Supplementary Materials Metabolic Flux Determination in Perfused
... The liver metabolic network involving all possible major liver-specific pathways such as gluconeogenesis, glycolysis, urea cycle, fatty acid metabolism, pentose phosphate pathway, TCA cycle, glycogen metabolism and amino acid metabolism is given in Table SI. For more detailed explanations about the ...
... The liver metabolic network involving all possible major liver-specific pathways such as gluconeogenesis, glycolysis, urea cycle, fatty acid metabolism, pentose phosphate pathway, TCA cycle, glycogen metabolism and amino acid metabolism is given in Table SI. For more detailed explanations about the ...
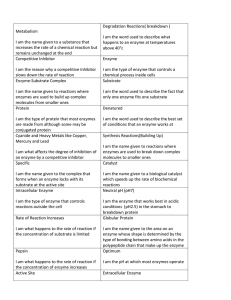
Enzymes
... (pH, I, T, cofactor) and comparison is only valid if all values have been measured under the same experimental conditions. ...
... (pH, I, T, cofactor) and comparison is only valid if all values have been measured under the same experimental conditions. ...
9/2/08 Transcript I - UAB School of Optometry
... Utilized in "Fight or Flight"- If confronted by a lion then you will fight or flee and use this type of process because it does not require any set up time or oxygen. There are 10 rxns which are the same in all cells, but may not happen at same rate. 2 Phases: 1. Converts glucose to two Glycer ...
... Utilized in "Fight or Flight"- If confronted by a lion then you will fight or flee and use this type of process because it does not require any set up time or oxygen. There are 10 rxns which are the same in all cells, but may not happen at same rate. 2 Phases: 1. Converts glucose to two Glycer ...
In the light of the haloarchaea metabolism
... The type of citric acid cycle seen in archaea depends on the class to which they belong. For example, halophiles metabolize pyruvate via an oxidative citric acid cycle. Sulphur dependent thermophiles generally fix carbon dioxide via a reductive citric acid cycle when growing autotrophically and use ...
... The type of citric acid cycle seen in archaea depends on the class to which they belong. For example, halophiles metabolize pyruvate via an oxidative citric acid cycle. Sulphur dependent thermophiles generally fix carbon dioxide via a reductive citric acid cycle when growing autotrophically and use ...
Ch 9 Notes - Dublin City Schools
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The chain’s function is to break the large free-energy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energ ...
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The chain’s function is to break the large free-energy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energ ...
metabolism - Chavis Biology
... increase in the reaction rate. Reaction rate will eventually level off as all available substrates are used up. Draw this: ...
... increase in the reaction rate. Reaction rate will eventually level off as all available substrates are used up. Draw this: ...
Purification and characterization of the 1-3
... coenzymes were determined at 37°C with potassium carbonate buffer (pH 9.7 for the oxidative reactions and pH 9.1 for the reductive reactions). They were determined from the results of experiments in which a fixed concentration of the substrate or coenzyme and an appropriate range of concentrations o ...
... coenzymes were determined at 37°C with potassium carbonate buffer (pH 9.7 for the oxidative reactions and pH 9.1 for the reductive reactions). They were determined from the results of experiments in which a fixed concentration of the substrate or coenzyme and an appropriate range of concentrations o ...
The Effect of Disulphides on Mitochondrial Oxidations
... 1960; Pihl & Lange, 1962). It should be stressed, however, that, in most of the cases of inhibition of enzymes by disulphide described, a disulphide with an oxidation potential far above that of cystamine has been used. The present paper describes the toxic effects of some disulphides on mitochondri ...
... 1960; Pihl & Lange, 1962). It should be stressed, however, that, in most of the cases of inhibition of enzymes by disulphide described, a disulphide with an oxidation potential far above that of cystamine has been used. The present paper describes the toxic effects of some disulphides on mitochondri ...
Enzymes
... (pH, I, T, cofactor) and comparison is only valid if all values have been measured under the same experimental conditions. ...
... (pH, I, T, cofactor) and comparison is only valid if all values have been measured under the same experimental conditions. ...
III. Metabolism
... The H-type predominates aerobic tissues such as heart muscle. The M-type predominates tissue that are subject to anaerobic conditions such as liver and skeletal muscle. H4 LDH has a low KM for pyruvate and is allosterically inhibited by it. M4 LDH has a low KM for pyruvate and is NOT allosterically ...
... The H-type predominates aerobic tissues such as heart muscle. The M-type predominates tissue that are subject to anaerobic conditions such as liver and skeletal muscle. H4 LDH has a low KM for pyruvate and is allosterically inhibited by it. M4 LDH has a low KM for pyruvate and is NOT allosterically ...
CHAPTER 6
... and muscle; triacylglycerols in adipose tissue; and protein, mostly in skeletal muscle • The usual order of preference for use of these is glycogen > triacylglycerol > protein • The tissues of the body work together to maintain energy homeostasis ...
... and muscle; triacylglycerols in adipose tissue; and protein, mostly in skeletal muscle • The usual order of preference for use of these is glycogen > triacylglycerol > protein • The tissues of the body work together to maintain energy homeostasis ...
Fatty Acid Oxidation
... pathological states. Following this lecture students should understand that ...
... pathological states. Following this lecture students should understand that ...
Cellular respiration
... Explain how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are necessary to provide energy that is required to sustain your life Explain why breathing is necessary to support cellular respiration Describe how cellular respiration produces energy that can be stored in ATP Explain why ATP is required for hum ...
