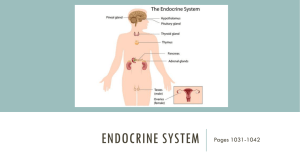
Pathology of the Endocrine System
... Hormones play an important function in regulation & control of body functions & metabolism Hormones exert control that is slower acting but of longer duration than nerve impulses Hormones secreted by endocrine glands go to a target organ How do specific hormones know where to go? – Receptors in the ...
... Hormones play an important function in regulation & control of body functions & metabolism Hormones exert control that is slower acting but of longer duration than nerve impulses Hormones secreted by endocrine glands go to a target organ How do specific hormones know where to go? – Receptors in the ...
Endocrine Organs - Histology on the Fly
... Function o Adrenal cortex – mesoderm origin, secrete steroid hormones o Adrenal medulla – neural crest origin; secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine ...
... Function o Adrenal cortex – mesoderm origin, secrete steroid hormones o Adrenal medulla – neural crest origin; secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... 4. Hormones are a. chemical signals, b. produced by endocrine glands, c. usually carried in the blood, and d. responsible for specific changes in target cells. 5. Hormones may also be released from specialized nerve cells called neurosecretory cells. B. 26.2 Hormones affect target cells using two ma ...
... 4. Hormones are a. chemical signals, b. produced by endocrine glands, c. usually carried in the blood, and d. responsible for specific changes in target cells. 5. Hormones may also be released from specialized nerve cells called neurosecretory cells. B. 26.2 Hormones affect target cells using two ma ...
Endocrine Notes
... Produce PARATHORMONE which helps control blood calcium level, prevents hypocalcemia THYMUS Endocrine gland and lymphatic organ Located behind the sternum, above and in front of the heart Begins to disappear at puberty ...
... Produce PARATHORMONE which helps control blood calcium level, prevents hypocalcemia THYMUS Endocrine gland and lymphatic organ Located behind the sternum, above and in front of the heart Begins to disappear at puberty ...
Endocrine System
... Produce PARATHORMONE which helps control blood calcium level, prevents hypocalcemia THYMUS Endocrine gland and lymphatic organ Located behind the sternum, above and in front of the heart Begins to disappear at puberty ...
... Produce PARATHORMONE which helps control blood calcium level, prevents hypocalcemia THYMUS Endocrine gland and lymphatic organ Located behind the sternum, above and in front of the heart Begins to disappear at puberty ...
The Endocrine System - respiratorytherapyfiles.net
... stimulates other glands to secrete specific hormones ...
... stimulates other glands to secrete specific hormones ...
Endocrine System
... Increases glucose use in ATP production Works in conjunction with hGH to regulate growth and development catecholamines Enhances the actions of epinephrine - norepinephrine ...
... Increases glucose use in ATP production Works in conjunction with hGH to regulate growth and development catecholamines Enhances the actions of epinephrine - norepinephrine ...
Lesson 8.2 Major Endocrine Organs
... the interior of the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are located on top of the kidneys. The noradrenalin and the adrenalin initiate and sustain what is known as the ‘Fight or Flight” response. They prepare the body to respond to danger in the following ways: 1. Increase the heart rate so that more ...
... the interior of the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are located on top of the kidneys. The noradrenalin and the adrenalin initiate and sustain what is known as the ‘Fight or Flight” response. They prepare the body to respond to danger in the following ways: 1. Increase the heart rate so that more ...
File
... Parathyroid Glands – Regulates calcium levels in the blood. The Parathyroid hormone (PTH), increases reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys and increase uptake of calcium from the digestive system. ...
... Parathyroid Glands – Regulates calcium levels in the blood. The Parathyroid hormone (PTH), increases reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys and increase uptake of calcium from the digestive system. ...
Endocrine System
... Growth hormone or GH - GH stimulates growth in childhood and is important for maintaining a healthy body composition. In adults it is also important for maintaining muscle mass and bone mass. It can affect fat distribution in the body. Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH - ACTH stimulates production of co ...
... Growth hormone or GH - GH stimulates growth in childhood and is important for maintaining a healthy body composition. In adults it is also important for maintaining muscle mass and bone mass. It can affect fat distribution in the body. Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH - ACTH stimulates production of co ...
