Punic Wars
... magistrate) of the newly acquired Roman territory •Organized financial reforms to pay back Rome for their prosecution of war •Political enemies accused him in Rome of conspiring with King Antiochus III of Syria •When Romans sent commission to investigate, fled Carthage and went into hiding ...
... magistrate) of the newly acquired Roman territory •Organized financial reforms to pay back Rome for their prosecution of war •Political enemies accused him in Rome of conspiring with King Antiochus III of Syria •When Romans sent commission to investigate, fled Carthage and went into hiding ...
The End of the Empire Rome`s Greatness
... This fighting caused Rome to have at least 23 emperors in 73 years. All but one were assassinated. ...
... This fighting caused Rome to have at least 23 emperors in 73 years. All but one were assassinated. ...
The end of the Empire
... This fighting caused Rome to have at least 23 emperors in 73 years. All but one were assassinated. ...
... This fighting caused Rome to have at least 23 emperors in 73 years. All but one were assassinated. ...
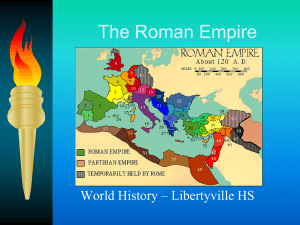
The Roman Empire
... • The independent farming family -- that had been the traditional source of soldiers -- disappeared • Roman commanders would have to build their armies from men from the underclass who tended to give their loyalty, not to the Roman state, but to their commander • This led to generals taking control ...
... • The independent farming family -- that had been the traditional source of soldiers -- disappeared • Roman commanders would have to build their armies from men from the underclass who tended to give their loyalty, not to the Roman state, but to their commander • This led to generals taking control ...
forum
... In Rome's earliest days, the Forum area was a swamp used as a cemetery by the people of surrounding villages. The Etruscans turned these villages into the city of Rome and drained the marshes, probably during the 500's B.C. Residents built shops and temples around the edges of the Forum area. The Fo ...
... In Rome's earliest days, the Forum area was a swamp used as a cemetery by the people of surrounding villages. The Etruscans turned these villages into the city of Rome and drained the marshes, probably during the 500's B.C. Residents built shops and temples around the edges of the Forum area. The Fo ...
Roman Republic
... (you know who you are). No laptops, no cell ‘phones. Your teacher is 800 years old AND a former World of Warcraft widow, and she hates these things. Please note that the graduate students have additional reading and meeting times. Ideally, I’d like to meet for one or two additional hours per week, ...
... (you know who you are). No laptops, no cell ‘phones. Your teacher is 800 years old AND a former World of Warcraft widow, and she hates these things. Please note that the graduate students have additional reading and meeting times. Ideally, I’d like to meet for one or two additional hours per week, ...
Roman Education Rome as a Kingdom: In early Roman days, kids
... learned to spin, weave, and sew. The rich had tutors for the children, but mostly, the kids were taught at home. In early Roman days, kids did not go to school. A Roman boy's education took place at home. If his father could read and write, he taught his son to do the same. The father instructed his ...
... learned to spin, weave, and sew. The rich had tutors for the children, but mostly, the kids were taught at home. In early Roman days, kids did not go to school. A Roman boy's education took place at home. If his father could read and write, he taught his son to do the same. The father instructed his ...
a full transcript of part 2 of the Julius Caesar movie
... Some northern tribes had already begun to develop trading relations with Rome, but the rest of Gaul still had no cities except for their fortified compounds called oppida, and were regarded as “barbarians” by both the Greeks and Romans. Caesar began his campaign in Gaul in 58 bce when the Helvetii b ...
... Some northern tribes had already begun to develop trading relations with Rome, but the rest of Gaul still had no cities except for their fortified compounds called oppida, and were regarded as “barbarians” by both the Greeks and Romans. Caesar began his campaign in Gaul in 58 bce when the Helvetii b ...
The Roman Empire
... cities springing up • Simpler life where people farmed, raised families, and lived their lives ...
... cities springing up • Simpler life where people farmed, raised families, and lived their lives ...
sample
... 753 BCE: The city of Rome is founded by Romulus on the banks of the Tiber River. 507 BCE: The Roman Republic begins after the Romans overthrow the Etruscan kings. 450 BCE: The first Roman code of law, called the Twelve Tables, is published. 387 BCE: The Gauls, from what is now France, attack and plu ...
... 753 BCE: The city of Rome is founded by Romulus on the banks of the Tiber River. 507 BCE: The Roman Republic begins after the Romans overthrow the Etruscan kings. 450 BCE: The first Roman code of law, called the Twelve Tables, is published. 387 BCE: The Gauls, from what is now France, attack and plu ...
13 Rome - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... -although they gave them Latin names, they believe in the Greek gods -they also imitated Greek achievements in science, art, history and literature ...
... -although they gave them Latin names, they believe in the Greek gods -they also imitated Greek achievements in science, art, history and literature ...
Livy – Cincinnatus Leaves his Plow
... put it into action, either by following the example of the Roman or by embracing a different set of values? Topic C: War was nearly a constant in Ancient Rome; the Romans were good at it, and their success made them the greatest power of the Ancient World. But Romans believed that there were right w ...
