الشريحة 1
... The ratio of these two catecholamines differs considerably among species: in humans, cats and chickens, roughly 80, 60 and 30% of the catecholamine output is epinephrine. Following release into blood, these hormones bind adrenergic receptors on target cells, where they induce essentially the same ef ...
... The ratio of these two catecholamines differs considerably among species: in humans, cats and chickens, roughly 80, 60 and 30% of the catecholamine output is epinephrine. Following release into blood, these hormones bind adrenergic receptors on target cells, where they induce essentially the same ef ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... located below larynx in front of trachea, consists of two lobes, composed of glandular epithelium w/ outer C.T. capsule, divided into smaller regions called follicles where hormones are actually produced and secreted ...
... located below larynx in front of trachea, consists of two lobes, composed of glandular epithelium w/ outer C.T. capsule, divided into smaller regions called follicles where hormones are actually produced and secreted ...
Chapter 26- Chemical Regulation
... glucose –it’s stored as glycogen and used for metabolic E – Blood sugar decreases- glucagon secreted- liver cells breakdown glycogen into glucose – Antagonistic- negative feedback- controls glucose level – Diabetes- hormonal disease, body cells are unable to absorb glucose from blood • Not enough in ...
... glucose –it’s stored as glycogen and used for metabolic E – Blood sugar decreases- glucagon secreted- liver cells breakdown glycogen into glucose – Antagonistic- negative feedback- controls glucose level – Diabetes- hormonal disease, body cells are unable to absorb glucose from blood • Not enough in ...
1) The endocrine system - Chiropractic National Board Review
... 1) The endocrine system: a) releases chemicals into the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body b) releases hormones that alter the metabolic activities of many different tissues and organs c) produces effects that can last for hours, days, or even longer d) can alter gene activity of cells ...
... 1) The endocrine system: a) releases chemicals into the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body b) releases hormones that alter the metabolic activities of many different tissues and organs c) produces effects that can last for hours, days, or even longer d) can alter gene activity of cells ...
Adrenal Fatigue - What Is It? - Blueprint Fitness
... So how does this occur? Firstly, adrenal fatigue is a consequence of the external environment and one's response to it. This especially refers to the stress response. When we detect a stressful situation (previously catching a glance of a lerking ...
... So how does this occur? Firstly, adrenal fatigue is a consequence of the external environment and one's response to it. This especially refers to the stress response. When we detect a stressful situation (previously catching a glance of a lerking ...
Document
... Caused by inability of pancreas to secrete insulin or a resistance to insulin, affecting glucose levels. Can lead to renal disease, blindness, gangrene – leading to amputation. ...
... Caused by inability of pancreas to secrete insulin or a resistance to insulin, affecting glucose levels. Can lead to renal disease, blindness, gangrene – leading to amputation. ...
A single bout of moderate exercise results in long
... 1. True or False: A single bout of moderate exercise results in long-term changes in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. 2. True or False: Delayed menarche is an effect of intense exercise on the female reproductive system. 3. True or False: Gonadal hormones drop after intense exercise. 4. Tr ...
... 1. True or False: A single bout of moderate exercise results in long-term changes in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. 2. True or False: Delayed menarche is an effect of intense exercise on the female reproductive system. 3. True or False: Gonadal hormones drop after intense exercise. 4. Tr ...
Nervous co-ordination gives control. Endocrine co
... exocrine gland: secretes pancreatic juice endocrine gland: secretes insulin (alpha cells) & glucagon (beta cells) diabetes mellitus: a disease due to insufficient insulin production ...
... exocrine gland: secretes pancreatic juice endocrine gland: secretes insulin (alpha cells) & glucagon (beta cells) diabetes mellitus: a disease due to insufficient insulin production ...
endocrine1
... beneficial for the person in terms of fuel supply? 3. After an overnight fast, a patient arrives for an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. The first blood sample (even before ingestion of the Tru-Glu cola shows a plasma glucose concentration of 150 mg/dl. A) Do you have the patient drink the Tru-Glu? Why ...
... beneficial for the person in terms of fuel supply? 3. After an overnight fast, a patient arrives for an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. The first blood sample (even before ingestion of the Tru-Glu cola shows a plasma glucose concentration of 150 mg/dl. A) Do you have the patient drink the Tru-Glu? Why ...
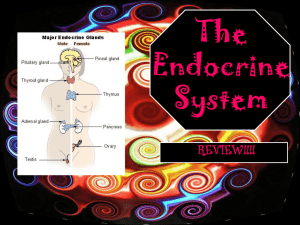
Endocrine System
... • Elevated metabolic rate, sweating, rapid heart rate, weight loss, protruding eyeballs ...
