* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Patricia Schwandt Courses
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
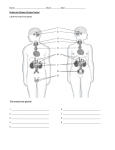
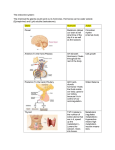
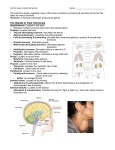
CHAPTER 14 OVERHEAD Endocrine gland hypothalamus Principal Endocrine Hormones Hormone secreted hypothalamic releasing- and inhibiting-hormone human growth hormone (hGH) thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) luteinizing hormone (LH) prolactin (PRL) antidiuretic hormone (ADH) oxytocin (OCT) anterior pituitary posterior pituitary thyroid thyroxine (T4) calcitonin parathyroid parathyroid hormone (PTH) adrenal cortex adrenal medulla pancreas glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol) mineralocorticoids (e.g., aldosterone) gonadocorticoids epinephrine and norepinephrine insulin ovaries glucagon estrogen progesterone testes testosterone BLM 14.0.1 Effects of hormone on target tissues/organs regulates anterior pituitary hormones stimulates cell division, bone and muscle growth, and metabolic functions stimulates the thyroid gland stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids stimulates production of ova and sperm from the ovaries and testes stimulates sex hormone production from the ovaries and testes stimulates milk production from the mammary glands promotes the retention of water by the kidneys stimulates uterine muscle contractions and release of milk by the mammary glands affects all tissues increases metabolic rate and regulates growth and development targets bones and kidneys to lower blood calcium from bone and reabsorption of calcium by kidneys raises blood calcium levels by stimulating the bone cells to release calcium, the intestine to absorb calcium from food, and the kidneys to reabsorb calcium stimulate tissues to raise blood glucose and break down protein promote reabsorption of sodium and water by the kidneys promote secondary sexual characteristics fight-or-flight hormones raise blood glucose levels lowers blood glucose levels and promotes the formation of glycogen in the liver raises blood glucose levels stimulates uterine lining growth and promotes development of the female secondary sexual characteristics promotes growth of the uterine lining and prevents uterine muscle contractions promotes sperm formation and development of the male secondary sexual characteristics Copyright © 2007, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a Subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher.