The T Cell Marker, CD3 Antigen and Antibodies
... and van Oers 2003, Smith-Garvin et al. 2009). Recruitment of ZAP-70, a syk kinase family member, binds to CD3-ζ. Bound ZAP-70 phosphorylates the transmembrane adapter protein linker of activated T cells (LAT) which then allows the cytosolic adapter protein SH2 domain containing leukocyte phosphoprot ...
... and van Oers 2003, Smith-Garvin et al. 2009). Recruitment of ZAP-70, a syk kinase family member, binds to CD3-ζ. Bound ZAP-70 phosphorylates the transmembrane adapter protein linker of activated T cells (LAT) which then allows the cytosolic adapter protein SH2 domain containing leukocyte phosphoprot ...
Tong, LF, Balakrishan G, Kochan JP, et al. Assessment of
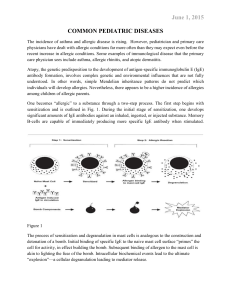
... All antigens initially elicit the production of IgM antibodies against an injected or inhaled allergen. With repeated exposure, the antigen may stimulate an event known as class switching, whereby the constant portion of the antibody will “switch” to another class (i.e., IgG, IgA, or IgE). The new a ...
... All antigens initially elicit the production of IgM antibodies against an injected or inhaled allergen. With repeated exposure, the antigen may stimulate an event known as class switching, whereby the constant portion of the antibody will “switch” to another class (i.e., IgG, IgA, or IgE). The new a ...
Chronic Inflammation
... accumulation of large numbers of foamy macrophages in the tissue. The macrophages are present diffusely in the tissue without aggregating into granulomas. The ability of the macrophage to kill the organism is limited because of the poor T cell response, permitting the organisms to multiply in th ...
... accumulation of large numbers of foamy macrophages in the tissue. The macrophages are present diffusely in the tissue without aggregating into granulomas. The ability of the macrophage to kill the organism is limited because of the poor T cell response, permitting the organisms to multiply in th ...
Review - International Federation of Cell Therapy Professionals
... benefit have been debated. In some studies, robust remuscularization of the infarcted myocardium by c -Kit+/lin– cells isolated from bone marrow was demonstrated,2 but this finding was contested in other studies, suggesting that bone marrow mononuclear cells do not transdifferentiate into cardiomyo ...
... benefit have been debated. In some studies, robust remuscularization of the infarcted myocardium by c -Kit+/lin– cells isolated from bone marrow was demonstrated,2 but this finding was contested in other studies, suggesting that bone marrow mononuclear cells do not transdifferentiate into cardiomyo ...
Document
... Two agents that are used for either induction or antirejection therapy are muromonab CD3 (OKT3) and antithymocyte globulin (ATG). Muromonab CD3 is a murine monoclonal immunoglobulin (IgG) to an antibody that binds to the CD3 antigen on human T cells. Antithymocyte globulin is a polyclonal antilympho ...
... Two agents that are used for either induction or antirejection therapy are muromonab CD3 (OKT3) and antithymocyte globulin (ATG). Muromonab CD3 is a murine monoclonal immunoglobulin (IgG) to an antibody that binds to the CD3 antigen on human T cells. Antithymocyte globulin is a polyclonal antilympho ...
Cord Blood: Biology, Transplantation, Banking, and Regulation Brochure
... The relatively new field of cord blood (CB) is still evolving, having seen vast change since the first successful CB transplantation over 20 years ago. This volume aims to continue advancing the clinical efficacy and relevance of this area by providing a solid understanding of its present status. Re ...
... The relatively new field of cord blood (CB) is still evolving, having seen vast change since the first successful CB transplantation over 20 years ago. This volume aims to continue advancing the clinical efficacy and relevance of this area by providing a solid understanding of its present status. Re ...
