Ancient Rome Review Scramble Italy is in the of the Mediterranean
... 1. Italy is in the __________________ of the Mediterranean Sea west of Greece, and Rome is located just inland on the Tiber River in west-central Italy. NECTRE 2. The Romans copied many things from the _________________, such as their gods and architectural styles. EGKRSE 3. Most Roman officials wer ...
... 1. Italy is in the __________________ of the Mediterranean Sea west of Greece, and Rome is located just inland on the Tiber River in west-central Italy. NECTRE 2. The Romans copied many things from the _________________, such as their gods and architectural styles. EGKRSE 3. Most Roman officials wer ...
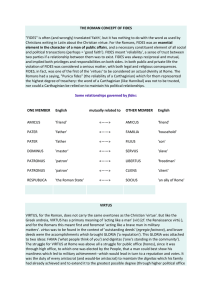
The Roman Republic - Mr. Challis
... Constantine—Roman emperor battles for control of Rome in A.D. 312. He has a vision of a cross—the Christian symbol— and places it on soldiers’ shields. He believes Christian God helped him win the battle and legalizes Christianity. In A.D. 380 the Emperor Theodosius makes Christianity the reli ...
... Constantine—Roman emperor battles for control of Rome in A.D. 312. He has a vision of a cross—the Christian symbol— and places it on soldiers’ shields. He believes Christian God helped him win the battle and legalizes Christianity. In A.D. 380 the Emperor Theodosius makes Christianity the reli ...
Classical Roman Writers on Race Mixing in
... “One certain example is that of the renowned boxer Nicaeus, born at Byzantium, whose mother was the daughter of adultery with a Negro. Her complexion was no different from that of the others [other white women], but her son Nicaeus appeared like his Negro grandfather.” - Naturalis Historia VII.12.51 ...
... “One certain example is that of the renowned boxer Nicaeus, born at Byzantium, whose mother was the daughter of adultery with a Negro. Her complexion was no different from that of the others [other white women], but her son Nicaeus appeared like his Negro grandfather.” - Naturalis Historia VII.12.51 ...
Roman_Style_-_Presentation
... The Etruscan Period - 700 to 500 BCE – 783 BCE: Rome Founded Between the 7th and 6th centuries BCE, the central regions of the Italian peninsula were dominated by the Etruscans, a Bronze Age people noted for their expert metalwork, who maintained trading ties all through the Mediterranean, including ...
... The Etruscan Period - 700 to 500 BCE – 783 BCE: Rome Founded Between the 7th and 6th centuries BCE, the central regions of the Italian peninsula were dominated by the Etruscans, a Bronze Age people noted for their expert metalwork, who maintained trading ties all through the Mediterranean, including ...
Roman virtues - WordPress.com
... VIRTUS, for the Roman, does not carry the same overtones as the Christian 'virtue'. But like the Greek andreia, VIRTUS has a primary meaning of 'acting like a man' (vir) [cf. the Renaissance virtù ), and for the Romans this meant first and foremost 'acting like a brave man in military matters'. virt ...
... VIRTUS, for the Roman, does not carry the same overtones as the Christian 'virtue'. But like the Greek andreia, VIRTUS has a primary meaning of 'acting like a man' (vir) [cf. the Renaissance virtù ), and for the Romans this meant first and foremost 'acting like a brave man in military matters'. virt ...
Polybian Romans - Aventine Miniatures
... alae, the above would be doubled so that two boxwidths of cavalry on each wing (six units) would lank eight box-widths of infantry (twenty-eight units). he infantry are deployed with a screen of skirmishing velites to the fore, screening the hastati and principles who will bear the brunt of the ight ...
... alae, the above would be doubled so that two boxwidths of cavalry on each wing (six units) would lank eight box-widths of infantry (twenty-eight units). he infantry are deployed with a screen of skirmishing velites to the fore, screening the hastati and principles who will bear the brunt of the ight ...
Early Roman Civilization
... The Early Republic (509-264 BCE): division of society into two classes, the aristocratic patricians and the plebeians The Middle Republic (264-133 BCE): the challenge of Carthage; the Punic Wars (264-146 BCE). The Late Republic (133-31 BCE): the rise of the equestrian order, a social class who gaine ...
... The Early Republic (509-264 BCE): division of society into two classes, the aristocratic patricians and the plebeians The Middle Republic (264-133 BCE): the challenge of Carthage; the Punic Wars (264-146 BCE). The Late Republic (133-31 BCE): the rise of the equestrian order, a social class who gaine ...
Name________________________Period
... He got rid of religion. c. He built temples and had his architects copy Greek buildings. How did Augustus strengthen the law? a. He limited his own power. b. He got rid of the military. c. He took over all the power. How did Augustus support the Roman Army? a. He established a special treasury for t ...
... He got rid of religion. c. He built temples and had his architects copy Greek buildings. How did Augustus strengthen the law? a. He limited his own power. b. He got rid of the military. c. He took over all the power. How did Augustus support the Roman Army? a. He established a special treasury for t ...
Overview of Roman Civilization, 509 BC
... the reformers themselves. The most famous of these were the Gracchus brothers, Tiberius and Gaius. Both men attempted to limit the size of estates and to grant a larger share of government to the equites, a class of businessmen. But the interests of the wealthy proved too strong. Elected tribune in ...
