, Mg2+, HPO42ADRENAL CORTEX of ADRENAL GLAND MINERALOCORTICOIDS aldosterone regulates blood levels of Na+, K+ helps adjust blood pressure & volume GLUCOCORTICOIDS cortisol (hydrocortisone), corticosterone, cortisone res ...
... promotes formation of calcitriol by kidneys which increases GI absorption of Ca2+, Mg2+, HPO42ADRENAL CORTEX of ADRENAL GLAND MINERALOCORTICOIDS aldosterone regulates blood levels of Na+, K+ helps adjust blood pressure & volume GLUCOCORTICOIDS cortisol (hydrocortisone), corticosterone, cortisone res ...
CHAPTER 18 STUDY GUIDE
... promotes formation of calcitriol by kidneys which increases GI absorption of Ca2+, Mg2+, HPO42ADRENAL CORTEX of ADRENAL GLAND MINERALOCORTICOIDS aldosterone regulates blood levels of Na+, K+ helps adjust blood pressure & volume GLUCOCORTICOIDS cortisol (hydrocortisone), corticosterone, cortisone res ...
... promotes formation of calcitriol by kidneys which increases GI absorption of Ca2+, Mg2+, HPO42ADRENAL CORTEX of ADRENAL GLAND MINERALOCORTICOIDS aldosterone regulates blood levels of Na+, K+ helps adjust blood pressure & volume GLUCOCORTICOIDS cortisol (hydrocortisone), corticosterone, cortisone res ...
Unit 7 Endocrine
... influences resistance to stress Cortisol (Hydrocortisone) – makes up 95% of glucocorticoids – primary role is that of gluconeogenesis l ...
... influences resistance to stress Cortisol (Hydrocortisone) – makes up 95% of glucocorticoids – primary role is that of gluconeogenesis l ...
Chapter 36 Integration: Endocrine Control I. The Endocrine System
... are secreted from neurons and act on immediately adjacent target cells for a short time. are secreted from cells of many different tissues; they act locally and are swiftly degraded , which are secreted by exocrine glands, have targets outside the body; they integrate social ...
... are secreted from neurons and act on immediately adjacent target cells for a short time. are secreted from cells of many different tissues; they act locally and are swiftly degraded , which are secreted by exocrine glands, have targets outside the body; they integrate social ...
glands of the human body
... Suprarenal gland- ACTH stimulates the cortex of the suprarenal glands to secrete steroid hormones that help the body resist stress, they also affect the metabolism. Thyroid gland- TSH stimulates the thyroid to secrete hormones that affect metabolism and body heat production, and promote normal devel ...
... Suprarenal gland- ACTH stimulates the cortex of the suprarenal glands to secrete steroid hormones that help the body resist stress, they also affect the metabolism. Thyroid gland- TSH stimulates the thyroid to secrete hormones that affect metabolism and body heat production, and promote normal devel ...
Endocrine System
... B)stimulates the retention of calcium by the kidneys C) stimulates the demineralization of bone D) causes blood phosphate level to decrease E) all of the above ...
... B)stimulates the retention of calcium by the kidneys C) stimulates the demineralization of bone D) causes blood phosphate level to decrease E) all of the above ...
No Slide Title
... Endocrine glands secrete their hormones directly into the blood stream All hormones only affect their Target Organs These organs contain receptor sites on the cell membrane or in the cytoplasm to which the hormone can attach. Cell Receptor Site Hormones are chemical messengers that help regulate cel ...
... Endocrine glands secrete their hormones directly into the blood stream All hormones only affect their Target Organs These organs contain receptor sites on the cell membrane or in the cytoplasm to which the hormone can attach. Cell Receptor Site Hormones are chemical messengers that help regulate cel ...
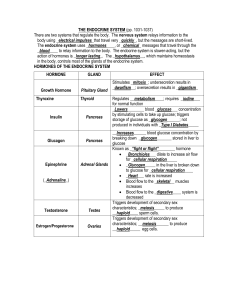
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (pp
... for normal function _Lowers________ blood _glucose___ concentration by stimulating cells to take up glucose; triggers storage of glucose as _glycogen______; not produced in individuals with _Type I Diabetes_____ ...
... for normal function _Lowers________ blood _glucose___ concentration by stimulating cells to take up glucose; triggers storage of glucose as _glycogen______; not produced in individuals with _Type I Diabetes_____ ...
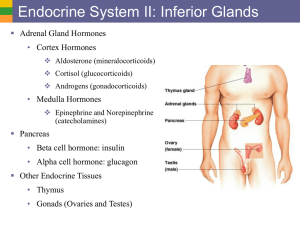
1c Endo Sys II - Inferior Glands
... Glucocorticoids and the Zona Fasciculata Type: Steroid hormone, classified as glucocorticoids, cortisol most important of these, made in the zona fasciculata of adreal cortex Regulation: Released in response to increased blood levels of ACTH produced by anterior pituitary; patterns of eating and ac ...
... Glucocorticoids and the Zona Fasciculata Type: Steroid hormone, classified as glucocorticoids, cortisol most important of these, made in the zona fasciculata of adreal cortex Regulation: Released in response to increased blood levels of ACTH produced by anterior pituitary; patterns of eating and ac ...
