Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Practice
... **Choose one question to complete for this section. Use bottom portion for graph** ...
... **Choose one question to complete for this section. Use bottom portion for graph** ...
Effect aliphatic alcohols on catalytic activity of bovine pancreatic α
... interest for nonaqueous enzymology, an innovation-promising scientific area. Nonaqueous organic media provide the possibility of conducting industrially important synthetic reactions that do not occur in aqueous media (peptide synthesis and esterification). The enzymatic catalysis in organic solvent ...
... interest for nonaqueous enzymology, an innovation-promising scientific area. Nonaqueous organic media provide the possibility of conducting industrially important synthetic reactions that do not occur in aqueous media (peptide synthesis and esterification). The enzymatic catalysis in organic solvent ...
Enzymes: Introduction • Enzymes are catalysts which speed up the
... Holoenzyme. Proteins in enzymes are usually globular. Their folded confirmation creates an area called as active site. The nature and arrangement of amino acids in the active site make it specific for only one type of substrate. The intermolecular and intramolecular bonds that hold proteins in t ...
... Holoenzyme. Proteins in enzymes are usually globular. Their folded confirmation creates an area called as active site. The nature and arrangement of amino acids in the active site make it specific for only one type of substrate. The intermolecular and intramolecular bonds that hold proteins in t ...
ENZYMES A CATALYST is a substance that speeds up a chemical
... The seemingly simple act of breaking down food molecules to release energy is actually a series of dozens of chemical reactions. Without enzymes to speed up these reactions, energy would not be released fast enough to support all but the smallest organisms. Enzymes are not changed during the chemica ...
... The seemingly simple act of breaking down food molecules to release energy is actually a series of dozens of chemical reactions. Without enzymes to speed up these reactions, energy would not be released fast enough to support all but the smallest organisms. Enzymes are not changed during the chemica ...
Page 1 Enzymes OK….so now we`ve done all of that Chemistry stuff
... An organism’s metabolism consists of thousands of different reactions and each one has a different catalyst or enzyme Metabolism consists of hundreds of reactions linked together where the product from one reaction is the substrate of the next ...
... An organism’s metabolism consists of thousands of different reactions and each one has a different catalyst or enzyme Metabolism consists of hundreds of reactions linked together where the product from one reaction is the substrate of the next ...
Biology STAAR EOC Review Sheets Alief
... Extreme Temperature are the most dangerous - high temps may denature (unfold) the enzyme. pH (most like 6 - 8 pH near neutral) Ionic concentration (salt ions) ...
... Extreme Temperature are the most dangerous - high temps may denature (unfold) the enzyme. pH (most like 6 - 8 pH near neutral) Ionic concentration (salt ions) ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... 10) What is the usual fuel for the brain under normal conditions? What ensures that the brain will be adequately supplied with this fuel? Under starvation conditions, what other fuel can the brain utilize. 11) What are the major fuels for muscle? At rest, what fuel is utilized? Why does this make se ...
... 10) What is the usual fuel for the brain under normal conditions? What ensures that the brain will be adequately supplied with this fuel? Under starvation conditions, what other fuel can the brain utilize. 11) What are the major fuels for muscle? At rest, what fuel is utilized? Why does this make se ...
Enzymes what are they - Laurel County Schools
... The active site involves a small number of key residues that actually bind thesubstrates The rest of the protein structure is needed to maintain these residues in position ...
... The active site involves a small number of key residues that actually bind thesubstrates The rest of the protein structure is needed to maintain these residues in position ...
Enzyme Kinetics II
... iii. That was the theory; however, over time, we began to figure out that the enzyme’s active site is mobile 1. In most cases, there are histidines in the active site usually in multiple conformations a. We call them side-chain rotamers b. They can be in many different positions 2. Once the substrat ...
... iii. That was the theory; however, over time, we began to figure out that the enzyme’s active site is mobile 1. In most cases, there are histidines in the active site usually in multiple conformations a. We call them side-chain rotamers b. They can be in many different positions 2. Once the substrat ...
Case 39 Inhibition of Alcohol Dehydrogenase Focus concept The
... metabolism of ethanol in the alcoholic beverages we consume. Five different isozymes of ADH have been identified, and it has been shown that the enzyme has a rather broad substrate specificity and can oxidize aldehydes as well as primary and secondary alcohols. For example, ADH can also oxidize meth ...
... metabolism of ethanol in the alcoholic beverages we consume. Five different isozymes of ADH have been identified, and it has been shown that the enzyme has a rather broad substrate specificity and can oxidize aldehydes as well as primary and secondary alcohols. For example, ADH can also oxidize meth ...
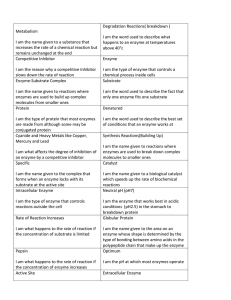
Chapter 2 I am - Mrs Smith`s Biology
... enzyme whose shape is determined by the type of bonding between amino acids in the polypeptide chain that make up the enzyme Optimum I am the pH at which most enzymes operate Extracellular Enzyme ...