... the reformers themselves. The most famous of these were the Gracchus brothers, Tiberius and Gaius. Both men attempted to limit the size of estates and to grant a larger share of government to the equites, a class of businessmen. But the interests of the wealthy proved too strong. Elected tribune in ...
Barbarians: The Goths
... 4. The important thing to remember about the late Roman Empire is that no emperor ever turned down a ready supply of troops (tradition dating back to the Roman Confederation). 5. The Goths adopted Christianity (tied to the traditional insistence on the worship of the gods of the Romans/the Roman sta ...
... 4. The important thing to remember about the late Roman Empire is that no emperor ever turned down a ready supply of troops (tradition dating back to the Roman Confederation). 5. The Goths adopted Christianity (tied to the traditional insistence on the worship of the gods of the Romans/the Roman sta ...
Roman Daily Life
... in everyday society. In Rome’s early history, a woman’s husband maintained complete control over her life. In fact, woman could not even make a simple suggestion to her husband. In this time, it would have been absurd to think a woman could vote or participate in government, as these were both restr ...
... in everyday society. In Rome’s early history, a woman’s husband maintained complete control over her life. In fact, woman could not even make a simple suggestion to her husband. In this time, it would have been absurd to think a woman could vote or participate in government, as these were both restr ...
Chapter 11: Rome and Christianity
... • Antony’s army was defeated, but he fled back to Egypt to be with Cleopatra. • Marc Antony and Cleopatra committed suicide because they didn’t want to be captured by Octavian. • Marc Antony and Cleopatra’s death made OCTAVIAN the sole ruler of the Roman Empire. ...
... • Antony’s army was defeated, but he fled back to Egypt to be with Cleopatra. • Marc Antony and Cleopatra committed suicide because they didn’t want to be captured by Octavian. • Marc Antony and Cleopatra’s death made OCTAVIAN the sole ruler of the Roman Empire. ...
Ancient Rome
... • The Po River, which is fed by melting snows from the Alps, provides water for the rich farming region of the northern plain. • Another mountain range, the Apennines (AP uh NiNZ), runs down the length of Italy. • Unlike the mountains in Greece, which isolated the city-states, the Apennines were a l ...
... • The Po River, which is fed by melting snows from the Alps, provides water for the rich farming region of the northern plain. • Another mountain range, the Apennines (AP uh NiNZ), runs down the length of Italy. • Unlike the mountains in Greece, which isolated the city-states, the Apennines were a l ...
DID ROME FALL, OR WAS IT PUSHED
... highest bidder. During the next 100 years, Rome had 37 different emperors - 25 of whom were removed from office by assassination. This contributed to the overall weaknesses of the empire. Unemployment During the latter years of the empire farming was done on large estates called latifundia that were ...
... highest bidder. During the next 100 years, Rome had 37 different emperors - 25 of whom were removed from office by assassination. This contributed to the overall weaknesses of the empire. Unemployment During the latter years of the empire farming was done on large estates called latifundia that were ...
Manlius & The Sacred Geese
... When the Gauls were trying to attack the Romans, their armor clattered too loud. This lead to the Sacred Geese in the capital to be awakened. The geese squawked which woke up a Roman soldier name Marcus Manlius. Marcus Manlius looked at down from the wall and saw the Gauls. He then made a Gaul soldi ...
... When the Gauls were trying to attack the Romans, their armor clattered too loud. This lead to the Sacred Geese in the capital to be awakened. The geese squawked which woke up a Roman soldier name Marcus Manlius. Marcus Manlius looked at down from the wall and saw the Gauls. He then made a Gaul soldi ...
Slide 1 - CoursePages
... the Roman empire to the Euphrates River. Upon his return to Rome the Senate refused to acknowledge his accomplishments. In frustration Pompey would from an alliance with Crassus and a talented young politician named Julius Caesar. ...
... the Roman empire to the Euphrates River. Upon his return to Rome the Senate refused to acknowledge his accomplishments. In frustration Pompey would from an alliance with Crassus and a talented young politician named Julius Caesar. ...
Note packet for Rome
... First Punic War: was largely a naval battle over the Straits of Mesina. Rome defeated ___________ and won Sicily, ___________ and _________________ Second Punic War : The Carthaginians sought ___________. The Carthaginian general ________________ led his army, including war elephants across the Pyre ...
... First Punic War: was largely a naval battle over the Straits of Mesina. Rome defeated ___________ and won Sicily, ___________ and _________________ Second Punic War : The Carthaginians sought ___________. The Carthaginian general ________________ led his army, including war elephants across the Pyre ...
The Culture of Ancient Rome
... for Roman citizens Generals who controlled the army became more powerful than Senators ...
... for Roman citizens Generals who controlled the army became more powerful than Senators ...
Cincinnatus Saves Rome There is perhaps no better account of how
... There is perhaps no better account of how the virtues of duty and simplicity enabled good Roman citizens to succeed during the difficulties of the fifth century BCE than Livy's account of Cincinnatus. “The city was thrown into a state of turmoil, and the general alarm was as great as if Rome herself ...
... There is perhaps no better account of how the virtues of duty and simplicity enabled good Roman citizens to succeed during the difficulties of the fifth century BCE than Livy's account of Cincinnatus. “The city was thrown into a state of turmoil, and the general alarm was as great as if Rome herself ...