antigen receptors and accessory molecules of t lymphocytes
... on the surface of immune cells that recognize antigens and instruct the immune cell to secrete more of the same antibody. Cell surface receptors for hormones were discovered many decades later in the second half of the 20th century but well before the identification of antigen receptors on lymphocyt ...
... on the surface of immune cells that recognize antigens and instruct the immune cell to secrete more of the same antibody. Cell surface receptors for hormones were discovered many decades later in the second half of the 20th century but well before the identification of antigen receptors on lymphocyt ...
Immune Memory and Vaccines
... immunity (active because the body actively produces antibodies to trigger a quick secondary response) – Naturally acquired active immunity: example— common cold viruses – “Artificially” acquired active immunity: Vaccines… Passive immunity: Antibodies come from outside source—body does not produce th ...
... immunity (active because the body actively produces antibodies to trigger a quick secondary response) – Naturally acquired active immunity: example— common cold viruses – “Artificially” acquired active immunity: Vaccines… Passive immunity: Antibodies come from outside source—body does not produce th ...
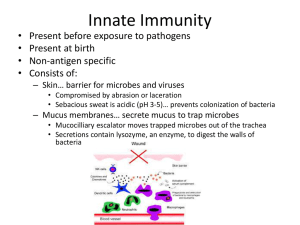
Innate Immunity - Santa Susana High School
... • Activation causes immediate clonal response producing 2 additional cells… 1 being a memory cell – Called the primary immune response » Maximum response 10-17 days after initial exposure • Sickness ensues awaiting max immune response ...
... • Activation causes immediate clonal response producing 2 additional cells… 1 being a memory cell – Called the primary immune response » Maximum response 10-17 days after initial exposure • Sickness ensues awaiting max immune response ...
Document
... B-cells with BCR that bind to self will undergo Apoptosis More complicated scheme of selection for T cells ...
... B-cells with BCR that bind to self will undergo Apoptosis More complicated scheme of selection for T cells ...
6_Autoimmune_2013
... •polyarthritis (joints become hot, red, swollen) •Sydenham’s chorea Infiltration of T and B (plasma) cells, macrophages. These look like granulomas…. They are called Aschoff bodies. However only 3% of all patients with untreated Streptococcal pharingytis develop rheumatic fever. Likely that genetic ...
... •polyarthritis (joints become hot, red, swollen) •Sydenham’s chorea Infiltration of T and B (plasma) cells, macrophages. These look like granulomas…. They are called Aschoff bodies. However only 3% of all patients with untreated Streptococcal pharingytis develop rheumatic fever. Likely that genetic ...
Therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia with purine - hem
... B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a clonal hematopoietic disorder characterized by proliferation and accumulation of small lymphocytes. It is the most common form of leukemia in North America and Europe. The management of CLL is determined by the stage and activity of the disease. Several ...
... B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a clonal hematopoietic disorder characterized by proliferation and accumulation of small lymphocytes. It is the most common form of leukemia in North America and Europe. The management of CLL is determined by the stage and activity of the disease. Several ...
B CELL
... QUESTION: How can so many different pathogens and other structures be recognized by antibodies? What drives and How the production of antibodies? ...
... QUESTION: How can so many different pathogens and other structures be recognized by antibodies? What drives and How the production of antibodies? ...
1 - Wk 1-2
... they bind primarily to bacteria, to bacterial toxins, and to free viruses, inactivating them temporarily and marking them for destruction by phagocytes or complement. Antibodies are fairly useless against infectious microorganisms like viruses and the tuberculosis bacillus that quickly slip inside b ...
... they bind primarily to bacteria, to bacterial toxins, and to free viruses, inactivating them temporarily and marking them for destruction by phagocytes or complement. Antibodies are fairly useless against infectious microorganisms like viruses and the tuberculosis bacillus that quickly slip inside b ...
Hypersensitivities
... Autoimmunity: majority of autoimmune diseases are Type II reactions Grave’s disease, Myasthenia gravis, MS, and very many others typically result in damage to target cell, but not its destruction Alloimmunity: bad blood transfusion, hemolytic disease of newborn (antibodies from mom attacking ...
... Autoimmunity: majority of autoimmune diseases are Type II reactions Grave’s disease, Myasthenia gravis, MS, and very many others typically result in damage to target cell, but not its destruction Alloimmunity: bad blood transfusion, hemolytic disease of newborn (antibodies from mom attacking ...
Blank Jeopardy
... This is the advanced stage of an HIV infection. HIV is a pathogen transmitted through blood that progressively damages or kills cells of the immune system. ...
... This is the advanced stage of an HIV infection. HIV is a pathogen transmitted through blood that progressively damages or kills cells of the immune system. ...
Immunity Student Outline
... AP Biology Organism Form and Function Unit 5: Immunology Outline J. Miller Learning Objectives: 2.28 The student is able to use representations or models to analyze quantitatively and qualitatively the effects of disruptions to dynamic homeostasis in biological systems. 2.29 The student can create r ...
... AP Biology Organism Form and Function Unit 5: Immunology Outline J. Miller Learning Objectives: 2.28 The student is able to use representations or models to analyze quantitatively and qualitatively the effects of disruptions to dynamic homeostasis in biological systems. 2.29 The student can create r ...
Unit 4 Mind Maps
... Describe the role of cytokines Damage to connective tissue causes, __________ cells to release a chemical ...
