* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download *Section 5 (152
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
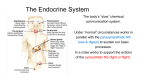
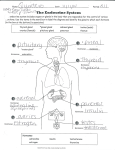
Coordination: endocrine system Endocrine glands Key words adrenalin basal metabolic rate endocrine gland hormone hypothalamus Male insulin pituitary gland pineal gland pituitary gland Endocrine glands Endocrine glands, sometimes called ductless glands, produce secretions that pass directly into the blood. ● Endocrine secretions are called hormones and change the functioning of a distant organ in the body. So, the hormone adrenalin, produced by the adrenal gland, increases the heart rate. ● The organ affected by a particular hormone is called the target organ. ● thyroid gland parathyroid glands thymus adrenal glands Hormonal coordination ● pancreas testes Female Hormonal coordination is used by the body to control many long-term changes, e.g., growth and development. ● The most important endocrine gland in the body is the pituitary gland, which secretes hormones that regulate other endocrine glands. Key endocrine glands hypothalamus pituitary gland pineal gland thyroid gland parathyroid glands thymus adrenal glands pancreas ovaries The adrenal glands secrete adrenalin, which stimulates the body to produce a “fight or flight” response to stress. ● Testes and ovaries secrete a range of hormones to control sexual development. ● The thyroid gland secretes a hormone that controls the basal metabolic rate. ● The pancreas contains cells that secrete insulin, which reduces the level of sugar in the blood. ● Parathyroid glands produce hormones that regulate the amount of calcium and phosphorus in the body. ● The pineal gland secretes melatonin, which plays a role in sleep, aging, and reproduction. ● The thymus and the pituitary and hypothalamus in the brain also have endocrine functions. ● The thymus gland is also involved in the production of T-lymphocytes, essential components of the immune system. © Diagram Visual Information Ltd. ●