Viruses We Eat
... concentration drops, these trimers fall apart, “unbuttoning” the overcoat. One interesting aspect of this uncoating is that neutralizing antibodies bind to the trimeric form of VP7. Virologists speculate that this binding may prevent the virus from shedding its coat by “clamping” the VP7 trimers tog ...
... concentration drops, these trimers fall apart, “unbuttoning” the overcoat. One interesting aspect of this uncoating is that neutralizing antibodies bind to the trimeric form of VP7. Virologists speculate that this binding may prevent the virus from shedding its coat by “clamping” the VP7 trimers tog ...
Lymphomas Involving Waldeyer`s Ring
... Health Organisation. Materials and Methods: Sources of data include international studies on Waldeyer’s ring lymphomas as well as from personal observations gleaned from lymphoma statistics of Singapore General Hospital, Changi General Hospital, Tan Tock Seng Hospital and National University Hospita ...
... Health Organisation. Materials and Methods: Sources of data include international studies on Waldeyer’s ring lymphomas as well as from personal observations gleaned from lymphoma statistics of Singapore General Hospital, Changi General Hospital, Tan Tock Seng Hospital and National University Hospita ...
Downloaded - The Journal of Immunology
... (Multiscreen HA filtration; Millipore) were coated overnight with four immune prevalent recombinant B. burgdorferi proteins all generated based on the N40 sequence, 1 mg/ml DbpA and 2 mg/ml each for outer surface protein C (OspC), arthritis related protein (Arp), and Borrelia membrane protein A (Bmp ...
... (Multiscreen HA filtration; Millipore) were coated overnight with four immune prevalent recombinant B. burgdorferi proteins all generated based on the N40 sequence, 1 mg/ml DbpA and 2 mg/ml each for outer surface protein C (OspC), arthritis related protein (Arp), and Borrelia membrane protein A (Bmp ...
Naturally produced opsonizing antibodies restrict the survival of
... Nonetheless, the mechanism by which Abs confer protection against intracellular infections largely remains obscure. Phagosome acidification through fusion with lysosomes is critical for killing of the bacilli within macrophages and its inhibition is a major survival mechanism employed by Mtb [13]. A ...
... Nonetheless, the mechanism by which Abs confer protection against intracellular infections largely remains obscure. Phagosome acidification through fusion with lysosomes is critical for killing of the bacilli within macrophages and its inhibition is a major survival mechanism employed by Mtb [13]. A ...
The evolution of natural killer cell receptors
... MHC-I expression, that unlike KIRs is highly conserved. Lemurs, on the other hand, exhibit only one single nonfunctional KIR gene in their LRC, but they have diversified the genes encoding CD94 and NKG2 (Averdam et al. 2009). Located in lemur chromosome 7, the NKC comprises three CD94 genes and five ...
... MHC-I expression, that unlike KIRs is highly conserved. Lemurs, on the other hand, exhibit only one single nonfunctional KIR gene in their LRC, but they have diversified the genes encoding CD94 and NKG2 (Averdam et al. 2009). Located in lemur chromosome 7, the NKC comprises three CD94 genes and five ...
Lecture 14
... Hb Iwate His F8(87)a Tyr “black mouth disease Japan They have chocolate brown blood. Changes at the a1-b2 interface usually have lower Hill coefficients. Stabilize either the T or R state Polycythemia, a ruddy complexion Hb Yakima Asp G1(99)b His eliminates H-bonding that stabilizes the T form ...
... Hb Iwate His F8(87)a Tyr “black mouth disease Japan They have chocolate brown blood. Changes at the a1-b2 interface usually have lower Hill coefficients. Stabilize either the T or R state Polycythemia, a ruddy complexion Hb Yakima Asp G1(99)b His eliminates H-bonding that stabilizes the T form ...
