Oxygen
... Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are transferred to electron acceptors, which produces a proton gradient Proton gradient used to drive synthesis of ATP. Chemiosmosis: ATP synthase allows H+ to flow across inner mitochondrial membrane down concentration gradient, which produces ATP. Ultimate acc ...
... Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are transferred to electron acceptors, which produces a proton gradient Proton gradient used to drive synthesis of ATP. Chemiosmosis: ATP synthase allows H+ to flow across inner mitochondrial membrane down concentration gradient, which produces ATP. Ultimate acc ...
ATP - TeacherWeb
... energy are called heterotrophs. They consume glucose which is broken down in the cell and the mitochondria to create energy. Cellular respiration is the process that breaks down glucose to give off energy. ...
... energy are called heterotrophs. They consume glucose which is broken down in the cell and the mitochondria to create energy. Cellular respiration is the process that breaks down glucose to give off energy. ...
S08 Glycolysis
... from citric acid that exceed the oxidative capacity of respiratory chain elevation of NADH/NAD+ ratio favoring the reduction of pyruvate to lactate accumulation drop of pH muscle cramps Much of lactate diffuses into the blood. * Consumption of Lactate -The direction of lactate dehydrogenase d ...
... from citric acid that exceed the oxidative capacity of respiratory chain elevation of NADH/NAD+ ratio favoring the reduction of pyruvate to lactate accumulation drop of pH muscle cramps Much of lactate diffuses into the blood. * Consumption of Lactate -The direction of lactate dehydrogenase d ...
enzymes - SD57 Mail
... genetically controlled (control of protein synthesis) • Increasing the amount of enzyme will increase the reaction rate (as long as substrate is present) ...
... genetically controlled (control of protein synthesis) • Increasing the amount of enzyme will increase the reaction rate (as long as substrate is present) ...
03Glycolysis
... from citric acid that exceed the oxidative capacity of respiratory chain elevation of NADH/NAD+ ratio favoring the reduction of pyruvate to lactate accumulation drop of pH muscle cramps Much of lactate diffuses into the blood. * Consumption of Lactate -The direction of lactate dehydrogenase d ...
... from citric acid that exceed the oxidative capacity of respiratory chain elevation of NADH/NAD+ ratio favoring the reduction of pyruvate to lactate accumulation drop of pH muscle cramps Much of lactate diffuses into the blood. * Consumption of Lactate -The direction of lactate dehydrogenase d ...
Enzymes - Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
... “how much substrate reacts in a particular amount of time” (usually per second) ...
... “how much substrate reacts in a particular amount of time” (usually per second) ...
Glucose Metabolism - vinci
... Glucose Metabolism The metabolism of glucose is central to mammalian life. Dynamic changes in any of the steps involved in processing glucose and its derivatives contribute to a wide range of diseases. Measuring the enzymes and metabolites is pivotal to biological and medical research. Cayman offers ...
... Glucose Metabolism The metabolism of glucose is central to mammalian life. Dynamic changes in any of the steps involved in processing glucose and its derivatives contribute to a wide range of diseases. Measuring the enzymes and metabolites is pivotal to biological and medical research. Cayman offers ...
HARVESTING CHEMICAL ENERGY: CELLULAR
... 3. Sugars are used during oxidative processes to make ATP during cellular respiration. E. During cellular respiration, cells make ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. 1. Glucose is the major fuel for cellular respiration. 2. Glucose transfers electrons to oxygen forming water during cellular respiratio ...
... 3. Sugars are used during oxidative processes to make ATP during cellular respiration. E. During cellular respiration, cells make ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. 1. Glucose is the major fuel for cellular respiration. 2. Glucose transfers electrons to oxygen forming water during cellular respiratio ...
Slides - WordPress.com
... rTCA cycle was originally discovered in green sulfur phototrophs and has since been identified in a variety of chemoautotrophs rTCA cycle specific enzymes are 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (Oor), fumarate reductase (Frd), and ATP citrate lyase (Acl) rTCA cycle pathway tends to be in ...
