a formulation containing silk protein
... was significantly superior to serine, glycine and antioxidant formulation, when compared to ethanol control, with respect to decreasing NAD/NADH ratios, increasing ADH activity, decreasing blood ethanol concentration at two hour post treatment. Introduction: The toxic effects of alcohol are directly ...
... was significantly superior to serine, glycine and antioxidant formulation, when compared to ethanol control, with respect to decreasing NAD/NADH ratios, increasing ADH activity, decreasing blood ethanol concentration at two hour post treatment. Introduction: The toxic effects of alcohol are directly ...
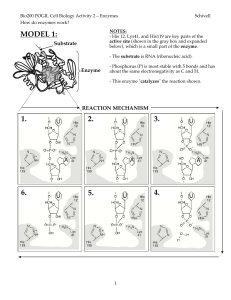
Enzymes
... • The product separates from the enzyme, leaving the enzyme molecule unchanged and free to combine again with more substrate molecules ...
... • The product separates from the enzyme, leaving the enzyme molecule unchanged and free to combine again with more substrate molecules ...
STRUCTURE OF ATP
... amount of energy in the chemical bonds.The breaking of Complex organic substances through oxidation releases energy.This process is called respiration. All living organism required energy to carry out various activities. This energy is obtained through respiration which is a catabolic process. It oc ...
... amount of energy in the chemical bonds.The breaking of Complex organic substances through oxidation releases energy.This process is called respiration. All living organism required energy to carry out various activities. This energy is obtained through respiration which is a catabolic process. It oc ...
The light reaction of photosynthesis does not include
... B) respiration breaks down energy-rich organics to synthesize ATP photosynthesis involves the oxidation of glucose; respiration involves the reduction C) of CO2 the primary function of photosynthesis is to use solar energy to synthesize ATP; the primary function of cellular respiration is to break d ...
... B) respiration breaks down energy-rich organics to synthesize ATP photosynthesis involves the oxidation of glucose; respiration involves the reduction C) of CO2 the primary function of photosynthesis is to use solar energy to synthesize ATP; the primary function of cellular respiration is to break d ...
Introduction to Enzymes - Rose
... different forms of lactate dehydrogenase are isoforms, while the M and H polypeptides are isozymes, because they are produced from separate genes. Why do organisms use more than one enzyme with the same activity? Different isozymes may be expressed in different tissues. This is important, because, i ...
... different forms of lactate dehydrogenase are isoforms, while the M and H polypeptides are isozymes, because they are produced from separate genes. Why do organisms use more than one enzyme with the same activity? Different isozymes may be expressed in different tissues. This is important, because, i ...
Cellular Respiration
... • Oxygen is required – Aerobic Respiration • A series of chemical rxns… a cycle – Pyruvic Acid is further broken down: • into Acetyl CoA • CO2 is produced and • released into the air from animal cells • Or in plants move to the chloroplasts to be used for photosynthesis ...
... • Oxygen is required – Aerobic Respiration • A series of chemical rxns… a cycle – Pyruvic Acid is further broken down: • into Acetyl CoA • CO2 is produced and • released into the air from animal cells • Or in plants move to the chloroplasts to be used for photosynthesis ...
Oxidation of Pyruvate and the Citric Acid Cycle
... however, these do not necessarily contain the most recently added carbon atoms. The two acetyl carbon atoms will eventually be released on later turns of the cycle; thus, all six carbon atoms from the original glucose molecule are eventually incorporated into carbon dioxide. Each turn of the cycle f ...
... however, these do not necessarily contain the most recently added carbon atoms. The two acetyl carbon atoms will eventually be released on later turns of the cycle; thus, all six carbon atoms from the original glucose molecule are eventually incorporated into carbon dioxide. Each turn of the cycle f ...
A1984TU03700001
... confirmed using isolated aleurone tissue. ’ This tissue is also the major source61of the inorganic phosphate, and some sucrose. Hydrolytic enzymes appeared that could degrade synthetic glycosides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, poly. saccharides, proteins, and dipeptides. Later DNA, RNA, and phosp ...
... confirmed using isolated aleurone tissue. ’ This tissue is also the major source61of the inorganic phosphate, and some sucrose. Hydrolytic enzymes appeared that could degrade synthetic glycosides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, poly. saccharides, proteins, and dipeptides. Later DNA, RNA, and phosp ...
L11_lipogenesis
... • Note about Coenzyme A – Often written as CoA-SH to emphasise that the functional part of the molecule is the sulphydryl group – Forms thioesters which are, themselves, quite ‘high energy’ bonds – Most common carrier of fatty acids and acetates ...
... • Note about Coenzyme A – Often written as CoA-SH to emphasise that the functional part of the molecule is the sulphydryl group – Forms thioesters which are, themselves, quite ‘high energy’ bonds – Most common carrier of fatty acids and acetates ...
Glycolysis
... It is a common motif for an enzyme active site to be located at an interface between protein domains that are connected by a flexible hinge region. The structural flexibility allows access to the active site, while permitting precise positioning of active site residues, and in some cases exclusion o ...
... It is a common motif for an enzyme active site to be located at an interface between protein domains that are connected by a flexible hinge region. The structural flexibility allows access to the active site, while permitting precise positioning of active site residues, and in some cases exclusion o ...
File
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
Key Terms PDF - QuizOver.com
... transfer of an amine group from one molecule to another as a way to turn nitrogen waste into ammonia ...
... transfer of an amine group from one molecule to another as a way to turn nitrogen waste into ammonia ...
Class3 POGIL Enzyme Mechanics Worksheet
... b. Which mutant helps to answer this question? ________ 14. When the transfer of a proton between the enzyme and substrate is prevented, is the reaction rate changed slightly or dramatically? __________ 15. Even if an R-group (that is part of the active site) does not normally accept or donate proto ...