INVESTIGATING ANTIGEN PRESENTATION BY INACTIVATED LYMPHOCYTIC CHORIOMENINGITIS VIRUS AND BY
... Figure 3: Direct and cross-presentation pathways.............................................................................. 8 Figure 4: Detection of LCMV nucleoprotein expression levels in pAPCs following infection with live or inactivated virus.................................................... ...
... Figure 3: Direct and cross-presentation pathways.............................................................................. 8 Figure 4: Detection of LCMV nucleoprotein expression levels in pAPCs following infection with live or inactivated virus.................................................... ...
Biologic response modifiers in retinal vasculitis Sandeep Saxena
... probably embarked on much specialised stratified care[4,5,18-23]. The treatment of noninfectious posterior uveitis can lead to severe vision loss, and the first-line conventional treatment includes systemic steroids. When the prednisone doses necessary to control intraocular inflammation are above 0 ...
... probably embarked on much specialised stratified care[4,5,18-23]. The treatment of noninfectious posterior uveitis can lead to severe vision loss, and the first-line conventional treatment includes systemic steroids. When the prednisone doses necessary to control intraocular inflammation are above 0 ...
The Regulation of HPV Late Gene Expression and the Potential
... HPV L1 and L2 late genes is found only in terminally differentiated epithelial cells. As L1 and L2 proteins are highly immunogenic, it is suggested that their suppression may prevent detection of the virus by the immune system, thus acting as a prerequisite for persistence of infection. Therefore, i ...
... HPV L1 and L2 late genes is found only in terminally differentiated epithelial cells. As L1 and L2 proteins are highly immunogenic, it is suggested that their suppression may prevent detection of the virus by the immune system, thus acting as a prerequisite for persistence of infection. Therefore, i ...
Selection of rules
... eliminate different pathogens in different ways. To achieve this, the immune system constantly creates new types of responses. These are subject to selection processes that favor more successful responses (i.e., lymphocytes that bind to pathogens). A memory of successful responses to pathogens is ma ...
... eliminate different pathogens in different ways. To achieve this, the immune system constantly creates new types of responses. These are subject to selection processes that favor more successful responses (i.e., lymphocytes that bind to pathogens). A memory of successful responses to pathogens is ma ...
Regulatory T cells - TARA
... years and a number of studies, primarily in murine models of infection with bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungi have demonstrated that Tr cells specific for pathogen antigens are induced during infection. Furthermore, studies involving depletion or transfer of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells have pr ...
... years and a number of studies, primarily in murine models of infection with bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungi have demonstrated that Tr cells specific for pathogen antigens are induced during infection. Furthermore, studies involving depletion or transfer of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells have pr ...
Epithelial microRNAs regulate gut mucosal immunity via epithelium
... MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as important regulators of many biological processes6,7. Hundreds of miRNAs, many evolution- arily conserved, have been identified in mammals, but their physio logical functions are just beginning to be elucidated8. Although it seems that the expression of some miRN ...
... MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as important regulators of many biological processes6,7. Hundreds of miRNAs, many evolution- arily conserved, have been identified in mammals, but their physio logical functions are just beginning to be elucidated8. Although it seems that the expression of some miRN ...
• - Utrecht University Repository
... The human immune system is the product of aeons of evolution, which have brought forth a system that is both delicate in its regulatory mechanisms and powerful in its actions. In order to remain functional and effective, the immune system must be kept in balance. An immune response that is too harsh ...
... The human immune system is the product of aeons of evolution, which have brought forth a system that is both delicate in its regulatory mechanisms and powerful in its actions. In order to remain functional and effective, the immune system must be kept in balance. An immune response that is too harsh ...
Read the text. - Cornell Virology
... the intestine (14, 15). In addition to their beneficial effects in the intestine, recent studies highlight the importance of gut bacterial composition in a number of pathological conditions including diabetes (18) and obesity (19–22). Inflammatory bowel disease can develop as a result of the emergence ...
