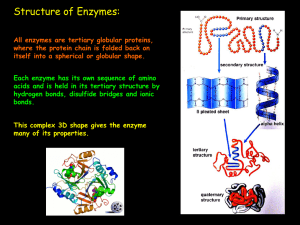
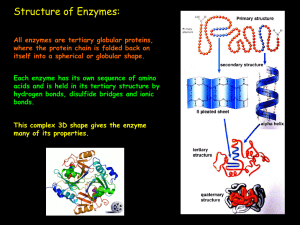
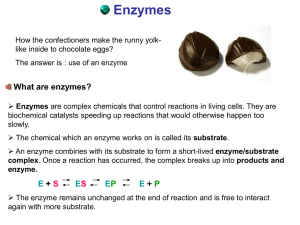
ENZYMES - Bio12.com
... 2. Non-competitive: These are not influenced by the concentration of the substrate. It inhibits by binding irreversibly to the enzyme but not at the active site Examples Cyanide combines with the Iron in the enzymes cytochrome oxidase Heavy metals, Ag or Hg, combine with –SH groups. These can be ...
... 2. Non-competitive: These are not influenced by the concentration of the substrate. It inhibits by binding irreversibly to the enzyme but not at the active site Examples Cyanide combines with the Iron in the enzymes cytochrome oxidase Heavy metals, Ag or Hg, combine with –SH groups. These can be ...
Catalase enzyme lab
... In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substance to be acted upon, or substrate, binds to the active site of the enzyme. The enzyme and substrate are held together in an enzyme-substrate complex by hydrophobic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and ionic bonds. The enzyme then converts the substrate to the reacti ...
... In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substance to be acted upon, or substrate, binds to the active site of the enzyme. The enzyme and substrate are held together in an enzyme-substrate complex by hydrophobic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and ionic bonds. The enzyme then converts the substrate to the reacti ...
1.4 Enzymes
... suggest that in the presence of the substrate, the active site may change in order to select the substrate’s shape. ...
... suggest that in the presence of the substrate, the active site may change in order to select the substrate’s shape. ...
Enzymes revision
... suggest that in the presence of the substrate, the active site may change in order to select the substrate’s shape. ...
... suggest that in the presence of the substrate, the active site may change in order to select the substrate’s shape. ...
27-36
... of the antibiotic. The molecular mass of penicillase is 30,000g/mol. The turnover number of the enzyme at 28°C is 2,000 s-1. If 6.4μg of penicillase catalyzes the destruction of 3.11mg of amoxicillin, an antibiotic with a molecular mass of 364 g/mol, in 20s at 28°C, how many active sites does the en ...
... of the antibiotic. The molecular mass of penicillase is 30,000g/mol. The turnover number of the enzyme at 28°C is 2,000 s-1. If 6.4μg of penicillase catalyzes the destruction of 3.11mg of amoxicillin, an antibiotic with a molecular mass of 364 g/mol, in 20s at 28°C, how many active sites does the en ...
Biology - WordPress.com
... Introduction: Today you’ll observe the action of the enzyme amylase on starch. Amylase changes starch into a simpler form the sugar maltose, which is soluble in water. Amylase is in our saliva, and begins to act on starchy food while in our mouth. Exposure to heat, extreme pH (acid or base) & an ino ...
... Introduction: Today you’ll observe the action of the enzyme amylase on starch. Amylase changes starch into a simpler form the sugar maltose, which is soluble in water. Amylase is in our saliva, and begins to act on starchy food while in our mouth. Exposure to heat, extreme pH (acid or base) & an ino ...
Chapter 10 Enzyme st..
... restricted possibilities for specificity as a result. More common knot constructions such as those in trypsin probably arising from some primordial gene duplication have had to evolve to head-to-head or tail-to-tail arrangements ...
... restricted possibilities for specificity as a result. More common knot constructions such as those in trypsin probably arising from some primordial gene duplication have had to evolve to head-to-head or tail-to-tail arrangements ...
Enzyme Notes
... happen to the pages of your text book as you sit here reading? They could spontaneously combust into flames. ...
... happen to the pages of your text book as you sit here reading? They could spontaneously combust into flames. ...
