Proteins
... -at all times there are billions of chemical reactions taking place in any organism -all organisms therefore need to control these chemical reactions that make up metabolism - Enzymes control chemical reactions and therefore ...
... -at all times there are billions of chemical reactions taking place in any organism -all organisms therefore need to control these chemical reactions that make up metabolism - Enzymes control chemical reactions and therefore ...
Extra Notes on Enzymes (Overview)
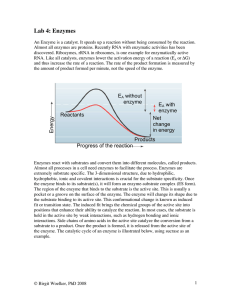
... Example: Enzymes are needed to break down food into smaller molecules that cells can use. Without enzymes, a Venus flytrap couldn’t break down its food, and neither could you. Activation energy The amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction Once a chemical reaction starts, it can be ...
... Example: Enzymes are needed to break down food into smaller molecules that cells can use. Without enzymes, a Venus flytrap couldn’t break down its food, and neither could you. Activation energy The amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction Once a chemical reaction starts, it can be ...
Human placenta glutathione transferase (EC2.5.1.18) T undergoes
... The disulfide formation causes changes in the tertiary structure of this transferase as it appears by CD, UV, and fluorometric analyses; evidence is provided that one or both tryptophanyl residues of each subunit together with a number of tyrosyl residues are exposed to a more hydrophilic environme ...
... The disulfide formation causes changes in the tertiary structure of this transferase as it appears by CD, UV, and fluorometric analyses; evidence is provided that one or both tryptophanyl residues of each subunit together with a number of tyrosyl residues are exposed to a more hydrophilic environme ...
ENZYME ACTIVITY LAB What factors affect enzyme activity? Please
... name of the enzyme is catalase (KAT-uh-LAYSS); it speeds up a reaction which breaks down hydrogen peroxide, a toxic chemical, into 2 harmless substances--water and oxygen. The reaction is: 2 H2O2 ----> 2 H2O + O2 This reaction is important to cells because hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is produced as a b ...
... name of the enzyme is catalase (KAT-uh-LAYSS); it speeds up a reaction which breaks down hydrogen peroxide, a toxic chemical, into 2 harmless substances--water and oxygen. The reaction is: 2 H2O2 ----> 2 H2O + O2 This reaction is important to cells because hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is produced as a b ...
biology lab: enzyme activity
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION: (Summarize the information below in your own words.) "Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts that affect the rate of biochemical reactions. In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substance to be acted upon, the substrate (S), binds to the active site of the enzyme (E). One ...
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION: (Summarize the information below in your own words.) "Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts that affect the rate of biochemical reactions. In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substance to be acted upon, the substrate (S), binds to the active site of the enzyme (E). One ...
Effect of Catalase Concentration on the
... poisonous byproduct of cell reactions. You have probably seen evidence of this reaction if you have ever poured hydrogen peroxide on a cut. The catalase decomposes hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. The oxygen gas is released as bubbles. The rate at which this occurs depends on the number of c ...
... poisonous byproduct of cell reactions. You have probably seen evidence of this reaction if you have ever poured hydrogen peroxide on a cut. The catalase decomposes hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. The oxygen gas is released as bubbles. The rate at which this occurs depends on the number of c ...
Catalase and Hydrogen Peroxide
... poisonous byproduct of cell reactions. You have probably seen evidence of this reaction if you have ever poured hydrogen peroxide on a cut. The catalase decomposes hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. The oxygen gas is released as bubbles. The rate at which this occurs depends on the number of c ...
... poisonous byproduct of cell reactions. You have probably seen evidence of this reaction if you have ever poured hydrogen peroxide on a cut. The catalase decomposes hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. The oxygen gas is released as bubbles. The rate at which this occurs depends on the number of c ...
