* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Filled In Endocrine System Notes
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
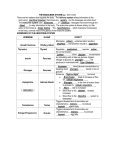
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (pp. 997 - 1008) There are two systems that regulate the body. The nervous system relays information to the body using _electrical impulses________ that travel very _quickly______, but the messages are short-lived. The endocrine system uses _hormones____, or _chemical_____ messages that travel through the _blood____ to relay information to the body. The endocrine system is slower-acting, but the action of hormones is _longer lasting________. The _hypothalamus______, which maintains homeostasis in the body, controls most of the glands of the endocrine system. I. ENDOCRINE GLAND FUNCTION A. Hormone Production Hormones help regulate growth, metabolism, appearance, behavior, growth, reproduction, and fluid balance. Most hormones are produced by _endocrine______ glands. Endocrine glands are unique because they are ductless; in other words, hormones are secreted into _capillaries______ and the _circulatory_______ system transports the hormone to its destination. Its destination is known as its _target_____. A hormone may have only one target, or it may have several. B. Control of Hormone Production Hormone release is regulated by a mechanism known as _negative feedback_____. Information about the effect of the hormone is “fed back” to the gland. When the desired condition is reached, the gland _is shut off_____ C. Types of Hormones – Hormones can be placed in two groups based on chemical structure: 1. Peptide hormones – Most hormones are composed of _proteins______ and are known as peptide hormones. 2. Steroids – _Lipid____ molecules derived from _cholesterol________. Include the sex hormones - _estrogen and testosterone_________ II. HORMONES OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM HORMONE GLAND EFFECT Stimulates _mitosis____; undersecretion results in Growth Hormone Pituitary Gland _dwarfism_______; oversecretion results in _gigantism____ Regulates __metabolism____; requires _iodine___ Thyroxine Thyroid for normal function _Lowers________ blood _glucose___ concentration Insulin Pancreas by stimulating cells to take up glucose; triggers storage of glucose as _glycogen______; not produced in individuals with _Type I Diabetes_____ __Increases______ blood glucose concentration by Glucagon Pancreas breaking down _glycogen_______ stored in liver to glucose Known as _”fight or flight”________ hormone Epinephrine Adrenal Glands _Bronchioles___ dilate to increase air flow for _cellular respiration_____ (_Adrenaline_) _Glycogen_____ in the liver is broken down to glucose for _cellular respiration____ _Heart___ rate is increased Blood flow to the _skeletal__ muscles increases Blood flow to the _digestive____ system is decreased Triggers development of secondary sex Testosterone Testes characteristics; _meiosis_____ to produce __haploid____ sperm cells. Triggers development of secondary sex Estrogen/ Progesterone Ovaries characteristics; __meiosis______ to produce __haploid_____ egg cells.