Practice Exam 3 Answers
... Name the two enzymes that catalyze a reaction in which ATP is consumed? __________________________________________ Which enzyme catalyzes a reaction in which NADH is produced? _____________________ Which enzyme converts G3P into 1,3 BPG? __________________________ Name two enzyme reactions from glyc ...
... Name the two enzymes that catalyze a reaction in which ATP is consumed? __________________________________________ Which enzyme catalyzes a reaction in which NADH is produced? _____________________ Which enzyme converts G3P into 1,3 BPG? __________________________ Name two enzyme reactions from glyc ...
Unit 3 Biology Webquest/Book quest - Mandarin High School
... Textbook: p. 222 15. Identify the mitochondria as the cellular structure involved in respiration stressing that internal membranes are the primary site of reactions. Textbook: p. 222, 227, 228 16. Identify tissues in the body that require high concentration of mitochondria due to high energy require ...
... Textbook: p. 222 15. Identify the mitochondria as the cellular structure involved in respiration stressing that internal membranes are the primary site of reactions. Textbook: p. 222, 227, 228 16. Identify tissues in the body that require high concentration of mitochondria due to high energy require ...
PL05_Glucdisp
... chain, the reduction/dehydration/reduction steps, moving the fatty acid to the right site and finally releasing it as FA-CoA ...
... chain, the reduction/dehydration/reduction steps, moving the fatty acid to the right site and finally releasing it as FA-CoA ...
Part II: Multiple Choice Questions
... C) Less than 50% of the chemical energy available in glucose is converted to ATP energy. D) Glycolysis and the "grooming" of pyruvate together produce more NADH per glucose molecule than does the citric acid cycle. E) Each FADH2 molecule yields 2 ATP molecules and each NADH molecule generates 3 ATP ...
... C) Less than 50% of the chemical energy available in glucose is converted to ATP energy. D) Glycolysis and the "grooming" of pyruvate together produce more NADH per glucose molecule than does the citric acid cycle. E) Each FADH2 molecule yields 2 ATP molecules and each NADH molecule generates 3 ATP ...
Document
... license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. ...
... license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. ...
Energy and Muscle Contraction
... Therefore, during this time, cellular respiration will be going at capacity, limited only by oxygen restraints. Glycolysis, on the other hand, will proceed at an accelerated rate for the purpose of gaining extra ATP. Note that during this time, pyruvate will be fed into the mitochondria as fast as s ...
... Therefore, during this time, cellular respiration will be going at capacity, limited only by oxygen restraints. Glycolysis, on the other hand, will proceed at an accelerated rate for the purpose of gaining extra ATP. Note that during this time, pyruvate will be fed into the mitochondria as fast as s ...
Exam 3 Study Guide
... Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex: Overall reaction, purpose of cofactors, metabolic purpose Citric acid Cycle: Structures of all intermediates, names of all intermediates, names of regulated enzymes, mechanisms presented in slides only Electron transport chain: know complexes by number, mobile carrier ...
... Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex: Overall reaction, purpose of cofactors, metabolic purpose Citric acid Cycle: Structures of all intermediates, names of all intermediates, names of regulated enzymes, mechanisms presented in slides only Electron transport chain: know complexes by number, mobile carrier ...
General Chemistry 110 Quiz 1
... Name (Last, First):_________________________Chem 355, Professor David L. Huffman, Test 3, FORM B a. The Calvin cycle b. Photon activation and electron flow in photosynthesis c. The mechanism of ATP production in oxidative phosphorylation d. Itemization of the moles of ATP produced from one mole of ...
... Name (Last, First):_________________________Chem 355, Professor David L. Huffman, Test 3, FORM B a. The Calvin cycle b. Photon activation and electron flow in photosynthesis c. The mechanism of ATP production in oxidative phosphorylation d. Itemization of the moles of ATP produced from one mole of ...
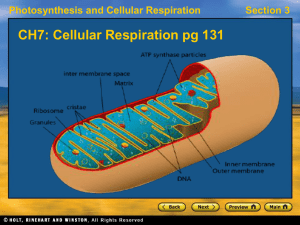
CH7Cellular-Respiration
... • In the 2nd stage, pyruvate EITHER passes through the Krebs cycle OR undergoes fermentation. – Fermentation recycles NAD+ but does not produce ATP. ...
... • In the 2nd stage, pyruvate EITHER passes through the Krebs cycle OR undergoes fermentation. – Fermentation recycles NAD+ but does not produce ATP. ...