... b. Which mutant helps to answer this question? ________ 14. When the transfer of a proton between the enzyme and substrate is prevented, is the reaction rate changed slightly or dramatically? __________ 15. Even if an R-group (that is part of the active site) does not normally accept or donate proto ...
$doc.title
... Glucose + oxygen Carbon dioxide + water +energy • Oxygen is the best electron acceptor, but what if it is not around? ...
... Glucose + oxygen Carbon dioxide + water +energy • Oxygen is the best electron acceptor, but what if it is not around? ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... • Three NADH, one FADH2 & 1 GTP/ATP is made in the citric acid cycle. • The citric acid cycle can be used to make precursors for ...
... • Three NADH, one FADH2 & 1 GTP/ATP is made in the citric acid cycle. • The citric acid cycle can be used to make precursors for ...
cellular respiration
... 1. Decarboxylation – Pyruvate (3C) is converted into 2C molecule by removing one CO2 2. Reduction – pyruvate is reduced producing 2 H+, NAD+ accept H+ and becomes NADH + H+ 3. The 2C compound called acetyl attaches to coenzyme A and form acetyl CoA ...
... 1. Decarboxylation – Pyruvate (3C) is converted into 2C molecule by removing one CO2 2. Reduction – pyruvate is reduced producing 2 H+, NAD+ accept H+ and becomes NADH + H+ 3. The 2C compound called acetyl attaches to coenzyme A and form acetyl CoA ...
3-Glycolysis BCH340
... Lactate released to the blood may be taken up by other tissues, or by skeletal muscle after exercise, and converted via Lactate Dehydrogenase back to pyruvate, which may be oxidized in Krebs Cycle or (in liver) converted to back to glucose via ...
... Lactate released to the blood may be taken up by other tissues, or by skeletal muscle after exercise, and converted via Lactate Dehydrogenase back to pyruvate, which may be oxidized in Krebs Cycle or (in liver) converted to back to glucose via ...
Enzymes - Healing Energies at London West
... lactose which is the main sugar in milk. If lactose cannot be broken down within the digestive system, symptoms such as nausea, cramps and bloating can result. We can understand a little more about the role of enzymes elsewhere in the body processes by looking at some different examples: The blood ...
... lactose which is the main sugar in milk. If lactose cannot be broken down within the digestive system, symptoms such as nausea, cramps and bloating can result. We can understand a little more about the role of enzymes elsewhere in the body processes by looking at some different examples: The blood ...
Phase-I metabolism
... Hydrolytic phase-I metabolism • By non-specific esterase and amidase enzymes that present in plasma, gut, liver and kidney. • It has a beneficial role in most of prodrugs that after hydrolysis inside the body release the active form of the drug. ...
... Hydrolytic phase-I metabolism • By non-specific esterase and amidase enzymes that present in plasma, gut, liver and kidney. • It has a beneficial role in most of prodrugs that after hydrolysis inside the body release the active form of the drug. ...
You Light Up My Life
... Electrons from first-stage reactions are delivered to NAD+ in mitochondria ...
... Electrons from first-stage reactions are delivered to NAD+ in mitochondria ...
Chapter 26 - s3.amazonaws.com
... A "secret" role of ATP in metabolism Metabolic pathways proceed in one direction Either catabolic or anabolic, not both Both directions of any pair of opposing pathways must be favorable, so that allosteric effectors can control the direction effectively The ATP coupling coefficient for any such seq ...
... A "secret" role of ATP in metabolism Metabolic pathways proceed in one direction Either catabolic or anabolic, not both Both directions of any pair of opposing pathways must be favorable, so that allosteric effectors can control the direction effectively The ATP coupling coefficient for any such seq ...
Chapter 5
... with most muscles: the lactate is carried by the blood from the muscle cells to the liver, where it can be converted to glucose. Thus, although lactate is formed at high rates when muscles are overworked and become fatigued, it is not directly the cause of muscle fatigue. As oxygen availability cann ...
... with most muscles: the lactate is carried by the blood from the muscle cells to the liver, where it can be converted to glucose. Thus, although lactate is formed at high rates when muscles are overworked and become fatigued, it is not directly the cause of muscle fatigue. As oxygen availability cann ...
Relationship between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... H+ ions must move back from a higher lower concentration Only return to inner compartment through ATP synthases, “gates of the dam” As they move through, activate ATP synthase to make ATP from ADP + Pi This process is called Chemiosmosis (ATP production linked to H+ gradient) ...
... H+ ions must move back from a higher lower concentration Only return to inner compartment through ATP synthases, “gates of the dam” As they move through, activate ATP synthase to make ATP from ADP + Pi This process is called Chemiosmosis (ATP production linked to H+ gradient) ...
PYRUVATE OXIDATION, KREBS CYCLE agnes je... 583KB Nov 04
... http://drchadedwards.com/244/energy-production-through-the-krebs-cycle/ Freeman, W.H. (2002). The Citric Acid Cycle. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21163/ Krebs cycle. (n.d.). Retrieved from ...
... http://drchadedwards.com/244/energy-production-through-the-krebs-cycle/ Freeman, W.H. (2002). The Citric Acid Cycle. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21163/ Krebs cycle. (n.d.). Retrieved from ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms, an oxidized and reduced form abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. In an alternative fashion, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD, but it has different roles in metabolism.Although NAD+ is written with a superscript plus sign because of the formal charge on a particular nitrogen atom, at physiological pH for the most part it is actually a singly charged anion (charge of minus 1), while NADH is a doubly charged anion.