Immune System
... • The Immune system must have the ability to distinguish between self and non-self molecules • Self Molecules- components of an organism’s body that can be distinguished from foreign substances by the immune system. Autoimmunity- immune reaction against self molecules • Non-self Molecules- recognize ...
... • The Immune system must have the ability to distinguish between self and non-self molecules • Self Molecules- components of an organism’s body that can be distinguished from foreign substances by the immune system. Autoimmunity- immune reaction against self molecules • Non-self Molecules- recognize ...
factors
... Type III – Immune-complexmediated reactions • Caused by antigen-antibody complexes formed in circulation and deposited in vessel walls or other tissues • Not organ specific • Effects caused by activation of complement – chemotaxis of neutrophils • Neutrophils release lysosomal enzymes into tissues ...
... Type III – Immune-complexmediated reactions • Caused by antigen-antibody complexes formed in circulation and deposited in vessel walls or other tissues • Not organ specific • Effects caused by activation of complement – chemotaxis of neutrophils • Neutrophils release lysosomal enzymes into tissues ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 5. Hybridoma technology was first developed by a) Kohler b) Mittelman c) Yallow ...
... 5. Hybridoma technology was first developed by a) Kohler b) Mittelman c) Yallow ...
Biology 2201
... Process of clonal selection explain why/how adaptive immune response act against any antigen. •Lymphocyte developed –with antigen receptor. •Then speciallized into B-cell receptor and T-cell receptor. •The receptor can react with specific epitopes of an antigen. •Each of receptor is different /iden ...
... Process of clonal selection explain why/how adaptive immune response act against any antigen. •Lymphocyte developed –with antigen receptor. •Then speciallized into B-cell receptor and T-cell receptor. •The receptor can react with specific epitopes of an antigen. •Each of receptor is different /iden ...
Secondary Immune Response
... Process of clonal selection explain why/how adaptive immune response act against any antigen. •Lymphocyte developed –with antigen receptor. •Then speciallized into B-cell receptor and T-cell receptor. •The receptor can react with specific epitopes of an antigen. •Each of receptor is different /iden ...
... Process of clonal selection explain why/how adaptive immune response act against any antigen. •Lymphocyte developed –with antigen receptor. •Then speciallized into B-cell receptor and T-cell receptor. •The receptor can react with specific epitopes of an antigen. •Each of receptor is different /iden ...
Document
... thought to form pores in cell membranes that allow antigens to gain access to the endogenous presentation pathway resulting in presentation by MHC class I and hence CTL activation. ...
... thought to form pores in cell membranes that allow antigens to gain access to the endogenous presentation pathway resulting in presentation by MHC class I and hence CTL activation. ...
specific defenses: the immune system
... 1. What signals does a T cell require in order to divide? ...
... 1. What signals does a T cell require in order to divide? ...
Immunobiology
... epitopes; T dependent and T independent antigens. (b) Major Histocompatibility Complex: Organization of MHC and inheritance in humans; concepts of polygeny and polymorphism with respect to MHC. (c) Antigen presenting cells, antigen processing and presentation pathway (cytosolic and endocytic), MLRs. ...
... epitopes; T dependent and T independent antigens. (b) Major Histocompatibility Complex: Organization of MHC and inheritance in humans; concepts of polygeny and polymorphism with respect to MHC. (c) Antigen presenting cells, antigen processing and presentation pathway (cytosolic and endocytic), MLRs. ...
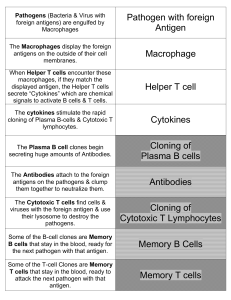
Pathogens (Bacteria with foreign antigens) are
... Pathogens (Bacteria & Virus with foreign antigens) are engulfed by Macrophages ...
... Pathogens (Bacteria & Virus with foreign antigens) are engulfed by Macrophages ...
Immune System
... antibodies stick out of B cell membranes while others are released directly into the blood stream Each antibody can hold onto more than one pathogen, causing them to clump together, which makes them easier to engulf They signal the complement system or phagocytes to destroy the pathogens You need ...
... antibodies stick out of B cell membranes while others are released directly into the blood stream Each antibody can hold onto more than one pathogen, causing them to clump together, which makes them easier to engulf They signal the complement system or phagocytes to destroy the pathogens You need ...
cell - immunology.unideb.hu
... Antibodies are natural products that appear on the cell surface as receptors and selectively react with the antigen Lymphocyte receptors are variable and carry various antigen-recognizing receptors ‘Non-self’ antigens/pathogens encounter the existing lymphocyte pool (repertoire) Antigens select thei ...
... Antibodies are natural products that appear on the cell surface as receptors and selectively react with the antigen Lymphocyte receptors are variable and carry various antigen-recognizing receptors ‘Non-self’ antigens/pathogens encounter the existing lymphocyte pool (repertoire) Antigens select thei ...
Immune System - wappingersschools.org
... to enter the infected tissues. They engulf and destroy bacteria. The infected tissue may become swollen and painful. ...
... to enter the infected tissues. They engulf and destroy bacteria. The infected tissue may become swollen and painful. ...
Forensic Biology by Richard Li
... immune response and is then capable of binding to the subsequently produced antibodies. Antigens are generally proteins or polysaccharides, but other substances such as nucleic acids can also be antigens. ...
... immune response and is then capable of binding to the subsequently produced antibodies. Antigens are generally proteins or polysaccharides, but other substances such as nucleic acids can also be antigens. ...
1. dia
... Normal tissue cells do not express MHC class II NO SIGNAL 1. for CD4+ Th activation Normal tissue cells do not express co-stimulatory molecules and do not produce T cell differentiating cytokines NO SIGNAL 2. for CD4+ Th activation Migration of naive T lymphocytes to normal tissues is limited Antige ...
... Normal tissue cells do not express MHC class II NO SIGNAL 1. for CD4+ Th activation Normal tissue cells do not express co-stimulatory molecules and do not produce T cell differentiating cytokines NO SIGNAL 2. for CD4+ Th activation Migration of naive T lymphocytes to normal tissues is limited Antige ...
Natural Defense Mechanisms
... Monocytes : Become Macrophages when they leave the blood and enter the tissues. Neutrophils: (Phagocytic cells) Eosinophils: (Allergy and Parasitic infections) Natural Killer (NK) cells: (Kill tumor cells and virus infected cells) (Cytotoxic cells work as natural killer) ...
... Monocytes : Become Macrophages when they leave the blood and enter the tissues. Neutrophils: (Phagocytic cells) Eosinophils: (Allergy and Parasitic infections) Natural Killer (NK) cells: (Kill tumor cells and virus infected cells) (Cytotoxic cells work as natural killer) ...
11.1 Defence against infectious disease – summary
... antibodies are made by B-cells / lymphocytes / plasma cells; antigen is engulfed by macrophages; antigen is presented on macrophage membrane; helper T-cells bind to antigen (on macrophage); helper T-cells are activated; helper T-cells activate B-cells; B-cells clone; into plasma cells and memory cel ...
... antibodies are made by B-cells / lymphocytes / plasma cells; antigen is engulfed by macrophages; antigen is presented on macrophage membrane; helper T-cells bind to antigen (on macrophage); helper T-cells are activated; helper T-cells activate B-cells; B-cells clone; into plasma cells and memory cel ...