O - VCU
... I don’t understand how to use the numbers near genes to find their sequences. I tried with the first number for Ava0001 (119), but that number doesn’t exist amongst the coordinates shown. ...
... I don’t understand how to use the numbers near genes to find their sequences. I tried with the first number for Ava0001 (119), but that number doesn’t exist amongst the coordinates shown. ...
Nucleic Acids
... • Attach one of the four bases above or below the deoxyribose molecule by removing an H from the phosphoric acid molecule. • Again, In order to join the molecules, you would have to remove an –OH end from one molecule and an -H end from another. 5. The -H and -OH ends that were removed can also fit ...
... • Attach one of the four bases above or below the deoxyribose molecule by removing an H from the phosphoric acid molecule. • Again, In order to join the molecules, you would have to remove an –OH end from one molecule and an -H end from another. 5. The -H and -OH ends that were removed can also fit ...
A Level Biology Nucleic Acids
... Can you explain that water has strong cohesion between water molecules; this supports columns of water in the tube-like transport cells of plants and produces surface tension where water meets air? ...
... Can you explain that water has strong cohesion between water molecules; this supports columns of water in the tube-like transport cells of plants and produces surface tension where water meets air? ...
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
... Many cancer cells grow anaerobically, and PDH is not active in these cells. Speculate the effect of DCA on cancer cells. Outline your train of thought. Inhibiting PDH-phosphorylase kinase would activate PDH, which allow the citric acid cycle to function at its full rate, thus maintain aerobic condit ...
... Many cancer cells grow anaerobically, and PDH is not active in these cells. Speculate the effect of DCA on cancer cells. Outline your train of thought. Inhibiting PDH-phosphorylase kinase would activate PDH, which allow the citric acid cycle to function at its full rate, thus maintain aerobic condit ...
VCE PE Unit 3: Preparing Students for the End of Year Exam
... and interplay of energy systems for physical activity and recovery in relation to duration, intensity and type of activity. • Describe the interplay of the energy systems using correct terminology • Analyse the relationship between energy systems and physical activity Sept 2009 ...
... and interplay of energy systems for physical activity and recovery in relation to duration, intensity and type of activity. • Describe the interplay of the energy systems using correct terminology • Analyse the relationship between energy systems and physical activity Sept 2009 ...
Unit 2 - OCCC.edu
... Pyruvate is chemically ____________________ for the citric acid cycle A large, multienzyme complex catalyzes three reactions in the mitochondrial matrix A carbon atom is ________________ from pyruvate and released in ___________ The remaining two-carbon compound is _______________________, and a mo ...
... Pyruvate is chemically ____________________ for the citric acid cycle A large, multienzyme complex catalyzes three reactions in the mitochondrial matrix A carbon atom is ________________ from pyruvate and released in ___________ The remaining two-carbon compound is _______________________, and a mo ...
citric acid cycle - usmle step 1 and 2 for android
... It essentially involves the oxidation of acetyl CoA to CO2 and H2O This cycle utilizes about 2/3rd of total oxygen consume dby body It is final common oxidative pathway for carbohydrates, fats and aminoacids It synthesizes energy and also provides many intermediates required fro synthesis of aminoac ...
... It essentially involves the oxidation of acetyl CoA to CO2 and H2O This cycle utilizes about 2/3rd of total oxygen consume dby body It is final common oxidative pathway for carbohydrates, fats and aminoacids It synthesizes energy and also provides many intermediates required fro synthesis of aminoac ...
U2-D3-03 – PO and Kreb
... The two molecules of acetyl-CoA enter the Krebs cycle where additional free energy transfers occur. The two molecules of NADH proceed to stage 4 (electron transport and chemiosmosis) to produce ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. The two CO 2 molecules produced during pyruvate oxidation diffuse out of ...
... The two molecules of acetyl-CoA enter the Krebs cycle where additional free energy transfers occur. The two molecules of NADH proceed to stage 4 (electron transport and chemiosmosis) to produce ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. The two CO 2 molecules produced during pyruvate oxidation diffuse out of ...
Biology 3A Exam 2 Study Guide The exam will consist of multiple
... • glycolysis - where does it take place, reactants, products, amount of ATP produced, where energy is required and produced, enzymes involved (as discussed in class) • primer reaction/grooming phase - where does it take place, reactants, products, amount of ATP produced • Citric acid cycle (Krebs or ...