Enzymes - Images
... o Active site of an enzyme includes many amino acids some of which have areas that are either positively or negatively charged o + and – of a substrate must match the opposite charge when the substrate is in the active site of an enzyme in order for the enzyme to have catalytic action o When a solut ...
... o Active site of an enzyme includes many amino acids some of which have areas that are either positively or negatively charged o + and – of a substrate must match the opposite charge when the substrate is in the active site of an enzyme in order for the enzyme to have catalytic action o When a solut ...
Enzyme Mechanisms
... system is the ribosome. The central catalytic activity of the ribosome (peptide bond formation) is catalyzed by an RNA component. ...
... system is the ribosome. The central catalytic activity of the ribosome (peptide bond formation) is catalyzed by an RNA component. ...
Lab 6 Enzymes
... Enzymes can be affected by other molecules. Many vitamins act as coenzymes, minerals act as cofactors for enzymes. Both will activate the enzymatic reaction by binding to the enzyme. Drugs and poisons are often inhibitors of enzymatic activity. Inhibitors may bind to the active site and directly com ...
... Enzymes can be affected by other molecules. Many vitamins act as coenzymes, minerals act as cofactors for enzymes. Both will activate the enzymatic reaction by binding to the enzyme. Drugs and poisons are often inhibitors of enzymatic activity. Inhibitors may bind to the active site and directly com ...
Enzyme Activity
... 20. List 2 internal environmental factors that affect how well enzymes function. 21. What happens to water when you heat it to 100°C? 22. What happens to proteins dissolved in that water when you heat it to 100°C? 23. What specific change happens to an enzyme that stops it from working when you heat ...
... 20. List 2 internal environmental factors that affect how well enzymes function. 21. What happens to water when you heat it to 100°C? 22. What happens to proteins dissolved in that water when you heat it to 100°C? 23. What specific change happens to an enzyme that stops it from working when you heat ...
14-7-SA-V1-S1__enzym..
... Question 1 : One of the enzymes involved in glycolysis, aldolase, requires Zn2+ for catalysis. Under conditions of zinc deficiency, when the enzyme may lack zinc, it would be referred to as the: a. holoenzyme b. prosthetic group c. apoenzyme d. coenzyme ...
... Question 1 : One of the enzymes involved in glycolysis, aldolase, requires Zn2+ for catalysis. Under conditions of zinc deficiency, when the enzyme may lack zinc, it would be referred to as the: a. holoenzyme b. prosthetic group c. apoenzyme d. coenzyme ...
Enzyme Kinetics - NC State: WWW4 Server
... binding energy. The entropy loss arises from the loss of translational and rotational degrees of freedom when the substrate is bound. The configurational entropy is: S = kB lnW where W is the number of degrees of freedom available to a molecule. ...
... binding energy. The entropy loss arises from the loss of translational and rotational degrees of freedom when the substrate is bound. The configurational entropy is: S = kB lnW where W is the number of degrees of freedom available to a molecule. ...
File
... This destroys the disulfide bridges and thus changing the tertiary structure of the enzyme Change in the shape results in the change in the active site thus the substrate cannot bind and cytochrome c oxidase is nonfuctional. ...
... This destroys the disulfide bridges and thus changing the tertiary structure of the enzyme Change in the shape results in the change in the active site thus the substrate cannot bind and cytochrome c oxidase is nonfuctional. ...
* Proteins, or polypeptides, are polymers made of monomers called
... It takes more energy to get the reaction to happen without the enzyme (blue hill) than with the enzyme (red ...
... It takes more energy to get the reaction to happen without the enzyme (blue hill) than with the enzyme (red ...
Bioinorganic Chemistry Glossar
... the antitumoractivity of this drug is its interaction with the nucleic acid bases of DNA. Cluster: Metal centers grouped close together which can have direct metal bonding or through a bridging ligand, e.g. ferredoxin. Cobalamin: Vitamin B12, substituted corrin-Co(III) complex. Coenzyme: A low-molec ...