... Explain how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are necessary to provide energy that is required to sustain your life Explain why breathing is necessary to support cellular respiration Describe how cellular respiration produces energy that can be stored in ATP Explain why ATP is required for hum ...
Slide 1
... GLUCONEOGENESIS Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from glucogenic precursors which are not of carbohydrate origin (gluconeogenic precursors) It occurs during prolonged fasting to synthesize glucose for tissues requiring continuous supply of glucose as a source of energy: Brain, RBCs, Kidn ...
... GLUCONEOGENESIS Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from glucogenic precursors which are not of carbohydrate origin (gluconeogenic precursors) It occurs during prolonged fasting to synthesize glucose for tissues requiring continuous supply of glucose as a source of energy: Brain, RBCs, Kidn ...
CHAPTER 7, CELLULAR RESPIRATION In Eukaryotic Cells, the
... 1. The ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN makes up the Second Stage of Aerobic Respiration. 2. In EUKARYOTIC CELLS the Electron Transport chain LINES the INNER MEMBRANE of the Mitochondrion, the inner membrane has many long folds called CRISTAE. 3. In Prokaryotes, the Electron Transport Chain LINES the CELL M ...
... 1. The ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN makes up the Second Stage of Aerobic Respiration. 2. In EUKARYOTIC CELLS the Electron Transport chain LINES the INNER MEMBRANE of the Mitochondrion, the inner membrane has many long folds called CRISTAE. 3. In Prokaryotes, the Electron Transport Chain LINES the CELL M ...
Biochemistry 3020 1. All of the following enzymes involved in the
... The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex converts pyruvate, the product of glycolysis, into acetyl-CoA, the starting material for the citric acid cycle. ...
... The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex converts pyruvate, the product of glycolysis, into acetyl-CoA, the starting material for the citric acid cycle. ...
Chapter 16 Glycolysis Control of glycolytic pathway
... Northern Europeans have a mutation that prevents the decline of lactase activity after weaning. In lactase-deficient individuals, gut bacteria metabolize lactose, generating CH4 and H2, and disrupt water balance in the intestine. ...
... Northern Europeans have a mutation that prevents the decline of lactase activity after weaning. In lactase-deficient individuals, gut bacteria metabolize lactose, generating CH4 and H2, and disrupt water balance in the intestine. ...
Enzyme Vs. Extremozyme -32
... salt-links, 10 hydrogen bonds and 74 Van der Waals interactions are established to thermostabilize lysozyme. The thermostability of a-amylase, glucoamylase and subtilisin have also been increased substantially by this approach. Organic Solvents 4: Usually enzymes do not function in organic solvents. ...
... salt-links, 10 hydrogen bonds and 74 Van der Waals interactions are established to thermostabilize lysozyme. The thermostability of a-amylase, glucoamylase and subtilisin have also been increased substantially by this approach. Organic Solvents 4: Usually enzymes do not function in organic solvents. ...
citric acid cycle
... The urea cycle and the reactions that feed amino group into it. Note that the enzymes catalyzing these reactions are distributed between the mitochondrial matrix and the cytosol. One amino group enters the urea cycle from carbamoyl phosphate (step 1), formed in the matrix; the other (entering at s ...
... The urea cycle and the reactions that feed amino group into it. Note that the enzymes catalyzing these reactions are distributed between the mitochondrial matrix and the cytosol. One amino group enters the urea cycle from carbamoyl phosphate (step 1), formed in the matrix; the other (entering at s ...
Title: Author - Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
... which were produced by the pyruvate dehydrogenase or by reactions of citric acid cycle could be oxidized within mitochondria. The NADH released in a glycolytic reaction (catalyzed by glyceraldehide-3-phosphate-dehidrogenase) requires a transport mechanism, because the inner mitochondrial membrane is ...
... which were produced by the pyruvate dehydrogenase or by reactions of citric acid cycle could be oxidized within mitochondria. The NADH released in a glycolytic reaction (catalyzed by glyceraldehide-3-phosphate-dehidrogenase) requires a transport mechanism, because the inner mitochondrial membrane is ...
lab1
... Nearly all known enzymes are proteins in nature with the exception of certain RNA molecules can be effective biocatalysts too. These RNA molecules have come to be known as ribozymes. synthesized by the living cells ...
... Nearly all known enzymes are proteins in nature with the exception of certain RNA molecules can be effective biocatalysts too. These RNA molecules have come to be known as ribozymes. synthesized by the living cells ...
Chapter 6: How Cells Harvest Energy
... Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are transferred to electron acceptors, which produces a proton gradient Proton gradient used to drive synthesis of ATP. Chemiosmosis: ATP synthase allows H+ to flow across inner mitochondrial membrane down concentration gradient, which produces ATP. Ultimate acc ...
... Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are transferred to electron acceptors, which produces a proton gradient Proton gradient used to drive synthesis of ATP. Chemiosmosis: ATP synthase allows H+ to flow across inner mitochondrial membrane down concentration gradient, which produces ATP. Ultimate acc ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms, an oxidized and reduced form abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. In an alternative fashion, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD, but it has different roles in metabolism.Although NAD+ is written with a superscript plus sign because of the formal charge on a particular nitrogen atom, at physiological pH for the most part it is actually a singly charged anion (charge of minus 1), while NADH is a doubly charged anion.