week3-3
... A)- Allosteric activators منشطات: It stabilizes the conformation that has a functional active site. B)- Allosteric inhibitors مثبطات: It stabilizes the conformation that lacks an active site. ...
... A)- Allosteric activators منشطات: It stabilizes the conformation that has a functional active site. B)- Allosteric inhibitors مثبطات: It stabilizes the conformation that lacks an active site. ...
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1
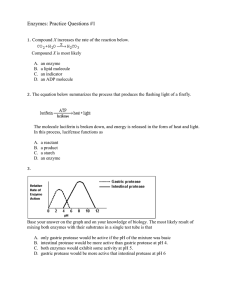
... The graph shows the relative rates of action of four enzymes, A, B, C, and D. A solution with a pH of 6 contains enzyme C and its substrate. If a base is gradually added to this solution, the rate of action of enzyme C would most likely A. B. C. D. ...
... The graph shows the relative rates of action of four enzymes, A, B, C, and D. A solution with a pH of 6 contains enzyme C and its substrate. If a base is gradually added to this solution, the rate of action of enzyme C would most likely A. B. C. D. ...
Catalase Design Lab - Westminster Public Schools Wiki
... Your task: Design a lab experiment that tests the effect of one variable on the enzyme catalase. Background Information: In your body, the enzyme catalase is produced by peroxisomes to break down hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is a toxic waste product that is part of your cell’s metabolism. Ca ...
... Your task: Design a lab experiment that tests the effect of one variable on the enzyme catalase. Background Information: In your body, the enzyme catalase is produced by peroxisomes to break down hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is a toxic waste product that is part of your cell’s metabolism. Ca ...
this lecture as PDF here
... uncatalysed reactions and several times greater than those of the corresponding chemically catalysed reactions. ...
... uncatalysed reactions and several times greater than those of the corresponding chemically catalysed reactions. ...
Enzymes A simulation of Invertase Activity
... functions. This entity is the protein based enzyme. Enzymes can catalyze (accelerate) very specific chemical reactions with incredible precision because of the specific shape assumed by the enzyme protein. The specific sequence of amino acids that compose a protein cause that protein to fold into a ...
... functions. This entity is the protein based enzyme. Enzymes can catalyze (accelerate) very specific chemical reactions with incredible precision because of the specific shape assumed by the enzyme protein. The specific sequence of amino acids that compose a protein cause that protein to fold into a ...
AP Bio – Enzyme Activity This activity is an alternative to the
... Refer to enzyme background found in the “Revised” AP Biology Lab Manual (2011) – lab #13 and / or the “Old” AP Biology Lab Manual (2009) – lab #2. The Activity In this exercise you will study the enzyme catalase, which accelerates the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide (a common product of oxidative met ...
... Refer to enzyme background found in the “Revised” AP Biology Lab Manual (2011) – lab #13 and / or the “Old” AP Biology Lab Manual (2009) – lab #2. The Activity In this exercise you will study the enzyme catalase, which accelerates the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide (a common product of oxidative met ...
Investigating Catalase - churchillcollegebiblio
... Cut a small (1cm-ish X 1cm-ish) square out of filter paper. Using forceps, dip the filter paper square into the enzyme solution, then remove it and drain it on a paper towel. Pour hydrogen peroxide into the plastic vial. Using the forceps, put the filter paper disc into the bottom of the vial of hyd ...
... Cut a small (1cm-ish X 1cm-ish) square out of filter paper. Using forceps, dip the filter paper square into the enzyme solution, then remove it and drain it on a paper towel. Pour hydrogen peroxide into the plastic vial. Using the forceps, put the filter paper disc into the bottom of the vial of hyd ...
Camp 1
... • synthesized/stored as trypsinogen, no enzyme activity. • Active only after a six-amino acid fragment is removed • Removal of amino acid fragment changes primary + tertiary structure, active form. ...
... • synthesized/stored as trypsinogen, no enzyme activity. • Active only after a six-amino acid fragment is removed • Removal of amino acid fragment changes primary + tertiary structure, active form. ...
What are enzymes and how do they work
... 12. How does reaction speed change when the active site is changed? It slows down ...
... 12. How does reaction speed change when the active site is changed? It slows down ...
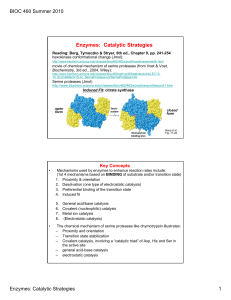
Lectures 13-14 Enzymes: Catalytic Strategies
... • structure presumed similar to that of transition state for its formation and breakdown, with negatively charged "carbonyl" oxygen (not a carbonyl group anymore), an OXYANION •The "oxyanion hole", an area in the active site of serine proteases that binds the transition state particularly tightly. • ...
... • structure presumed similar to that of transition state for its formation and breakdown, with negatively charged "carbonyl" oxygen (not a carbonyl group anymore), an OXYANION •The "oxyanion hole", an area in the active site of serine proteases that binds the transition state particularly tightly. • ...