Endocrine System Vocabulary Acromegaly Adrenal Glands
... 1. Adrenal Glands: paired almond shaped glands that sit on top of the kidneys & are often referred to as suprarenal glands due to their location. They are broken down into 2 parts: the inner adrenal medulla that is part of the sympathetic nervous system secreting epinephrine & norepinephrine (import ...
... 1. Adrenal Glands: paired almond shaped glands that sit on top of the kidneys & are often referred to as suprarenal glands due to their location. They are broken down into 2 parts: the inner adrenal medulla that is part of the sympathetic nervous system secreting epinephrine & norepinephrine (import ...
Endocrine (regulatory) System
... • Adrenal cortex (corticosteroids): •glucocorticoids (cortisol)~ raise blood glucose •mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)~ reabsorption of Na+ and K+ ...
... • Adrenal cortex (corticosteroids): •glucocorticoids (cortisol)~ raise blood glucose •mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)~ reabsorption of Na+ and K+ ...
Chapter 1 A Perspective on Human Genetics
... • Adrenal cortex – Consists of three layers or zones • Zona glomerulosa – outermost layer (Mineralocorticoids) Medulla • Zona fasciculata – middle and largest portion (Glucocorticoids) • Zona reticularis – innermost zone (Sex hormones) ...
... • Adrenal cortex – Consists of three layers or zones • Zona glomerulosa – outermost layer (Mineralocorticoids) Medulla • Zona fasciculata – middle and largest portion (Glucocorticoids) • Zona reticularis – innermost zone (Sex hormones) ...
The Endocrine System
... • There are four parathyroid glands which are normally about the size and shape of a grain of rice. • The sole purpose of the parathyroid glands are to regulate the calcium level in our bodies within a very narrow range so that the nervous and muscular systems can function properly. ...
... • There are four parathyroid glands which are normally about the size and shape of a grain of rice. • The sole purpose of the parathyroid glands are to regulate the calcium level in our bodies within a very narrow range so that the nervous and muscular systems can function properly. ...
Endocrine Labs
... A. Define the term metabolism, and explain how the hormones in this lab help to maintain it. B. Explain the roles of thyroxine and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) in maintaining metabolic rate C. Describe how estrogen and estrogen replacement therapy affect bone density D. Explain how a fasting pl ...
... A. Define the term metabolism, and explain how the hormones in this lab help to maintain it. B. Explain the roles of thyroxine and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) in maintaining metabolic rate C. Describe how estrogen and estrogen replacement therapy affect bone density D. Explain how a fasting pl ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Secretes insulin and glucagon from groups of cells called Islets of langerhans ...
... Secretes insulin and glucagon from groups of cells called Islets of langerhans ...
Surgical importance of Thyroid Gland
... Hyperadrenalism-Cushing’s Syndrome Hypercortisolism can occur from; (1) Adenomas of: - Anterior pituitary ↑ ACTH, adrenal hyperplasia and excess cortisol secretion; Hypothalamus high levels of corticotropin- releasing hormone (CRH), ↑ ACTH release; Tumors “ectopic secretion” of ACTH by a tumors, ...
... Hyperadrenalism-Cushing’s Syndrome Hypercortisolism can occur from; (1) Adenomas of: - Anterior pituitary ↑ ACTH, adrenal hyperplasia and excess cortisol secretion; Hypothalamus high levels of corticotropin- releasing hormone (CRH), ↑ ACTH release; Tumors “ectopic secretion” of ACTH by a tumors, ...
• Two hormones are produced: (vasopressin) Thyroid Gland The
... Other glands that secrete substances are the o They have o They deliver their products directly to a specific site General Characteristics of the Endocrine System • The endocrine and nervous systems communicate using chemical signals Neurons release neurotransmitters into a synapse affecting postsyn ...
... Other glands that secrete substances are the o They have o They deliver their products directly to a specific site General Characteristics of the Endocrine System • The endocrine and nervous systems communicate using chemical signals Neurons release neurotransmitters into a synapse affecting postsyn ...
Human Endocrine System
... Parathormone controls calcium metabolism Calcium is necessary for proper growth of teeth and bones, blood clotting, and nerve function ...
... Parathormone controls calcium metabolism Calcium is necessary for proper growth of teeth and bones, blood clotting, and nerve function ...
Chapter 18
... • Secrete PTH – Increases blood calcium levels – Stimulates osteoclasts – Promotes calcium reabsorption by kidneys ...
... • Secrete PTH – Increases blood calcium levels – Stimulates osteoclasts – Promotes calcium reabsorption by kidneys ...
Physiology of the Stress Response 001
... noradrenaline which is released a the nerve endings. The stress response also includes the activity of the adrenal, pituitary and thyroid glands. The two adrenal glands are located one on top of each kidney. The middle part of the adrenal gland is called the adrenal medulla and is connected to the s ...
... noradrenaline which is released a the nerve endings. The stress response also includes the activity of the adrenal, pituitary and thyroid glands. The two adrenal glands are located one on top of each kidney. The middle part of the adrenal gland is called the adrenal medulla and is connected to the s ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.