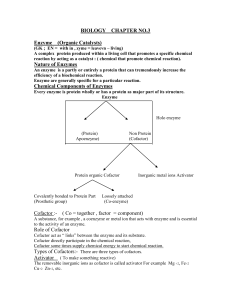
Nature of Enzymes
... collision with each other and with enzyme. Above optimum, further supply of heat energy increases the vibrations of atom making enzyme molecules. Such strong vibrations destroy globular structure of enzymes. Enzyme Denaturation :- Any change in molecular structure or chemical composition of enzyme b ...
... collision with each other and with enzyme. Above optimum, further supply of heat energy increases the vibrations of atom making enzyme molecules. Such strong vibrations destroy globular structure of enzymes. Enzyme Denaturation :- Any change in molecular structure or chemical composition of enzyme b ...
Enzyme Kinetics
... urease catalyzed reaction occurs at a rate of 3 x 104 s-1 20 oC (half life of 23 microseconds) which represents close to 1014-fold acceleration in rate. ...
... urease catalyzed reaction occurs at a rate of 3 x 104 s-1 20 oC (half life of 23 microseconds) which represents close to 1014-fold acceleration in rate. ...
BIOLOGY -ENZYME LAB- (Effect of temperature)
... • In this experiment we used urease enzyme in soya bean to breakdown urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide. • We can detect the presence of ammonia by using red cabbage indicator. ...
... • In this experiment we used urease enzyme in soya bean to breakdown urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide. • We can detect the presence of ammonia by using red cabbage indicator. ...
Lecture 11 Enzymes: Kinetics
... complementary to groups it is binding (best complementarity may be present in ES complex but NOT in free enzyme -- induced fit) • Enzymes flexible -- conformational changes can occur when substrate binds during the reaction, to get maximal complementarity to the transition state. • induced fit: conf ...
... complementary to groups it is binding (best complementarity may be present in ES complex but NOT in free enzyme -- induced fit) • Enzymes flexible -- conformational changes can occur when substrate binds during the reaction, to get maximal complementarity to the transition state. • induced fit: conf ...
Name
... Enzymes are made from amino acids. When an enzyme is formed, it is made by stringing together between 100 and 1,000 amino acids in a very specific and unique order. The chain of amino acids then folds into a unique shape. That shape allows the enzyme to carry out specific chemical reactions -- an en ...
... Enzymes are made from amino acids. When an enzyme is formed, it is made by stringing together between 100 and 1,000 amino acids in a very specific and unique order. The chain of amino acids then folds into a unique shape. That shape allows the enzyme to carry out specific chemical reactions -- an en ...
The following Text was taken from the Student Lab Manual for
... This cycle begins when an enzyme (E) binds to a substrate (S) to form an enzymesubstrate complex (ES). Enzyme-substrate complexes typically form as a result of weak bonds between amino acids in the active site and atoms of the substrate. Depending on the type of reaction catalyzed by the enzyme, the ...
... This cycle begins when an enzyme (E) binds to a substrate (S) to form an enzymesubstrate complex (ES). Enzyme-substrate complexes typically form as a result of weak bonds between amino acids in the active site and atoms of the substrate. Depending on the type of reaction catalyzed by the enzyme, the ...
Vanadium bromoperoxidase, an example of a peroxo
... Maruf Khan and Martha S. Reynolds Colgate University A peroxometal complex is involved in the oxidation of bromide by vanadium bromoperoxidase, an enzyme found in seaweed. The resulting hypobromite ion combines with an organic molecule to form an irritant that protects against bacteria, fungi and pr ...
... Maruf Khan and Martha S. Reynolds Colgate University A peroxometal complex is involved in the oxidation of bromide by vanadium bromoperoxidase, an enzyme found in seaweed. The resulting hypobromite ion combines with an organic molecule to form an irritant that protects against bacteria, fungi and pr ...
