THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... While we are on the topic of glands, there are two other glands in the body that deserve mention. These are the pineal gland and the thymus. Neither ofthese is an endocrine gland. For lack ofa better place, they are discussed here. Pineal gland The pineal gland secretes melatonin, which is a derivat ...
... While we are on the topic of glands, there are two other glands in the body that deserve mention. These are the pineal gland and the thymus. Neither ofthese is an endocrine gland. For lack ofa better place, they are discussed here. Pineal gland The pineal gland secretes melatonin, which is a derivat ...
Endocrine System
... insulin produced Type II = low or not responsive to insulin (insulin resistance) ...
... insulin produced Type II = low or not responsive to insulin (insulin resistance) ...
Endocrine System Study Guide Anatomy
... Endocrine System Study Guide Anatomy Adrenal Glands - endocrine glands are located above the kidneys divided into the cortex and medulla Produces response to stress Stimulates fight or flight ...
... Endocrine System Study Guide Anatomy Adrenal Glands - endocrine glands are located above the kidneys divided into the cortex and medulla Produces response to stress Stimulates fight or flight ...
17. Pituitary and Adrenal Glands
... hGH – is the primary hormone that regulates overall body growth, also important in general metabolism. ...
... hGH – is the primary hormone that regulates overall body growth, also important in general metabolism. ...
Filled In Endocrine System Notes
... endocrine system is slower-acting, but the action of hormones is _longer lasting________. The _hypothalamus______, which maintains homeostasis in the body, controls most of the glands of the endocrine system. I. ENDOCRINE GLAND FUNCTION A. Hormone Production Hormones help regulate growth, metabolism ...
... endocrine system is slower-acting, but the action of hormones is _longer lasting________. The _hypothalamus______, which maintains homeostasis in the body, controls most of the glands of the endocrine system. I. ENDOCRINE GLAND FUNCTION A. Hormone Production Hormones help regulate growth, metabolism ...
19_endocrine
... – Produces hormones which enhance lymphocyte production – Development Childhood – large Puberty – largest Adulthood – decreases in size ...
... – Produces hormones which enhance lymphocyte production – Development Childhood – large Puberty – largest Adulthood – decreases in size ...
1-The immune system and endocrine disorders 2017)
... cause mild beta cell injury, which is followed by an autoimmune reaction against altered beta cells in persons with HLA-linked susceptibility. Type 1 IDDM patients (aprox.10%) are prone to other autoimmune disorders ...
... cause mild beta cell injury, which is followed by an autoimmune reaction against altered beta cells in persons with HLA-linked susceptibility. Type 1 IDDM patients (aprox.10%) are prone to other autoimmune disorders ...
Photosynthesis Review Questions
... 12. What group of hormones released by the adrenal glands help to increase blood sugar levels? 13. What is Type 2 diabetes? How can it be managed/controlled? 14. What hormone causes an increase in blood calcium levels? a decrease in blood calcium levels? 15. Describe how a deficiency in iodine cause ...
... 12. What group of hormones released by the adrenal glands help to increase blood sugar levels? 13. What is Type 2 diabetes? How can it be managed/controlled? 14. What hormone causes an increase in blood calcium levels? a decrease in blood calcium levels? 15. Describe how a deficiency in iodine cause ...
Chapter 18 - Endocrine
... Produces parathyroid hormone (PTH) which helps regulate blood Ca++ levels. Target organs of PTH are bone, kidneys and intestines. Histologically it contains numerous small chief cells and rare large oxyphilic cells. – Chief cells secrete PTH. – Oxyphilic cells are probably inactive or immature chief ...
... Produces parathyroid hormone (PTH) which helps regulate blood Ca++ levels. Target organs of PTH are bone, kidneys and intestines. Histologically it contains numerous small chief cells and rare large oxyphilic cells. – Chief cells secrete PTH. – Oxyphilic cells are probably inactive or immature chief ...
Lab 2
... • Structurally and functionally, they are two glands in one – Adrenal medulla – nervous tissue that acts as part of the SNS – Adrenal cortex – glandular tissue derived from embryonic mesoderm ...
... • Structurally and functionally, they are two glands in one – Adrenal medulla – nervous tissue that acts as part of the SNS – Adrenal cortex – glandular tissue derived from embryonic mesoderm ...
Endocrine System
... kinase activity (phosphorylation) on proteins alters its activity which therefore leads to altered function (ie change in metabolism) Phospholipids and Ca2+ can also function as secondary messengers ...
... kinase activity (phosphorylation) on proteins alters its activity which therefore leads to altered function (ie change in metabolism) Phospholipids and Ca2+ can also function as secondary messengers ...
Dr Watson Chapter 11 The Endocrine System
... The parathyroid glands regulate the release of calcium. With too much or too little, problems result. What are they? Disorder with very low level of calcium in the blood: ______________________ Body’s response to this very low level of calcium: ___________________________________ Low blood level of ...
... The parathyroid glands regulate the release of calcium. With too much or too little, problems result. What are they? Disorder with very low level of calcium in the blood: ______________________ Body’s response to this very low level of calcium: ___________________________________ Low blood level of ...
Endocrine system
... regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target cells). ...
... regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target cells). ...
Health Link - survivorshipguidelines.org
... information from the endocrine glands through the bloodstream to the body’s cells. The endocrine system makes many hormones (such as growth hormone, sex hormones, adrenal and thyroid hormones) that work together to maintain specific bodily functions. What is central adrenal insufficiency? ...
... information from the endocrine glands through the bloodstream to the body’s cells. The endocrine system makes many hormones (such as growth hormone, sex hormones, adrenal and thyroid hormones) that work together to maintain specific bodily functions. What is central adrenal insufficiency? ...
The Endocrine System
... kidneys. These contain two parts, the adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla. The adrenal cortex produces corticosteroids which help to balance the levels of water and salt in the body. These can be altered based on sexual development, the function of the metabolism or signals from the immune system. Th ...
... kidneys. These contain two parts, the adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla. The adrenal cortex produces corticosteroids which help to balance the levels of water and salt in the body. These can be altered based on sexual development, the function of the metabolism or signals from the immune system. Th ...
correct - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
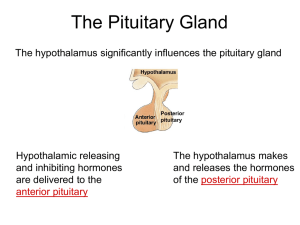
... mother's mammary glands when her baby is nursing. d. all of the above 12 : Hypothalamic releasing and releaseinhibiting hormones are transported from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary by way of __________. a. the general bloodstream b. a portal system of blood vessels directly connecting th ...
... mother's mammary glands when her baby is nursing. d. all of the above 12 : Hypothalamic releasing and releaseinhibiting hormones are transported from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary by way of __________. a. the general bloodstream b. a portal system of blood vessels directly connecting th ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.