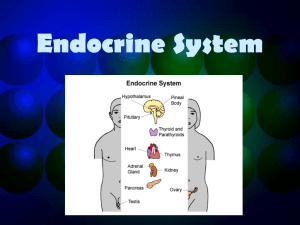
The Endocrine System
... • It is produced when calcium levels in the blood increase • Causes an uptake of calcium by bone • produced by the thyroid and NOT the hypothalamus The Parathyroid glands Produces parathyroid hormone (PTH) • When calcium levels in the blood are low • Stimulates bone breakdown (osteoclast) and reabso ...
... • It is produced when calcium levels in the blood increase • Causes an uptake of calcium by bone • produced by the thyroid and NOT the hypothalamus The Parathyroid glands Produces parathyroid hormone (PTH) • When calcium levels in the blood are low • Stimulates bone breakdown (osteoclast) and reabso ...
What is the Endocrine System? What do Hormones Do?
... Structurally and functionally, they are two glands in one ...
... Structurally and functionally, they are two glands in one ...
Endocrine System ppt
... increased blood flow to the muscles increased blood pressure increase in the depth of breathing ...
... increased blood flow to the muscles increased blood pressure increase in the depth of breathing ...
1 - Lone Star College
... Peptide hormone binds to a receptor Peptide hormone “first messenger” activates a “second messenger” (cyclic AMP and calcium) Second messenger sets in motion an enzyme cascade that leads to: ...
... Peptide hormone binds to a receptor Peptide hormone “first messenger” activates a “second messenger” (cyclic AMP and calcium) Second messenger sets in motion an enzyme cascade that leads to: ...
Endocrine system
... inhibits bone resorption and enhances Ca2+ release by the kidney. In humans calcitonin not used except during extensive bone growth of childhood. Adrenal medulla: (fight or flight/stress hormones stimulated by nervous system) Catecholamines – class of amine hormones made from tyrosine. Epinephrine ( ...
... inhibits bone resorption and enhances Ca2+ release by the kidney. In humans calcitonin not used except during extensive bone growth of childhood. Adrenal medulla: (fight or flight/stress hormones stimulated by nervous system) Catecholamines – class of amine hormones made from tyrosine. Epinephrine ( ...
The Endocrine System
... Insulin the rate at which various body cells take up glucose. Thus, insulin lowers the blood glucose level. ...
... Insulin the rate at which various body cells take up glucose. Thus, insulin lowers the blood glucose level. ...
The Endocrine System Negative Feedback Mechanism
... development, and its responses tend to be long-lasting, whereas nervous system responses tend to be rapid and discrete. • What’s the benefit of the endocrine system’s longlasting responses? How can it be a detriment? ...
... development, and its responses tend to be long-lasting, whereas nervous system responses tend to be rapid and discrete. • What’s the benefit of the endocrine system’s longlasting responses? How can it be a detriment? ...
the endocrine system
... This means that when levels are unbalanced the body recognizes this and hormones are released to balance this back again. Remember homeostasis. Think of this process like a thermostat. It is set to maintain a balance in temperature. When it goes over or under the set temperature, it cuts in or out t ...
... This means that when levels are unbalanced the body recognizes this and hormones are released to balance this back again. Remember homeostasis. Think of this process like a thermostat. It is set to maintain a balance in temperature. When it goes over or under the set temperature, it cuts in or out t ...
Chapter 41 Endocrine System
... A. Adrenal Medulla The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine under conditions of stress. They bring about all those responses we associate with the “fight or flight” reaction: the blood glucose level and the metabolic rate increases, as do breathing and heart rate. The blood vessel ...
... A. Adrenal Medulla The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine under conditions of stress. They bring about all those responses we associate with the “fight or flight” reaction: the blood glucose level and the metabolic rate increases, as do breathing and heart rate. The blood vessel ...
The Endocrine System and Homeostasis
... Promotes the conversion of glycogen to glucose. As glycogen is converted to glucose in the liver, the blood sugar level returns to normal. Other hormones, such as hGH, cortisol, and epinephrine also contribute to increasing the level of blood glucose. Insulin causes a decrease in blood sugar level, ...
... Promotes the conversion of glycogen to glucose. As glycogen is converted to glucose in the liver, the blood sugar level returns to normal. Other hormones, such as hGH, cortisol, and epinephrine also contribute to increasing the level of blood glucose. Insulin causes a decrease in blood sugar level, ...
Endocrine System PPT - Effingham County Schools
... Endocrine - secretions go into the blood stream. Exocrine - secretions go into ducts. The endocrine system utilizes endocrine glands, not exocrine. ...
... Endocrine - secretions go into the blood stream. Exocrine - secretions go into ducts. The endocrine system utilizes endocrine glands, not exocrine. ...
Human Endocrine Glands Section 39-2 pgs 1003-1008
... ________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________ and by increasing the uptake of calcium from the digestive system. ...
... ________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________ and by increasing the uptake of calcium from the digestive system. ...
Endocrine System
... gland selects and removes materials from the blood, processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body. ...
... gland selects and removes materials from the blood, processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body. ...
The Endocrine System
... This gland lies in the lower part of the neck and attains a maximum length of about 6cm. After puberty, the thymus begins to atrophy so that in the adult only fibrous remnants is found. Its secretion is thought to act as a brake on the development of sex organs so that as the thymus atrophies, the s ...
... This gland lies in the lower part of the neck and attains a maximum length of about 6cm. After puberty, the thymus begins to atrophy so that in the adult only fibrous remnants is found. Its secretion is thought to act as a brake on the development of sex organs so that as the thymus atrophies, the s ...
Both controlled by the posterior pituitary gland, vasopressin ______
... Gland regulation of oxyphil cells results in an increase or decrease of calcium in the blood. ...
... Gland regulation of oxyphil cells results in an increase or decrease of calcium in the blood. ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Suspended from the base of the hypothalamus by a slender stalk is a pea-size lobed gland called the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland has anterior and posterior lobes. The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland also stores and secretes two of the hormones that are synthesized in the hypothal ...
... Suspended from the base of the hypothalamus by a slender stalk is a pea-size lobed gland called the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland has anterior and posterior lobes. The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland also stores and secretes two of the hormones that are synthesized in the hypothal ...
Endocrine System Bookwork KEY
... levels of the stimulated hormones increase, the stimulus substance is either turned off (in the case of tropic hormones) or ceases to exist (because hormonal action results in a “correction” of the blood levels of the trigger substances). Once there is no stimulus, the previously stimulated endocrin ...
... levels of the stimulated hormones increase, the stimulus substance is either turned off (in the case of tropic hormones) or ceases to exist (because hormonal action results in a “correction” of the blood levels of the trigger substances). Once there is no stimulus, the previously stimulated endocrin ...
Stress Psychophysiology Introduction The Brain
... • Influenced by ACTH, the adrenal cortex (outer portion of the adrenal gland) will release two types of hormones, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. • The primary glucocorticoid is cortisol, which is responsible for providing the body with increased energy (more glucose and fat are released int ...
... • Influenced by ACTH, the adrenal cortex (outer portion of the adrenal gland) will release two types of hormones, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. • The primary glucocorticoid is cortisol, which is responsible for providing the body with increased energy (more glucose and fat are released int ...
Study Guide - Belle Vernon Area School District
... insufficient or defective insulin receptors on target cells. _______________________________4. Secreted from alpha cells when blood glucose levels are low. ...
... insufficient or defective insulin receptors on target cells. _______________________________4. Secreted from alpha cells when blood glucose levels are low. ...
*Section 5 (152
... Hormonal coordination is used by the body to control many long-term changes, e.g., growth and development. ● The most important endocrine gland in the body is the pituitary gland, which secretes hormones that regulate other endocrine glands. ...
... Hormonal coordination is used by the body to control many long-term changes, e.g., growth and development. ● The most important endocrine gland in the body is the pituitary gland, which secretes hormones that regulate other endocrine glands. ...
Practice Quiz
... Increasing plasma concentration of Ka+ Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I Angiontensin II Renin ACTH ...
... Increasing plasma concentration of Ka+ Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I Angiontensin II Renin ACTH ...
Endocrine System
... • Endocrine glands: secrete hormones in small amounts directly into the bloodstream. • Specific hormones effect specific body parts. • They travel through the bloodstream until they reach their target cells (they cell that the hormone acts on) • Hormones do NOT affect other cells other than the targ ...
... • Endocrine glands: secrete hormones in small amounts directly into the bloodstream. • Specific hormones effect specific body parts. • They travel through the bloodstream until they reach their target cells (they cell that the hormone acts on) • Hormones do NOT affect other cells other than the targ ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.