Chapter 5: Enzymes
... 3. Oxidation of Glucose Release of Energy to do work Involves a series of enzyme catalysed reactions 4. Breakdown of toxic materials Hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen catalysed by catalase. Enzymes catalyse almost all reactions in body. There are many different types of enzymes and each is ...
... 3. Oxidation of Glucose Release of Energy to do work Involves a series of enzyme catalysed reactions 4. Breakdown of toxic materials Hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen catalysed by catalase. Enzymes catalyse almost all reactions in body. There are many different types of enzymes and each is ...
Name: ENZYME FUNCTION LAB 9 PURPOSE To explore the role of
... Enzymes are some of the most important kinds of molecules found in living cells. Cells could not function without enzymes. They control the chemical reactions of the cells. To understand how enzymes work, you will be observing some simple chemical reactions with hydrogen peroxide. you may have hydro ...
... Enzymes are some of the most important kinds of molecules found in living cells. Cells could not function without enzymes. They control the chemical reactions of the cells. To understand how enzymes work, you will be observing some simple chemical reactions with hydrogen peroxide. you may have hydro ...
Exploration Activity: Enzymes
... Below you’ll find graphs that show how pH affects four different enzymes. For each, explain the trend you see, and where the enzyme is most efficient, shown by the optimum, or best pH. I. Chymotrypsin (enzyme that digests proteins):: ...
... Below you’ll find graphs that show how pH affects four different enzymes. For each, explain the trend you see, and where the enzyme is most efficient, shown by the optimum, or best pH. I. Chymotrypsin (enzyme that digests proteins):: ...
Factors Affecting the Rate of Enzyme Reaction in Liver
... too slowly to be useful. Enzymes speed up these reactions by bringing the reactants into close proximity and helping their interaction. Liver contains a specific enzyme called catalase. When hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is added to liver, a chemical reaction occurs which results in the products of oxyge ...
... too slowly to be useful. Enzymes speed up these reactions by bringing the reactants into close proximity and helping their interaction. Liver contains a specific enzyme called catalase. When hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is added to liver, a chemical reaction occurs which results in the products of oxyge ...
Enzyme Wi(Re) - Honors Bio
... a. In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme b. In noncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to the allosteric site of the substrate c. In irreversible inhibition, a poison binds to the enzyme so that it can never work again d. Most inhibitors act in a reve ...
... a. In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme b. In noncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to the allosteric site of the substrate c. In irreversible inhibition, a poison binds to the enzyme so that it can never work again d. Most inhibitors act in a reve ...
Essential Questions: What is an enzyme? How do enzymes work
... – Extreme temperature and pH can change the shape of the enzyme, affecting the binding “active” site. – Recall: What is the term for destroying an enzymes (or any protein)? – Enzymes in our body work best at 37°C (98.6°F) and at a pH between 6.5 to 7.5. ...
... – Extreme temperature and pH can change the shape of the enzyme, affecting the binding “active” site. – Recall: What is the term for destroying an enzymes (or any protein)? – Enzymes in our body work best at 37°C (98.6°F) and at a pH between 6.5 to 7.5. ...
Enzymes - Mr. hawkins
... Enzyme has a particular shape into which the substrate or substrates fit exactly. This is often referred to as the ‘lock and key’ hypothesis where the substrate is imagined being like a key whose shape is complementary to the enzyme or lock. The site where the substrate bonds in the enzyme is know ...
... Enzyme has a particular shape into which the substrate or substrates fit exactly. This is often referred to as the ‘lock and key’ hypothesis where the substrate is imagined being like a key whose shape is complementary to the enzyme or lock. The site where the substrate bonds in the enzyme is know ...
CHAPTER-II ENZYMES
... Some enzymes do not need any additional components to show full activity. However, others require non-protein molecules called cofactors to be bound for activity. Cofactors can be either inorganic (e.g., metal ions and iron-sulfur clusters) or organic compounds (e.g., flavin and heme). Organic cofac ...
... Some enzymes do not need any additional components to show full activity. However, others require non-protein molecules called cofactors to be bound for activity. Cofactors can be either inorganic (e.g., metal ions and iron-sulfur clusters) or organic compounds (e.g., flavin and heme). Organic cofac ...
