Chapter 19
... • Allograft: Use of tissue from another person • Xenotransplantation product: Use of non-human tissue • Graft-versus-host disease can result from transplanted bone marrow that contains immunocompetent cells ...
... • Allograft: Use of tissue from another person • Xenotransplantation product: Use of non-human tissue • Graft-versus-host disease can result from transplanted bone marrow that contains immunocompetent cells ...
Immunity - CIE Alevel notes!
... A B-lymphocytes places some of its specific receptor molecules in its cell surface membrane. If it encounters an antigen that binds with this receptor, the B-lymphocytes is activated. It divides repeatedly by mitosis to produce a clone of genetically identical plasma cells. Some of these synthesis a ...
... A B-lymphocytes places some of its specific receptor molecules in its cell surface membrane. If it encounters an antigen that binds with this receptor, the B-lymphocytes is activated. It divides repeatedly by mitosis to produce a clone of genetically identical plasma cells. Some of these synthesis a ...
Project Overview
... ◦ William B. Coley, MD, formed the basis for the use of cytokines ◦ Hybridoma Technology The production of large quantities of very pure antibodies (monoclonal antibodies) ...
... ◦ William B. Coley, MD, formed the basis for the use of cytokines ◦ Hybridoma Technology The production of large quantities of very pure antibodies (monoclonal antibodies) ...
MATURE T-LYMPHOCYTE MARKERS
... IL-4 and IL-15 are the most likely to function as T-cell growth factors in the absence of IL-2. Hence, if IL-4 production predominates in a particular T-cell response, as it does in response to parasites and allergens, one may observe T-cell proliferation, but this proliferation may be restricted on ...
... IL-4 and IL-15 are the most likely to function as T-cell growth factors in the absence of IL-2. Hence, if IL-4 production predominates in a particular T-cell response, as it does in response to parasites and allergens, one may observe T-cell proliferation, but this proliferation may be restricted on ...
The humoral immune response defends against pathogens that are
... release cytokines that induce the B cell to divide rapidly, making thousands of identical (clonal) cells. These daughter cells become either plasma cells or memory B cells. The memory B cells remain inactive at this point. A later encounter with the antigen, caused by a reinfection by the same bact ...
... release cytokines that induce the B cell to divide rapidly, making thousands of identical (clonal) cells. These daughter cells become either plasma cells or memory B cells. The memory B cells remain inactive at this point. A later encounter with the antigen, caused by a reinfection by the same bact ...
Immunology for Dummies_ The B cell receptor and antibodies
... infection. Now, let’s find out what they can actually do. The functions of antibodies are merely neutralisation of viruses and toxins, complement activation and opsonisation, opsonisation and lastly antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). Neutralisation - Antibodies can bind to toxin m ...
... infection. Now, let’s find out what they can actually do. The functions of antibodies are merely neutralisation of viruses and toxins, complement activation and opsonisation, opsonisation and lastly antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). Neutralisation - Antibodies can bind to toxin m ...
Blood and the Immune System
... B-cell leukocytes are anti-body producing. Each B-cell produces a single type of antibody. Super-antibody-producing cells are called plasma cells which produce 2000 antibody molecules/sec ...
... B-cell leukocytes are anti-body producing. Each B-cell produces a single type of antibody. Super-antibody-producing cells are called plasma cells which produce 2000 antibody molecules/sec ...
Comparative Vertebrate Physiology
... 2 types of T-cells, CD4 (TH) and CD8 (TC) T-cells activate by double recognition ...
... 2 types of T-cells, CD4 (TH) and CD8 (TC) T-cells activate by double recognition ...
T cell-mediated immune response
... clonal expansion → differentiation → effector & memory cells → effector cells die after elimination of infection ...
... clonal expansion → differentiation → effector & memory cells → effector cells die after elimination of infection ...