... Describe the role of cytokines Damage to connective tissue causes, __________ cells to release a chemical ...
IMMUNOLOGY 2010™ Poster Symposia Schedule
... Effector Cells and Tissue Damage in Autoimmunity Host Defense: Innate Immune Receptors and Signal Transduction Immune Regulation of Host Immunity during Viral Infection Immune System Regulation iTreg, Th17, and CD4 CTL Differentiation Leukocyte Activation, Adhesion, and Recruitment Mechanisms of Dis ...
... Effector Cells and Tissue Damage in Autoimmunity Host Defense: Innate Immune Receptors and Signal Transduction Immune Regulation of Host Immunity during Viral Infection Immune System Regulation iTreg, Th17, and CD4 CTL Differentiation Leukocyte Activation, Adhesion, and Recruitment Mechanisms of Dis ...
MCB 181 (Nov 4 – Dec 4) Information and Heredity
... lymphocytes and antibodies of the immune system. • There are two main types of lymphocytes: B lymphocytes (B cells) and T lymphocytes (T cells) • Both are types of white blood cells produced in bone marrow. They circulate in blood and lymph, and are concentrated in spleen, lymph nodes, and other lym ...
... lymphocytes and antibodies of the immune system. • There are two main types of lymphocytes: B lymphocytes (B cells) and T lymphocytes (T cells) • Both are types of white blood cells produced in bone marrow. They circulate in blood and lymph, and are concentrated in spleen, lymph nodes, and other lym ...
Suggested Answers for Case Study, Chapter 16, Mechanisms of
... involves the administration of two or three antiretroviral medications that collectively destroy the HIV at various stages of replication. The aim of the therapy is to reduce the presence of HIV RNA to an undetectable level while increasing CD4+ cell counts. Zidovudine is a particularly effective an ...
... involves the administration of two or three antiretroviral medications that collectively destroy the HIV at various stages of replication. The aim of the therapy is to reduce the presence of HIV RNA to an undetectable level while increasing CD4+ cell counts. Zidovudine is a particularly effective an ...
Hadassah University Hospital
... Eschar - ideal ground for microorganisms (avascular tissue is not accessible to most systemic antibiotics). ...
... Eschar - ideal ground for microorganisms (avascular tissue is not accessible to most systemic antibiotics). ...
Immunity & Abnormal Responses
... – Group of inactive plasma proteins, part of non-specific immunity – Especially active against invading bacteria – When activated, system compliments action of antibodies by; – Destruction of target cell membranes – Attracts phagocytes (chemotaxis) – Stimulates & enhances phagocytosis – Stimulates i ...
... – Group of inactive plasma proteins, part of non-specific immunity – Especially active against invading bacteria – When activated, system compliments action of antibodies by; – Destruction of target cell membranes – Attracts phagocytes (chemotaxis) – Stimulates & enhances phagocytosis – Stimulates i ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... a) B cells b) cytotoxic Tcells c) TNFγ d) macrophages 5. Immuno suppression is not induced by a) anti histamines b) removal of lymphoid tissue c)use of anti lymphocyte antibodies d) cytotoxic drugs II. State True or False.If false Give reasons ...
... a) B cells b) cytotoxic Tcells c) TNFγ d) macrophages 5. Immuno suppression is not induced by a) anti histamines b) removal of lymphoid tissue c)use of anti lymphocyte antibodies d) cytotoxic drugs II. State True or False.If false Give reasons ...
Immunological Memory And Role Of T Lymphocytes During Viral
... successfully eradicated deadly viruses such as variola virus (small pox) and which to date represents the most effective means of controlling human infectious disease. T cells play a key role in the protective immunity towards viruses. The anti-viral T cell response that is generated during infectio ...
... successfully eradicated deadly viruses such as variola virus (small pox) and which to date represents the most effective means of controlling human infectious disease. T cells play a key role in the protective immunity towards viruses. The anti-viral T cell response that is generated during infectio ...
Chapter 18 Quantitative and Thought Questions 18.1 Both would be
... 18.3 The drug may reduce but would not eliminate the action of complement, because this system destroys cells directly (via the membrane attack complex) as well as by facilitating phagocytosis. 18.4 Antibodies would bind normally to antigen but may not be able to activate complement, act as opsonins ...
... 18.3 The drug may reduce but would not eliminate the action of complement, because this system destroys cells directly (via the membrane attack complex) as well as by facilitating phagocytosis. 18.4 Antibodies would bind normally to antigen but may not be able to activate complement, act as opsonins ...
Allergic Reaction
... Injected penicillin and bee/wasp stings are the two most common causes of anaphylaxis. ...
... Injected penicillin and bee/wasp stings are the two most common causes of anaphylaxis. ...
Thesis Abstract Drug hypersensitivity reactions represent a major
... Drug hypersensitivity reactions represent a major problem in clinical practice. Their clinical characteristics are very heterogeneous as drugs can elicit all types of immune reactions. The antigenicity of drugs relies on the fact that small molecules can bind covalently to carrier proteins, which be ...
... Drug hypersensitivity reactions represent a major problem in clinical practice. Their clinical characteristics are very heterogeneous as drugs can elicit all types of immune reactions. The antigenicity of drugs relies on the fact that small molecules can bind covalently to carrier proteins, which be ...