... rTCA cycle was originally discovered in green sulfur phototrophs and has since been identified in a variety of chemoautotrophs rTCA cycle specific enzymes are 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (Oor), fumarate reductase (Frd), and ATP citrate lyase (Acl) rTCA cycle pathway tends to be in ...
biochem ch 20 [2-9
... When thioester bond of acetyl-CoA cleaved in citrate synthase reaction, energy released, giving reaction a large negative ΔG0’, which helps keep TCA cycle going in forward direction o CoASH synthesized from vitamin pantothenate in sequence of reactions that phosphorylate pantothenate, add sulfhydr ...
... When thioester bond of acetyl-CoA cleaved in citrate synthase reaction, energy released, giving reaction a large negative ΔG0’, which helps keep TCA cycle going in forward direction o CoASH synthesized from vitamin pantothenate in sequence of reactions that phosphorylate pantothenate, add sulfhydr ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY - Illinois State University
... NAD+ and NADP+ are cosubstrates for dehydrogenases • Oxidation by NAD+ and NADP+ occurs two electrons at a time • Dehydrogenases transfer a hydride ion (H:-) from a substrate to pyridine ring C-4 of NAD+ or NADP+ • The net reaction is: NAD(P)+ + 2e- + 2H+ ...
... NAD+ and NADP+ are cosubstrates for dehydrogenases • Oxidation by NAD+ and NADP+ occurs two electrons at a time • Dehydrogenases transfer a hydride ion (H:-) from a substrate to pyridine ring C-4 of NAD+ or NADP+ • The net reaction is: NAD(P)+ + 2e- + 2H+ ...
acetyl-CoA
... are known). The major symptom is either an acute episodic or (rarely) a chronic hemolysis. The disease is X-linked recessive. Female heterozygous for G6PDH deficiency have increased resistance to malaria. Consequently, the deficiency is seen more commonly in families from regions where malaria is e ...
... are known). The major symptom is either an acute episodic or (rarely) a chronic hemolysis. The disease is X-linked recessive. Female heterozygous for G6PDH deficiency have increased resistance to malaria. Consequently, the deficiency is seen more commonly in families from regions where malaria is e ...
Cellular Respiration
... 6.6 Overview: Cellular respiration occurs in three main stages Stage 3: Oxidative phosphorylation – involves electrons carried by NADH and FADH2, – shuttles these electrons to the electron transport chain embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane, – involves chemiosmosis, and – generates ATP t ...
... 6.6 Overview: Cellular respiration occurs in three main stages Stage 3: Oxidative phosphorylation – involves electrons carried by NADH and FADH2, – shuttles these electrons to the electron transport chain embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane, – involves chemiosmosis, and – generates ATP t ...
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
... Hans Krebs showed that the oxidation of acetate is accomplished by a cycle TCA cycle, Citric Acid Cycle or Krebs Cycle • Pyruvate from glycolysis is oxidatively decarboxylated to acetate and then degraded to CO2 in TCA cycle • Some ATP is produced • More NADH and FADH2 are made • NADH goes on to ma ...
... Hans Krebs showed that the oxidation of acetate is accomplished by a cycle TCA cycle, Citric Acid Cycle or Krebs Cycle • Pyruvate from glycolysis is oxidatively decarboxylated to acetate and then degraded to CO2 in TCA cycle • Some ATP is produced • More NADH and FADH2 are made • NADH goes on to ma ...
Why Bacteria are not Enzymes, and other Essentials
... An example of a success story is the change in the formulation of detergents that are composed of branching chemical structures to ones that have straight chemical chains, which are more easily biodegraded by microorganisms. Bacteria, Not Enzymes Bacteria are not enzymes. Like all living cells, bac ...
... An example of a success story is the change in the formulation of detergents that are composed of branching chemical structures to ones that have straight chemical chains, which are more easily biodegraded by microorganisms. Bacteria, Not Enzymes Bacteria are not enzymes. Like all living cells, bac ...
Glycolysis
... from citric acid that exceed the oxidative capacity of respiratory chain elevation of NADH/NAD+ ratio favoring the reduction of pyruvate to lactate accumulation drop of pH muscle cramps Much of lactate diffuses into the blood. * Consumption of Lactate -The direction of lactate dehydrogenase d ...
