MICR 201 Microbiology for Health Related Sciences
... Type II — Antibodies react with cell-surface antigens in specific organs Type III (Immune Complex) — IgM and/or IgG react with soluble cell material, complexes are deposited, initiate complement activation, inflammation Type IV — Mediated by cytotoxic T cells ...
... Type II — Antibodies react with cell-surface antigens in specific organs Type III (Immune Complex) — IgM and/or IgG react with soluble cell material, complexes are deposited, initiate complement activation, inflammation Type IV — Mediated by cytotoxic T cells ...
Immune system
... kill cells which have abnormally low MHCgpI expression (some tumor and virus infected cells) ...
... kill cells which have abnormally low MHCgpI expression (some tumor and virus infected cells) ...
TOLERANCE
... enter the circulation as naïve cells • “Peripheral tolerance” acts as a back up to eliminate potentially autoreactive lymphocytes AFTER they enter the circulation. • Some cells are DELETED, some cells are ANERGISED. • ANERGIC cells can be re-activated if a “DANGER” signal is encountered ...
... enter the circulation as naïve cells • “Peripheral tolerance” acts as a back up to eliminate potentially autoreactive lymphocytes AFTER they enter the circulation. • Some cells are DELETED, some cells are ANERGISED. • ANERGIC cells can be re-activated if a “DANGER” signal is encountered ...
Section 18 Immunity in the Fetus and Newborn
... migrate to the thymus and bursa at 5 to 7 days of incubation. • IgM+ lymphocytes are detected in the bursa by day 14. Antibodies are produced by 16 and 18d. • IgY+ lymphocytes develop on day 21 around the time of hatching. • IgA+ lymphocytes first appear in the intestine 3 to 7 days after hatching. ...
... migrate to the thymus and bursa at 5 to 7 days of incubation. • IgM+ lymphocytes are detected in the bursa by day 14. Antibodies are produced by 16 and 18d. • IgY+ lymphocytes develop on day 21 around the time of hatching. • IgA+ lymphocytes first appear in the intestine 3 to 7 days after hatching. ...
Immunoglobulin and Monoclonal antibodies
... interacting with antigen. b) Involved in allergic reactions - As a consequence of its binding to basophils an mast cells, IgE is involved in allergic reactions. Binding of the allergen to the IgE on the cells results in the release of various pharmacological mediators that ...
... interacting with antigen. b) Involved in allergic reactions - As a consequence of its binding to basophils an mast cells, IgE is involved in allergic reactions. Binding of the allergen to the IgE on the cells results in the release of various pharmacological mediators that ...
ImmunThe(NoTP)
... within 15 months of diagnosis -- showed that the vaccine safely increased average survival to nearly 48 weeks, compared with about 33 weeks among patients who didn't receive the treatment. The sixmonth survival rate was 93 percent for the vaccinated group, compared with 68 percent for 86 other gliob ...
... within 15 months of diagnosis -- showed that the vaccine safely increased average survival to nearly 48 weeks, compared with about 33 weeks among patients who didn't receive the treatment. The sixmonth survival rate was 93 percent for the vaccinated group, compared with 68 percent for 86 other gliob ...
Reading Worksheet KEY 6.4, pg 250 6.4_rw_key
... Blood type B attacks the other and the person can become ill and die 14. Define and give an example of autoimmune diseases: Causes the body to damage itself Arthritis, Multiple sclerosis Immune System Memory page 255 15. What is memory of infection? The ability of certain immune cells to remember an ...
... Blood type B attacks the other and the person can become ill and die 14. Define and give an example of autoimmune diseases: Causes the body to damage itself Arthritis, Multiple sclerosis Immune System Memory page 255 15. What is memory of infection? The ability of certain immune cells to remember an ...
IN RESPONSE TO DAMAGE Innate, or nonspecific, immunity
... Complement is important in resisting bacteria that are hard to destroy in other ways. For example, some of the bacteria that cause pneumonia have a slimy coating, making it hard for macrophages to ingest and eliminate them. However, if IgM and IgG antibodies bind to the pneumonia bacteria and activa ...
... Complement is important in resisting bacteria that are hard to destroy in other ways. For example, some of the bacteria that cause pneumonia have a slimy coating, making it hard for macrophages to ingest and eliminate them. However, if IgM and IgG antibodies bind to the pneumonia bacteria and activa ...
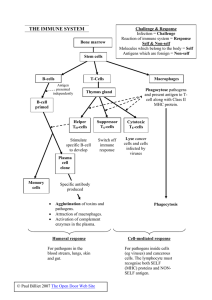
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... Reaction of immune system = Response Self & Non-self Molecules which belong to the body = Self Antigens which are foreign = Non-self ...
... Reaction of immune system = Response Self & Non-self Molecules which belong to the body = Self Antigens which are foreign = Non-self ...
Document
... • When a pathogen invades the body, it is engulfed by wandering macrophages which present the antigenic fragments on its surface • This macrophage becomes an antigen-presenting cell, and presents the antigen to helper T cells (TH cells) • The TH cells bind to the antigen and become activated, and in ...
... • When a pathogen invades the body, it is engulfed by wandering macrophages which present the antigenic fragments on its surface • This macrophage becomes an antigen-presenting cell, and presents the antigen to helper T cells (TH cells) • The TH cells bind to the antigen and become activated, and in ...