... enzyme whose shape is determined by the type of bonding between amino acids in the polypeptide chain that make up the enzyme Optimum I am the pH at which most enzymes operate Extracellular Enzyme ...
Proteins and Nucleic Acids
... a substance on which an enzyme acts during a chemical reaction *enzymes act only on specific substrates ...
... a substance on which an enzyme acts during a chemical reaction *enzymes act only on specific substrates ...
An introduction to enzyme structure and function
... A more recent explanation to the fitting of enzymes is the induced-fit hypothesis. This hypothesis still states that one substrate fits one active site, this is scientific fact. But this hypothesis suggests that the enzyme molecule slightly changes shape when it collides with substrate, making the a ...
... A more recent explanation to the fitting of enzymes is the induced-fit hypothesis. This hypothesis still states that one substrate fits one active site, this is scientific fact. But this hypothesis suggests that the enzyme molecule slightly changes shape when it collides with substrate, making the a ...
Enzymes
... catalysts used by cells to initiate chemical reactions. Cells can regulate which reactions occur and how quickly by regulating which enzymes are present. ...
... catalysts used by cells to initiate chemical reactions. Cells can regulate which reactions occur and how quickly by regulating which enzymes are present. ...
Enzymes - SBI4UAssumption
... products have less free energy than that of the reactants and energy is given off from the system. ...
... products have less free energy than that of the reactants and energy is given off from the system. ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 03
... rate of particular chemical reactions. The basis for enzyme specificity is molecular shape. The enzyme is able to lower the activation energy of a reaction by holding substrate molecules in particular orientations that lead to much increased reaction rates. Enzymes are proteins produced by the trans ...
... rate of particular chemical reactions. The basis for enzyme specificity is molecular shape. The enzyme is able to lower the activation energy of a reaction by holding substrate molecules in particular orientations that lead to much increased reaction rates. Enzymes are proteins produced by the trans ...
Enzyme Catalysis Introduction
... disrupted. Likewise, as the pH is raised, the enzymes will lose H+ ions and eventually lose its active shape. Many of the enzymes function properly in the neutral pH range and are denatured at either an extremely high or low pH. Some enzymes, such as pepsin, which acts in the human stomach where th ...
... disrupted. Likewise, as the pH is raised, the enzymes will lose H+ ions and eventually lose its active shape. Many of the enzymes function properly in the neutral pH range and are denatured at either an extremely high or low pH. Some enzymes, such as pepsin, which acts in the human stomach where th ...
Chemistry 326 Name_____________________ Fall 2009 Check
... _____a. PLP/PMP act through a Schiff base mechanism. _____b. NAD contains a sugar alcohol. _____c. Lipoamide can exist in an oxidized or reduced form of the disulfide bridge. _____d. NAD works in redox reactions that involve alkyl groups. _____e. Tetrohydrofolate carries the most oxidized form of ca ...
... _____a. PLP/PMP act through a Schiff base mechanism. _____b. NAD contains a sugar alcohol. _____c. Lipoamide can exist in an oxidized or reduced form of the disulfide bridge. _____d. NAD works in redox reactions that involve alkyl groups. _____e. Tetrohydrofolate carries the most oxidized form of ca ...
The enzyme
... thus has to be catalyzed”. • Isolation, purification and physico-chemical characterization of enzymes would be important for understanding the nature of life. • Without catalysis, the chemical reactions needed to sustain life could not occur on a ...
... thus has to be catalyzed”. • Isolation, purification and physico-chemical characterization of enzymes would be important for understanding the nature of life. • Without catalysis, the chemical reactions needed to sustain life could not occur on a ...
enzyme
... Active sites are restricted regions of the enzyme molecule that bind to the substrate The active site is typically a pocket or a groove on the surface of the protein ...
... Active sites are restricted regions of the enzyme molecule that bind to the substrate The active site is typically a pocket or a groove on the surface of the protein ...
Department of Chemistry - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... (d) Not only do nucleic acids require monovalent and/or divalent cations to stabilize their structures but the specific cation is important in many cases. ...
... (d) Not only do nucleic acids require monovalent and/or divalent cations to stabilize their structures but the specific cation is important in many cases. ...
Cell Physiology
... Binding of a molecule to a site other than the active site may result in an enzyme conformational change that either turns the enzyme “on or off” If the modulator is bound by non-covalent forces; it is allosteric modulation (the most common type); if bound covalently, it is covalent modulation (wh ...
... Binding of a molecule to a site other than the active site may result in an enzyme conformational change that either turns the enzyme “on or off” If the modulator is bound by non-covalent forces; it is allosteric modulation (the most common type); if bound covalently, it is covalent modulation (wh ...
Enzymes
... An enzyme is not only substrate specific, but it can only catalyze a reaction in ONE direction. So, it either builds up, or breaks down …but not both ...
... An enzyme is not only substrate specific, but it can only catalyze a reaction in ONE direction. So, it either builds up, or breaks down …but not both ...