Chapter 11: Endocrine System Theory Lecture Outline
... o Stimulates the lymphoid cells responsible for production of T cells which fight certain diseases o Critical to the development of the immune system Adrenal Glands • Located on top of each kidney • Gland has two parts – the cortex and the medulla a. Cortex 1. ACTH from the pituitary gland stimulate ...
... o Stimulates the lymphoid cells responsible for production of T cells which fight certain diseases o Critical to the development of the immune system Adrenal Glands • Located on top of each kidney • Gland has two parts – the cortex and the medulla a. Cortex 1. ACTH from the pituitary gland stimulate ...
Endocrine Review
... 1. Which of the following controls the activity of all the others? a. thyroid gland b. pituitary gland c. adrenal cortex d. hypothalamus e. ovaries 2. The pancreas increases its output of insulin in response to a. an increase in body temperature b. changing cycles of light and dark c. a decrease in ...
... 1. Which of the following controls the activity of all the others? a. thyroid gland b. pituitary gland c. adrenal cortex d. hypothalamus e. ovaries 2. The pancreas increases its output of insulin in response to a. an increase in body temperature b. changing cycles of light and dark c. a decrease in ...
Pathology of the Endocrine System Topics
... Adrenal Gland • Attached to the upper pole of each kidney • Adrenal cortex • Adrenal medulla ...
... Adrenal Gland • Attached to the upper pole of each kidney • Adrenal cortex • Adrenal medulla ...
FILL IN THE BLANKS: ENDOCRINE HORMONES (Student Copy
... release of calcium into the blood, increasing calcium reabsorption from intestine, and decreasing kidney tubule reabsorption of calcium Decreases blood phosphate levels by increasing phosphate loss in ...
... release of calcium into the blood, increasing calcium reabsorption from intestine, and decreasing kidney tubule reabsorption of calcium Decreases blood phosphate levels by increasing phosphate loss in ...
Ativity 21 - PCC - Portland Community College
... • Are male sex hormones that are produced in small quantities and converted to estrogens (female sex hormones) when they enter the blood • Epinephrine & Norepinephrine • Fight or flight response • Increase heart rate, increase skeletal muscle blood flow, decrease skin blood flow ...
... • Are male sex hormones that are produced in small quantities and converted to estrogens (female sex hormones) when they enter the blood • Epinephrine & Norepinephrine • Fight or flight response • Increase heart rate, increase skeletal muscle blood flow, decrease skin blood flow ...
Endocrine System
... that control several other endocrine glands The production and secretion of pituitary hormones can be influenced by factors such as emotions and changes in the ...
... that control several other endocrine glands The production and secretion of pituitary hormones can be influenced by factors such as emotions and changes in the ...
Adrenal medulla
... both adrenal glands caused by a tumor RESULT: aldosterone affects the renal tubules hypernatremia, hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis: ...
... both adrenal glands caused by a tumor RESULT: aldosterone affects the renal tubules hypernatremia, hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis: ...
Endocrine System
... throughout the entire body. • The response of hormones is slower and longerlasting than those of nerve impulses. The effects may last up to several hours or days. • The functions of the endocrine system include regulation of growth, development, and maturation as well as regulation of chemicals and ...
... throughout the entire body. • The response of hormones is slower and longerlasting than those of nerve impulses. The effects may last up to several hours or days. • The functions of the endocrine system include regulation of growth, development, and maturation as well as regulation of chemicals and ...
Unit 8 Endocrine revised
... Increases glucose use in ATP production Works in conjunction with hGH to regulate growth and development catecholamines Enhances the actions of epinephrine - norepinephrine ...
... Increases glucose use in ATP production Works in conjunction with hGH to regulate growth and development catecholamines Enhances the actions of epinephrine - norepinephrine ...
Chapter 16 Notes
... – nervous system, immune system, and endocrine system Endocrine system is especially important during teen years – regulate growth and development Endocrine glands – ductless, tubeless organs or groups of cells that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones – chemical substances ...
... – nervous system, immune system, and endocrine system Endocrine system is especially important during teen years – regulate growth and development Endocrine glands – ductless, tubeless organs or groups of cells that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones – chemical substances ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.