... • glycolysis - where does it take place, reactants, products, amount of ATP produced, where energy is required and produced, enzymes involved (as discussed in class) • primer reaction/grooming phase - where does it take place, reactants, products, amount of ATP produced • Citric acid cycle (Krebs or ...
• How to get rid of the RHP zero? • What are the new tradeoffs?
... • small k and/or • large q Correctly predicts conditions with “glycolytic oscillations” ...
... • small k and/or • large q Correctly predicts conditions with “glycolytic oscillations” ...
K - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... The 7 reversible enzymes are the same, but 4 gluconeogeneic enzymes are needed to catalyze the opposite of the 3 irrevesible glycolytic enzymes. To get back to glucose, cells liberate 2 phosphate groups. Why use hydrolyases (glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose 1,6-bisphosphotase) instead of kinases? ...
... The 7 reversible enzymes are the same, but 4 gluconeogeneic enzymes are needed to catalyze the opposite of the 3 irrevesible glycolytic enzymes. To get back to glucose, cells liberate 2 phosphate groups. Why use hydrolyases (glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose 1,6-bisphosphotase) instead of kinases? ...
pptx
... The 7 reversible enzymes are the same, but 4 gluconeogeneic enzymes are needed to catalyze the opposite of the 3 irrevesible glycolytic enzymes. To get back to glucose, cells liberate 2 phosphate groups. Why use hydrolyases (glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose 1,6-bisphosphotase) instead of kinases? ...
... The 7 reversible enzymes are the same, but 4 gluconeogeneic enzymes are needed to catalyze the opposite of the 3 irrevesible glycolytic enzymes. To get back to glucose, cells liberate 2 phosphate groups. Why use hydrolyases (glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose 1,6-bisphosphotase) instead of kinases? ...
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA), Krebs Cycle
... numerous transport proteins that permit the passage of specific molecules. 1- ATP-ADP transport, see oxid-phospho, Transporter for ADP & Pi from cytosol into mitochondria by specialized carriers ( adenine nucleotide carrier) which transport ADP from cytosol into mitochondria, while exporting ATP fro ...
... numerous transport proteins that permit the passage of specific molecules. 1- ATP-ADP transport, see oxid-phospho, Transporter for ADP & Pi from cytosol into mitochondria by specialized carriers ( adenine nucleotide carrier) which transport ADP from cytosol into mitochondria, while exporting ATP fro ...
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme often called the ""molecular unit of currency"" of intracellular energy transfer.ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism. It is one of the end products of photophosphorylation, cellular respiration, and fermentation and used by enzymes and structural proteins in many cellular processes, including biosynthetic reactions, motility, and cell division. One molecule of ATP contains three phosphate groups, and it is produced by a wide variety of enzymes, including ATP synthase, from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and various phosphate group donors. Substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration, and photophosphorylation in photosynthesis are three major mechanisms of ATP biosynthesis.Metabolic processes that use ATP as an energy source convert it back into its precursors. ATP is therefore continuously recycled in organisms: the human body, which on average contains only 250 grams (8.8 oz) of ATP, turns over its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day.ATP is used as a substrate in signal transduction pathways by kinases that phosphorylate proteins and lipids. It is also used by adenylate cyclase, which uses ATP to produce the second messenger molecule cyclic AMP. The ratio between ATP and AMP is used as a way for a cell to sense how much energy is available and control the metabolic pathways that produce and consume ATP. Apart from its roles in signaling and energy metabolism, ATP is also incorporated into nucleic acids by polymerases in the process of transcription. ATP is the neurotransmitter believed to signal the sense of taste.The structure of this molecule consists of a purine base (adenine) attached by the 9' nitrogen atom to the 1' carbon atom of a pentose sugar (ribose). Three phosphate groups are attached at the 5' carbon atom of the pentose sugar. It is the addition and removal of these phosphate groups that inter-convert ATP, ADP and AMP. When ATP is used in DNA synthesis, the ribose sugar is first converted to deoxyribose by ribonucleotide reductase.ATP was discovered in 1929 by Karl Lohmann, and independently by Cyrus Fiske and Yellapragada Subbarow of Harvard Medical School, but its correct structure was not determined until some years later. It was proposed to be the intermediary molecule between energy-yielding and energy-requiring reactions in cells by Fritz Albert Lipmann in 1941. It was first artificially synthesized by Alexander Todd in 1948.