Ch 12 2nd and 3rd Lines of Defense
... Self-Antigens Human cells have many surface proteins Our immune cells do not attack our own proteins Our cells in another person’s body can trigger an immune response because they are foreign - Restricts donors for transplants ...
... Self-Antigens Human cells have many surface proteins Our immune cells do not attack our own proteins Our cells in another person’s body can trigger an immune response because they are foreign - Restricts donors for transplants ...
2-immune system
... What are the cell types involved with immune responses? What are the important immunological tissues? ...
... What are the cell types involved with immune responses? What are the important immunological tissues? ...
Other Players in the IMMUNE RESPONSE
... immunoglobin. Produced by the B cells. An effector of the immune response. • Antigen—ANTIbody GENerator. A foreign macromolecule that elicits an immune response. • The specificity between the shapes of antigens and antibodies are the basis of the immune response. ...
... immunoglobin. Produced by the B cells. An effector of the immune response. • Antigen—ANTIbody GENerator. A foreign macromolecule that elicits an immune response. • The specificity between the shapes of antigens and antibodies are the basis of the immune response. ...
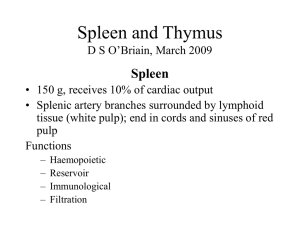
Spleen-thymus-09
... • Adults, mixture of epithelial cells and lymphocytes • Most (80%) encapsulated and histologically benign (benign thymoma) • Some (10%) similar histology but locally invasive (invasive thymoma; 75% 10-year survival) • Malignant thymoma (10%); histologically malignant, usually invasive, 25% 5-year su ...
... • Adults, mixture of epithelial cells and lymphocytes • Most (80%) encapsulated and histologically benign (benign thymoma) • Some (10%) similar histology but locally invasive (invasive thymoma; 75% 10-year survival) • Malignant thymoma (10%); histologically malignant, usually invasive, 25% 5-year su ...
Chapter 11 Immune
... - production occurs primarily in lymph nodes; also in spleen and bone marrow Humoral Immunity - production of antibodies in response to an antigen IMMUNITY AND IMMUNE RESPONSE Distinguish between passive/active immunity, humoral/cellular immunity. Explain primary and secondary immune response. How d ...
... - production occurs primarily in lymph nodes; also in spleen and bone marrow Humoral Immunity - production of antibodies in response to an antigen IMMUNITY AND IMMUNE RESPONSE Distinguish between passive/active immunity, humoral/cellular immunity. Explain primary and secondary immune response. How d ...
Immune System Reading and Questions
... There are nutritional things a person can do to help strengthen his/her immune system. Vitamins A, C, and E area collectively known as the anticancer vitamins. The immune system needs these plus minerals like zinc (Zn) and selenium (Se) to do its job. Dark green leafy vegetables, especially cabbage ...
... There are nutritional things a person can do to help strengthen his/her immune system. Vitamins A, C, and E area collectively known as the anticancer vitamins. The immune system needs these plus minerals like zinc (Zn) and selenium (Se) to do its job. Dark green leafy vegetables, especially cabbage ...
Humoral Immunity
... mutation) generate many clones of B cells bearing surface BCRs with different affinities towards the same antigen ...
... mutation) generate many clones of B cells bearing surface BCRs with different affinities towards the same antigen ...
Strive for Five- Ch 31 Concept 31.1 Identify each of these examples
... 10. Suppose that you were exposed to a newly synthesized “artificial” bacterium. After exposure, all signs of the bacterium from your body were gone within 24 hours. Assume further that this bacterium is novel enough that it does not share chemical identity signals with other bacteria. Decide if you ...
... 10. Suppose that you were exposed to a newly synthesized “artificial” bacterium. After exposure, all signs of the bacterium from your body were gone within 24 hours. Assume further that this bacterium is novel enough that it does not share chemical identity signals with other bacteria. Decide if you ...