Enzymes! - Mrs. Ahrens` Science Site
... therefore enzymes bind to substrates based on shape. – the substrates are based on the complementary shape of their specific enzyme. ...
... therefore enzymes bind to substrates based on shape. – the substrates are based on the complementary shape of their specific enzyme. ...
enzymes
... The fourth level of protein structure, quaternary structure, consists of the interactions between different polypeptide chains in proteins composed of more than one polypeptide. Hemoglobin, for example, is composed of four polypeptide chains held together by the same types of interactions that maint ...
... The fourth level of protein structure, quaternary structure, consists of the interactions between different polypeptide chains in proteins composed of more than one polypeptide. Hemoglobin, for example, is composed of four polypeptide chains held together by the same types of interactions that maint ...
Enzymes
... Metabolic pathways are often localized in cell • Cellular structures organize and concentrate components of enzymatic pathways ...
... Metabolic pathways are often localized in cell • Cellular structures organize and concentrate components of enzymatic pathways ...
Enzymes: Catalytic Strategies
... reactive intermediate in the reaction that was supposed to transfer its reactive group to another substrate. 3. TIGHT TRANSITION STATE BINDING • used to be called "strain and distortion" • Enzyme binds transition state very tightly, tighter than substrate (stabilizes T.S.) • Free energy of transitio ...
... reactive intermediate in the reaction that was supposed to transfer its reactive group to another substrate. 3. TIGHT TRANSITION STATE BINDING • used to be called "strain and distortion" • Enzyme binds transition state very tightly, tighter than substrate (stabilizes T.S.) • Free energy of transitio ...
Course Notes
... ‘emergency energy’. The amino acids are deaminated by removing the amine group. This leaves a carbohydrate like substance that can be used as a substrate to produce ATP. The waste product NH3 (ammonia) is toxic and is converted to urea in the liver. Both NH3 and urea need to excreted from the body i ...
... ‘emergency energy’. The amino acids are deaminated by removing the amine group. This leaves a carbohydrate like substance that can be used as a substrate to produce ATP. The waste product NH3 (ammonia) is toxic and is converted to urea in the liver. Both NH3 and urea need to excreted from the body i ...
Biochemistry 3100 Sample Problems Binding proteins, Kinetics & Catalysis eg
... carboxylate containing residue (Glu most likely) and His. Note: the pkas can be determined by extrapolating the slope of each side of the bell curve and the plateau region. The intersection between the extrapolated slope and plateau lines gives the pkas. 13b – If the catalytic residues had pKa's th ...
... carboxylate containing residue (Glu most likely) and His. Note: the pkas can be determined by extrapolating the slope of each side of the bell curve and the plateau region. The intersection between the extrapolated slope and plateau lines gives the pkas. 13b – If the catalytic residues had pKa's th ...
Enzymes and Protein Structure
... - Enzyme types by reaction catalyzed: - Oxidoreductase (oxidation/reduction, e.g. HRP) - Transferase (transfer of a reactive group, e.g. DNA methyltransferase) - Hydrolase (hydrolysis of a bond, e.g. proteases) - Lyase (non-oxidative, non-hydrolytic bond making/breaking, e.g. adenylyl cyclase (cAMP) ...
... - Enzyme types by reaction catalyzed: - Oxidoreductase (oxidation/reduction, e.g. HRP) - Transferase (transfer of a reactive group, e.g. DNA methyltransferase) - Hydrolase (hydrolysis of a bond, e.g. proteases) - Lyase (non-oxidative, non-hydrolytic bond making/breaking, e.g. adenylyl cyclase (cAMP) ...
What Are Enzymes?
... your hands with a napkin. 5. Take another bite from the opposite side of your apple. 6. Set your apple aside. ...
... your hands with a napkin. 5. Take another bite from the opposite side of your apple. 6. Set your apple aside. ...
Catalysts in biochemical reactions
... reactions. On their Characteristics is that they increases the rate of reactions by several orders of magnitude A very dramatic example of enzyme kinetics is given by decomposition of hydrogen Peroxide. Enzymes are usually protein molecules that manipulate other molecules — the enzymes' substrates. ...
... reactions. On their Characteristics is that they increases the rate of reactions by several orders of magnitude A very dramatic example of enzyme kinetics is given by decomposition of hydrogen Peroxide. Enzymes are usually protein molecules that manipulate other molecules — the enzymes' substrates. ...
Amino Acids Proteins, and Enzymes
... • enzyme structure is flexible, not rigid. • enzyme and substrate adjust the shape of the active site to bind substrate. • the range of substrate specificity increases. • shape changes improve catalysis during reaction. ...
... • enzyme structure is flexible, not rigid. • enzyme and substrate adjust the shape of the active site to bind substrate. • the range of substrate specificity increases. • shape changes improve catalysis during reaction. ...
Bio1A Unit 1-5 Metabolism Notes File
... • Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed • The first law is also called the principle of conservation of ...
... • Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed • The first law is also called the principle of conservation of ...