Fuel for the Future
... the MnO2 itself is broken down to form the oxygen ). Enzymes as catalysts are capable of increasing the reaction rate by as much as 1020. They are able to do this in many ways: reduce the activation energy, reduce energy of transition state, temporarily react with the chemical creating a compound fo ...
... the MnO2 itself is broken down to form the oxygen ). Enzymes as catalysts are capable of increasing the reaction rate by as much as 1020. They are able to do this in many ways: reduce the activation energy, reduce energy of transition state, temporarily react with the chemical creating a compound fo ...
Bchm2000_P3 v1 - U of L Class Index
... (5) The enyzme urease enhances the rate of urea hydrolysis at pH 8.0 and 20°C by a factor of 1014. If a given quantity of urease can completely hydrolyze a given quantity of urea in 5.0 min at 20°C and pH 8.0, how long would it take for this amount of urea to be hydrolyzed under the same conditions ...
... (5) The enyzme urease enhances the rate of urea hydrolysis at pH 8.0 and 20°C by a factor of 1014. If a given quantity of urease can completely hydrolyze a given quantity of urea in 5.0 min at 20°C and pH 8.0, how long would it take for this amount of urea to be hydrolyzed under the same conditions ...
Immobilization of Enzymes
... spectacular combination of hydrophobic effects and the critical formation of several salt-linkages per enzyme molecule ...
... spectacular combination of hydrophobic effects and the critical formation of several salt-linkages per enzyme molecule ...
Enzyme Control of Metabolic Pathways
... Enzyme Control of Metabolic Pathways It is essential that the various biochemical processes occurring within an organism are adaptable. This means that the rates of biochemical reactions need to vary in response to change. In humans, for instance, these reactions need to cope with a sudden abundance ...
... Enzyme Control of Metabolic Pathways It is essential that the various biochemical processes occurring within an organism are adaptable. This means that the rates of biochemical reactions need to vary in response to change. In humans, for instance, these reactions need to cope with a sudden abundance ...
Bio 114: Virtual Enzyme Lab
... http://bioweb.wku.edu/courses/Biol120/Web/enzyme1b.asp Use Internet Explorer 8. Why is it important to let the test tubes “acclimate” to the temperature of the ...
... http://bioweb.wku.edu/courses/Biol120/Web/enzyme1b.asp Use Internet Explorer 8. Why is it important to let the test tubes “acclimate” to the temperature of the ...
j-catalysts-2
... A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being _______________. Catalysts appear to work in two different ways. They either stabilize the ________________________ state and as a result lower the activation energy of an elementary step, but otherwise leave the reaction mec ...
... A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being _______________. Catalysts appear to work in two different ways. They either stabilize the ________________________ state and as a result lower the activation energy of an elementary step, but otherwise leave the reaction mec ...
Crystal Structures of Human Glutaminyl Cyclase, an Enzyme
... may be related to several pathological processes, such as osteoporosis and amyloidotic diseases. This N-terminal cyclization reaction, once thought to proceed spontaneously, is greatly facilitated by the enzyme glutaminyl cyclase (QC). To probe this important but poorly understood modification, we h ...
... may be related to several pathological processes, such as osteoporosis and amyloidotic diseases. This N-terminal cyclization reaction, once thought to proceed spontaneously, is greatly facilitated by the enzyme glutaminyl cyclase (QC). To probe this important but poorly understood modification, we h ...
Name: Date: ______ Per: ______ Chemical Reactions and
... B Most enzymes can catalyze many different reactions. C An enzyme binds to a specific substrate (reactant) for the reaction catalyzed. D Enzymes are transported to specific substrates (reactants) by ribosomes. 14. Some snake venoms are harmful because they contain enzymes that destroy blood cells or ...
... B Most enzymes can catalyze many different reactions. C An enzyme binds to a specific substrate (reactant) for the reaction catalyzed. D Enzymes are transported to specific substrates (reactants) by ribosomes. 14. Some snake venoms are harmful because they contain enzymes that destroy blood cells or ...
Enzyme Inhibition
... other substrates from binding As a result, folic acid is not longer made and the bacterial cell dies Since animal cells don’t make folic acid themselves, they do not ...
... other substrates from binding As a result, folic acid is not longer made and the bacterial cell dies Since animal cells don’t make folic acid themselves, they do not ...