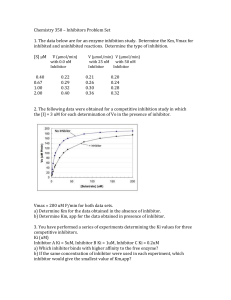
Chemistry 350 – Inhibitors Problem Set 1. The data below are for an
... the apparent Km values for phenylalanine were 3.5 x 10-4 M for the full-term infant and 3.8 x 10-4 M for the adult preparations, respectively. For the synthetic cofactor, apparent Km values were 6.8 x 10-5 M and 6.6 x 10-5 M, respectively . The activity of the enzyme was assayed, by using various co ...
... the apparent Km values for phenylalanine were 3.5 x 10-4 M for the full-term infant and 3.8 x 10-4 M for the adult preparations, respectively. For the synthetic cofactor, apparent Km values were 6.8 x 10-5 M and 6.6 x 10-5 M, respectively . The activity of the enzyme was assayed, by using various co ...
lecture notes-enzyme-web
... - the binding force between enzyme and carrier is so strong that no leakage of the enzymes occurs. ...
... - the binding force between enzyme and carrier is so strong that no leakage of the enzymes occurs. ...
Enzyme Lab - marric.us
... INTRODUCTION: What would happen to your cells if they made a poisonous chemical as a byproduct? You might think that they would die. In fact, your cells are always making poisonous chemicals. They do not die because your cells use enzymes to break down these poisonous chemicals into harmless substan ...
... INTRODUCTION: What would happen to your cells if they made a poisonous chemical as a byproduct? You might think that they would die. In fact, your cells are always making poisonous chemicals. They do not die because your cells use enzymes to break down these poisonous chemicals into harmless substan ...
Product:
... Triterpene Glycosides inhibit cytochrome P450 3A enzymes. They enhance the absorption of drug-like compounds and prevent their breakdown in the liver. Physiological Mechanism: During the inhibition of the cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) enzymes, triterpene glycosides lose their glycoside portion due to ...
... Triterpene Glycosides inhibit cytochrome P450 3A enzymes. They enhance the absorption of drug-like compounds and prevent their breakdown in the liver. Physiological Mechanism: During the inhibition of the cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) enzymes, triterpene glycosides lose their glycoside portion due to ...
Enzyme Inhibition
... The effect of enzyme inhibition 2. Non-competitive: These are not influenced by the concentration of the substrate. It inhibits by binding irreversibly to the enzyme but not at the active site Examples Cyanide combines with the Iron in the enzymes cytochrome oxidase Heavy metals, Ag or Hg, comb ...
... The effect of enzyme inhibition 2. Non-competitive: These are not influenced by the concentration of the substrate. It inhibits by binding irreversibly to the enzyme but not at the active site Examples Cyanide combines with the Iron in the enzymes cytochrome oxidase Heavy metals, Ag or Hg, comb ...
Enzymes: Molecules That Speed Up Reactions - juan-roldan
... which is the energy required to break down existing bonds between atoms Enzymes speed up two types of reactions: 1. Exergonic Reactions 2. Endergonic Reactions ...
... which is the energy required to break down existing bonds between atoms Enzymes speed up two types of reactions: 1. Exergonic Reactions 2. Endergonic Reactions ...
Catalytic mechanism of the inverting N
... Ring distortions induced by these enzymes in ground states have been assumed to be crucial for their reaction mechanism. As the acceptor substrate binds in the active site, the catalytic reaction begins and the GlcNAc residue becomes distorted while moving away from the nucleotide moiety. These subt ...
... Ring distortions induced by these enzymes in ground states have been assumed to be crucial for their reaction mechanism. As the acceptor substrate binds in the active site, the catalytic reaction begins and the GlcNAc residue becomes distorted while moving away from the nucleotide moiety. These subt ...
Pinpointing dynamic coupling in enzymes for efficient drug design
... TST has underpinned the design of transition state analogues for enzyme inhibition and the creation of catalytic antibodies. The rationale behind transition state analogues is that if enzymes have evolved to bind tightly to the transition state of a reaction then a stable but unreactive molecule tha ...
... TST has underpinned the design of transition state analogues for enzyme inhibition and the creation of catalytic antibodies. The rationale behind transition state analogues is that if enzymes have evolved to bind tightly to the transition state of a reaction then a stable but unreactive molecule tha ...
Enzymes-1 C2
... way – but these reactions are very slow because of the activation energy barrier. The enzymes open a certain reaction route. ...
... way – but these reactions are very slow because of the activation energy barrier. The enzymes open a certain reaction route. ...
... through their perturbed ionization behavior. Predictions often include not only the residues that directly contact the substrate but also residues farther away. These distal residues may not contact the substrate directly, yet they can still contribute greatly to catalysis, as we have verified th ...
AP Biology
... This activity is designed to give you a hands-on experience of enzyme kinetics. In this activity, one member of the group will act as a protease, an enzyme that digests proteins. The “enzyme” student will act as many proteases do: she will break a peptide bond following a specific amino acid. Peptid ...
... This activity is designed to give you a hands-on experience of enzyme kinetics. In this activity, one member of the group will act as a protease, an enzyme that digests proteins. The “enzyme” student will act as many proteases do: she will break a peptide bond following a specific amino acid. Peptid ...
Chapter Eight: Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Kinetics
... 29. Why would you expect thrombin to have greater substrate specificity than trypsin? Answer: Thrombin carries out a specific reaction in blood clotting. Trypsin is responsible for the digestion of proteins in the digestive system, and must be able to cleave thousands of different proteins. Thus, i ...
... 29. Why would you expect thrombin to have greater substrate specificity than trypsin? Answer: Thrombin carries out a specific reaction in blood clotting. Trypsin is responsible for the digestion of proteins in the digestive system, and must be able to cleave thousands of different proteins. Thus, i ...
Slide 1
... amino acids. Enzymes are present in all living cells, where they help converting nutrients into energy and fresh cell material. Enzymes breakdown of food materials into simpler ...
... amino acids. Enzymes are present in all living cells, where they help converting nutrients into energy and fresh cell material. Enzymes breakdown of food materials into simpler ...
Slide 1
... It’s activity is controlled by a complex allosteric regulation. This reaction commits the cells to channel glucose to glycolysis. ATP is the end product of glycolysis as well as it is substrate for PFK-1. In presence of high concentration of ATP, ATP binds to inhibition site of PFK, and thereby decr ...
... It’s activity is controlled by a complex allosteric regulation. This reaction commits the cells to channel glucose to glycolysis. ATP is the end product of glycolysis as well as it is substrate for PFK-1. In presence of high concentration of ATP, ATP binds to inhibition site of PFK, and thereby decr ...
Enzymes & pH - SchoolWorld an Edline Solution
... The rate at which enzymes catalyze their reactions changes as the conditions inside the cell change! Conditions that effect enzyme reaction rate are: 1. Temperature 2. Relative concentrations of enzyme and substrate 3. pH (acidic, basic, neutral) ...
... The rate at which enzymes catalyze their reactions changes as the conditions inside the cell change! Conditions that effect enzyme reaction rate are: 1. Temperature 2. Relative concentrations of enzyme and substrate 3. pH (acidic, basic, neutral) ...
Name: Date: ______ Block: ______ ENZYMES A CATALYST is a
... The seemingly simple act of breaking down food molecules to release energy is actually a series of dozens of chemical reactions. Without enzymes to speed up these reactions, energy would not be released fast enough to support all but the smallest organisms. Enzymes are not changed during the chemica ...
... The seemingly simple act of breaking down food molecules to release energy is actually a series of dozens of chemical reactions. Without enzymes to speed up these reactions, energy would not be released fast enough to support all but the smallest organisms. Enzymes are not changed during the chemica ...