... • Elevated metabolic rate, sweating, rapid heart rate, weight loss, protruding eyeballs ...
AIM: What system of the human body regulates hormones?
... •Ex: estrogen, testosterone •Work by causing cells to initiate protein synthesis •Lipid soluble (can diffuse through membrane) ...
... •Ex: estrogen, testosterone •Work by causing cells to initiate protein synthesis •Lipid soluble (can diffuse through membrane) ...
The Endocrine System - St. Ambrose School
... • If a cell does not have receptors, or the receptors do not respond to a particular hormone, the hormone has no effect on it • The body’s response to hormones are slower and longerlasting • It may take several minutes, hours or days for a hormone to have its full effect on its target cells ...
... • If a cell does not have receptors, or the receptors do not respond to a particular hormone, the hormone has no effect on it • The body’s response to hormones are slower and longerlasting • It may take several minutes, hours or days for a hormone to have its full effect on its target cells ...
File - Patricia Schwandt Courses
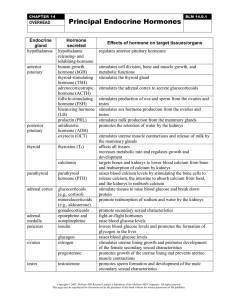
... stimulates cell division, bone and muscle growth, and metabolic functions stimulates the thyroid gland stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids stimulates production of ova and sperm from the ovaries and testes stimulates sex hormone production from the ovaries and testes stimulates ...
... stimulates cell division, bone and muscle growth, and metabolic functions stimulates the thyroid gland stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids stimulates production of ova and sperm from the ovaries and testes stimulates sex hormone production from the ovaries and testes stimulates ...
Adrenal Insufficiency
... How should adrenal insufficiency be treated during times of stress and illness? The body needs more cortisol than usual at times of stress and illness. A person with adrenal insufficiency who is sick with an infection and fever (temperature higher than 38o C) should take double the usual dose of cor ...
... How should adrenal insufficiency be treated during times of stress and illness? The body needs more cortisol than usual at times of stress and illness. A person with adrenal insufficiency who is sick with an infection and fever (temperature higher than 38o C) should take double the usual dose of cor ...
Study Guide Answer Keys - I
... 1. a. Melatonin: Produced by the pineal gland; helps regulate sleep cycles b. TSH: Produced by the anterior pituitary gland; stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones c. Adrenaline: Produced by the adrenal medulla; activates the response to stress d. Insulin: Produced by the beta cell ...
... 1. a. Melatonin: Produced by the pineal gland; helps regulate sleep cycles b. TSH: Produced by the anterior pituitary gland; stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones c. Adrenaline: Produced by the adrenal medulla; activates the response to stress d. Insulin: Produced by the beta cell ...
endocrine glands - Catawba County Schools
... • When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
... • When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
Synthesis of Steroid Hormones
... Derived from cholesterol & differ only in the ring structure & side chains attached to it. Lipid soluble & thus are freely permeable to membranes so are not stored in cells ...
... Derived from cholesterol & differ only in the ring structure & side chains attached to it. Lipid soluble & thus are freely permeable to membranes so are not stored in cells ...
the endocrine system
... messages, hormones, into the blood stream. It contains 2 types of glands, the endocrine and exocrine glands. The endocrine glands form what is generally referred to as a system, yet the fact that they are not directly inter-connected seems to contradict this classification. These glands occur throug ...
... messages, hormones, into the blood stream. It contains 2 types of glands, the endocrine and exocrine glands. The endocrine glands form what is generally referred to as a system, yet the fact that they are not directly inter-connected seems to contradict this classification. These glands occur throug ...
The endocrine system is founded on hormones and glands.
... Attached to the thryoid are four small glands called the parathyroids, which, with the help of calcitonin, control the calcium level. ...
... Attached to the thryoid are four small glands called the parathyroids, which, with the help of calcitonin, control the calcium level. ...
The Endocrine System
... 1. Once considered the master gland because it is the source of hormones that stimulate reproductive organs, the adrenal cortex, thyroid. 2. Hypothalamus stimulates or inhibits production of pituitary hormones 3. Produces growth hormone also called somatotropin which stimulates growth of bone, inhib ...
... 1. Once considered the master gland because it is the source of hormones that stimulate reproductive organs, the adrenal cortex, thyroid. 2. Hypothalamus stimulates or inhibits production of pituitary hormones 3. Produces growth hormone also called somatotropin which stimulates growth of bone, inhib ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.