... from citric acid that exceed the oxidative capacity of respiratory chain elevation of NADH/NAD+ ratio favoring the reduction of pyruvate to lactate accumulation drop of pH muscle cramps Much of lactate diffuses into the blood. * Consumption of Lactate -The direction of lactate dehydrogenase d ...
10) water soluble vitamins
... • Participate in citric acid cycle and beta oxidation and electron transport • Remove ammonia during deamination of ...
... • Participate in citric acid cycle and beta oxidation and electron transport • Remove ammonia during deamination of ...
Full Text PDF - Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. publishers
... (VLCFA, C ‡ 22:0) and VLCFA-CoA esters into the peroxisome for degradation (66). Defective function of the ABCD1 transporter leads to VLCFA accumulation in most organs and plasma; and elevated levels of VLCFA are used as a biomarker for the biochemical diagnosis of the disease. Classical inactivatio ...
... (VLCFA, C ‡ 22:0) and VLCFA-CoA esters into the peroxisome for degradation (66). Defective function of the ABCD1 transporter leads to VLCFA accumulation in most organs and plasma; and elevated levels of VLCFA are used as a biomarker for the biochemical diagnosis of the disease. Classical inactivatio ...
ENZYMES
... Enzymes are soluble ,colloidal organic catalyst ,specific in action , protein in nature. They catalyze the hundreds of stepwise reactions that degrade nutrient molecules ,conserve and transform chemical energy from simple precursors. Wilhelm Kühne first used the term enzymes. For e.g. maltose is the ...
... Enzymes are soluble ,colloidal organic catalyst ,specific in action , protein in nature. They catalyze the hundreds of stepwise reactions that degrade nutrient molecules ,conserve and transform chemical energy from simple precursors. Wilhelm Kühne first used the term enzymes. For e.g. maltose is the ...
BioN08 Metabolism of lipids Summer 2015
... • Heart muscles prefer ketone bodies over glucose when fatty acids are in short supply. • When energy production from glucose is inadequate due to starvation, the production of ketone bodies accelerates. • During the early stages of starvation, heart and muscle tissues burn larger quantities of acet ...
... • Heart muscles prefer ketone bodies over glucose when fatty acids are in short supply. • When energy production from glucose is inadequate due to starvation, the production of ketone bodies accelerates. • During the early stages of starvation, heart and muscle tissues burn larger quantities of acet ...
Essentiality and damage in metabolic networks
... number 2, 4, 6 and 10) are involved in the production of chorismate, which is an important link to the biosynthesis of aromatic aminoacids, folate and ubiquinone. The enzyme with the highest damage, ribose-phosphate-pyrophosphokinase, generates phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate, which is the initial comp ...
... number 2, 4, 6 and 10) are involved in the production of chorismate, which is an important link to the biosynthesis of aromatic aminoacids, folate and ubiquinone. The enzyme with the highest damage, ribose-phosphate-pyrophosphokinase, generates phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate, which is the initial comp ...
Enzyme - Mercer Island School District
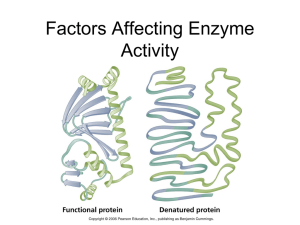
... • All the previous factors also affect an enzyme’s rate of reaction. • Since enzymes are ______________ with specifically shaped _______________, the ________________ (unfolding) of an enzyme also affects its ability to _________________ . • Extreme _____________ and extreme ______conditions denatur ...
... • All the previous factors also affect an enzyme’s rate of reaction. • Since enzymes are ______________ with specifically shaped _______________, the ________________ (unfolding) of an enzyme also affects its ability to _________________ . • Extreme _____________ and extreme ______conditions denatur ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms, an oxidized and reduced form abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. In an alternative fashion, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD, but it has different roles in metabolism.Although NAD+ is written with a superscript plus sign because of the formal charge on a particular nitrogen atom, at physiological pH for the most part it is actually a singly charged anion (charge of minus 1), while NADH is a doubly charged anion.