... the antitumoractivity of this drug is its interaction with the nucleic acid bases of DNA. Cluster: Metal centers grouped close together which can have direct metal bonding or through a bridging ligand, e.g. ferredoxin. Cobalamin: Vitamin B12, substituted corrin-Co(III) complex. Coenzyme: A low-molec ...
The Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions
... • Biochemically, enzymes are highly specific for their substrates and generally catalyze only one type of reaction at rates thousands and millions times higher than non-enzymatic reactions. • Two main principles to remember about enzymes are a) they act as CATALYSTS (they are not consumed in a react ...
... • Biochemically, enzymes are highly specific for their substrates and generally catalyze only one type of reaction at rates thousands and millions times higher than non-enzymatic reactions. • Two main principles to remember about enzymes are a) they act as CATALYSTS (they are not consumed in a react ...
File
... anemia. What type of anatomy is this in the scope of? a. Histology b. Gross Anatomy c. Cytology d. Cell in-depth analysis 2. Fill in the following list a. _____________ level: includes biomolecules, atoms and electrolytes b. _____________ level: Capable of carrying out all of life’s processes c. ___ ...
... anemia. What type of anatomy is this in the scope of? a. Histology b. Gross Anatomy c. Cytology d. Cell in-depth analysis 2. Fill in the following list a. _____________ level: includes biomolecules, atoms and electrolytes b. _____________ level: Capable of carrying out all of life’s processes c. ___ ...
Enzymes - Kevan Kruger
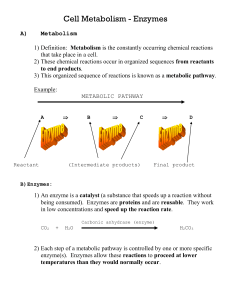
... 2) Each step of a metabolic pathway is controlled by one or more specific enzyme(s). Enzymes allow these reactions to proceed at lower temperatures than they would normally occur. ...
... 2) Each step of a metabolic pathway is controlled by one or more specific enzyme(s). Enzymes allow these reactions to proceed at lower temperatures than they would normally occur. ...
Case 13 Inhibition of Alcohol Dehydrogenase
... metabolism of ethanol in the alcoholic beverages we consume. Five different isozymes of ADH have been identified, and it has been shown that the enzyme has a rather broad substrate specificity and can oxidize aldehydes as well as primary and secondary alcohols. For example, ADH can also oxidize meth ...
... metabolism of ethanol in the alcoholic beverages we consume. Five different isozymes of ADH have been identified, and it has been shown that the enzyme has a rather broad substrate specificity and can oxidize aldehydes as well as primary and secondary alcohols. For example, ADH can also oxidize meth ...
Open file
... from the active site of the enzyme and the enzyme can be used again. By increasing the substrate concentration in the experiment, the enzyme is more ...
... from the active site of the enzyme and the enzyme can be used again. By increasing the substrate concentration in the experiment, the enzyme is more ...
Enzymes
... • The Enzyme – substrate complex then breaks up to form the product and the free enzyme which can react again • This theory is known as the LOCK AND KEY ...
... • The Enzyme – substrate complex then breaks up to form the product and the free enzyme which can react again • This theory is known as the LOCK AND KEY ...
Running Head: EFFECT OF PH ON AMYLASE ACTIVITY 1 Lab
... that occur in living organisms (Adams, 2003). They attach themselves to slots on the substrates called active sites to speed up a particular chemical reaction. There are different types of enzymes each with a particular reaction in which it catalyses. Once the reaction is complete, the enzyme de-tou ...
... that occur in living organisms (Adams, 2003). They attach themselves to slots on the substrates called active sites to speed up a particular chemical reaction. There are different types of enzymes each with a particular reaction in which it catalyses. Once the reaction is complete, the enzyme de-tou ...
G-protein linked receptors
... cytoplasm. • Often has multiple steps using relay proteins such as Protein Kinases. ...
... cytoplasm. • Often has multiple steps using relay proteins such as Protein Kinases. ...