... put it into action, either by following the example of the Roman or by embracing a different set of values? Topic C: War was nearly a constant in Ancient Rome; the Romans were good at it, and their success made them the greatest power of the Ancient World. But Romans believed that there were right w ...
Considerations on the Causes of
... In violating Lucretia, his son Sextus did the sort of thing that has almost always caused tyrants to be expelled from the city they ruled. Such an action makes the people keenly aware of their servitude, and they immediately go to extremes. A people can easily endure the exaction of new tributes: it ...
... In violating Lucretia, his son Sextus did the sort of thing that has almost always caused tyrants to be expelled from the city they ruled. Such an action makes the people keenly aware of their servitude, and they immediately go to extremes. A people can easily endure the exaction of new tributes: it ...
The Roman Empire (after 27 BC)
... Senate, once their service was complete. Consuls The two consuls jointly administered the Roman Republic (in order to prevent the return of tyranny). They consuls had supreme power (called ‘imperium’) in both military and civil matters. They also had the power of veto (Latin for “I forbid it”), so b ...
... Senate, once their service was complete. Consuls The two consuls jointly administered the Roman Republic (in order to prevent the return of tyranny). They consuls had supreme power (called ‘imperium’) in both military and civil matters. They also had the power of veto (Latin for “I forbid it”), so b ...
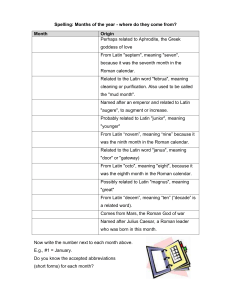
Months of the year and abbreviations.
... From Latin "octo", meaning "eight", because it was the eighth month in the Roman calendar. ...
... From Latin "octo", meaning "eight", because it was the eighth month in the Roman calendar. ...
Power Point for ROme
... • Romans excelled in engineering or the application of science and mathematics to develop useful structures and machines such as roads, bridges, harbors throughout the empire • Aqueducts were bridge like stone structures that brought water from the hills into Roman cities • Ptolemy proposed that the ...
... • Romans excelled in engineering or the application of science and mathematics to develop useful structures and machines such as roads, bridges, harbors throughout the empire • Aqueducts were bridge like stone structures that brought water from the hills into Roman cities • Ptolemy proposed that the ...
Chapter 13 Beginnings Chapter Focus On the hill known as the
... SOCIAL ORDER – how groups of people are classed. The Etruscan social order was made up of an upper class(wealthy landowners), middle class(farmers, traders, city workers) and lower class(enslaved people). Religious Beliefs Etruscans had many gods – much like the Greek gods. At first, they worshi ...
... SOCIAL ORDER – how groups of people are classed. The Etruscan social order was made up of an upper class(wealthy landowners), middle class(farmers, traders, city workers) and lower class(enslaved people). Religious Beliefs Etruscans had many gods – much like the Greek gods. At first, they worshi ...
Service Provider for Hungry Legionaries Wreck of a Roman
... explained the yield of the Germanic farms was not able to satisfy the needs of the legionaries. ...
... explained the yield of the Germanic farms was not able to satisfy the needs of the legionaries. ...
20130508152079
... Swiss alps into Italy with 40,000 men, supplies and 37 “war elephants” • Suffered heavy losses • Arrived with 26,000 men and 3 elephants • Surprised Roman army by land in the north ...
... Swiss alps into Italy with 40,000 men, supplies and 37 “war elephants” • Suffered heavy losses • Arrived with 26,000 men and 3 elephants • Surprised Roman army by land in the north ...
Roman Britain - Text, Images and Quiz (Reading Level C)
... This Roman victory ended further resistance against the Romans within southern Britain and Roman rule was accepted for the next 350 years. Hadrian’s Wall By about AD 100, over 50 years after they first invaded Britain, the Romans had finally secured all of what is now England and Wales. However, tri ...
... This Roman victory ended further resistance against the Romans within southern Britain and Roman rule was accepted for the next 350 years. Hadrian’s Wall By about AD 100, over 50 years after they first invaded Britain, the Romans had finally secured all of what is now England and Wales. However, tri ...
The Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire (30 BCE
... • Most powerful time of Empire= Pax Romana both praised and condemned – Brute military conquest and destruction vs. peace and prosperity ...
... • Most powerful time of Empire= Pax Romana both praised and condemned – Brute military conquest and destruction vs. peace and prosperity ...
Lecture: Early Rome and the Beginnings of Roman Imperialism
... Romulus, the Sabine Women, and the Politics of Inclusion “ ‘If you regret,’ [the Sabine women] continued, ‘the relationship that unites you, if you regret the marriage tie, turn your anger against us; we are the cause of the war, the cause of the wounds, and even death to both our husbands and our ...
... Romulus, the Sabine Women, and the Politics of Inclusion “ ‘If you regret,’ [the Sabine women] continued, ‘the relationship that unites you, if you regret the marriage tie, turn your anger against us; we are the cause of the war, the cause of the wounds, and even death to both our husbands and our ...