... the intestine (14, 15). In addition to their beneficial effects in the intestine, recent studies highlight the importance of gut bacterial composition in a number of pathological conditions including diabetes (18) and obesity (19–22). Inflammatory bowel disease can develop as a result of the emergence ...
Are Targeted by NK Cells Hematopoietic Progenitors Express H60
... However, a major challenge to the therapeutic application of ES cell derivatives is their potential for recognition by the immune system. The first reports on ES cell immunogenicity demonstrated that undifferentiated ES cells and differentiated cells derived from the embryoid body (EB) expressed low ...
... However, a major challenge to the therapeutic application of ES cell derivatives is their potential for recognition by the immune system. The first reports on ES cell immunogenicity demonstrated that undifferentiated ES cells and differentiated cells derived from the embryoid body (EB) expressed low ...
disruption of macrophage signalling by bacterial pathogens
... As macrophages need to recognize many diverse foreign microbes rapidly, they express a repertoire of receptors that bind characteristic conserved microbial molecular patterns8. Signalling that is instigated by these ‘patternrecognition receptors’ increases the macrophage’s antimicrobial abilities. H ...
... As macrophages need to recognize many diverse foreign microbes rapidly, they express a repertoire of receptors that bind characteristic conserved microbial molecular patterns8. Signalling that is instigated by these ‘patternrecognition receptors’ increases the macrophage’s antimicrobial abilities. H ...
FUNCTIONS AND APPLICATIONS OF EXOSOMES
... Abstract: The cells continuously secrete a large number of different types of microvesicles including macroand micro-molecules into the extracellular fluids. One of them are exosomes, which are nano-sized vesicles capable of transferring the DNAs, microRNAs, non-coding RNAs and lipids with or withou ...
... Abstract: The cells continuously secrete a large number of different types of microvesicles including macroand micro-molecules into the extracellular fluids. One of them are exosomes, which are nano-sized vesicles capable of transferring the DNAs, microRNAs, non-coding RNAs and lipids with or withou ...
1 - Webgarden
... Background Human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) E7 is an unstable oncoprotein with low immunogenicity. In previous work, we prepared the E7GGG gene containing point mutations resulting in substitution of three amino acids in the pRb-binding site of the HPV16 E7 protein. Methods and Results To increa ...
... Background Human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) E7 is an unstable oncoprotein with low immunogenicity. In previous work, we prepared the E7GGG gene containing point mutations resulting in substitution of three amino acids in the pRb-binding site of the HPV16 E7 protein. Methods and Results To increa ...
Cancer immunotherapy

Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncology) is the use of the immune system to treat cancer. Immunotherapies fall into three main groups: cellular, antibody and cytokine. They exploit the fact that cancer cells often have subtly different molecules on their surface that can be detected by the immune system. These molecules, known as cancer antigens, are most commonly proteins, but also include molecules such as carbohydrates. Immunotherapy is used to provoke the immune system into attacking the tumor cells by using these antigens as targets.Antibody therapies are the most successful immunotherapy, treating a wide range of cancers. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that bind to a target antigen on the cell surface. In normal physiology the immune system uses them to fight pathogens. Each antibody is specific to one or a few proteins. Those that bind to cancer antigens are used to treat cancer. Cell surface receptors are common targets for antibody therapies and include the CD20, CD274, and CD279. Once bound to a cancer antigen, antibodies can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, activate the complement system, or prevent a receptor from interacting with its ligand, all of which can lead to cell death. Multiple antibodies are approved to treat cancer, including Alemtuzumab, Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, Ofatumumab, and Rituximab.Cellular therapies, also known as cancer vaccines, usually involve the removal of immune cells from the blood or from a tumor. Immune cells specific for the tumor are activated, cultured and returned to the patient where the immune cells attack the cancer. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells, cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells. The only cell-based therapy approved in the US is Dendreon's Provenge, for the treatment of prostate cancer.Interleukin-2 and interferon-α are examples of cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behaviour of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.