* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13 Beginnings Chapter Focus On the hill known as the
Survey
Document related concepts
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of ancient Roman religion wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Catacombs of Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Roman temple wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
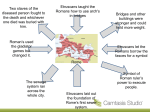
Chapter 13 Beginnings Chapter Focus On the hill known as the Palatine, an early people founded a settlement later known as Rome. Section 1 Founding Rome Legend of the founding of Rome: About 800 B.C., a Latin princess gave birth to twin sons fathered by a god. As punishment, her sons, Romulus and Remus, were taken from her and raised by a she-wolf and then a shepherd and his wife. Later, the brothers built a city on the Tiber River and let the gods choose the city’s ruler. The two fought, Remus was killed, and Romulus became king of Rome. The area where the Latins settled had a pleasant climate, fertile soil, thick forests, salt and fish carried from the coast. Most Latins were farmers who lived in wooden huts. Their main crops were wheat and barley. Section 2 The Etruscans Around 800B.C., people called the Etruscans settled in Etruria. They were Italy’s first highly civilized people. They were known as “the people of the sea”. They were feared and envied pirates. They were admired and respected traders. Etruscan farmers used iron tools to grow barley, millet, wheat, grapes; raised pigs, goats, sheep, ducks, chickens and cattle. They mined copper, lead, iron and tin which they used to make weapons, utensils and jewelry. They had a strong army and learned about weapons and battle techniques from the Greeks. The Etruscans had a weapon that no one else had: heavy leather shoes that laced up the ankle and made it easier for them to get around on hills or rough ground. Daily Life Enjoyed bright colors, riches and a good time. They gambled, wrestled, had races, boxed and raced horses. Loved music and dancing – had a special instrument called a lyre – dancing was done to get favors from gods. Women were allowed to dance, take part in public celebrations and own property! SOCIAL ORDER – how groups of people are classed. The Etruscan social order was made up of an upper class(wealthy landowners), middle class(farmers, traders, city workers) and lower class(enslaved people). Religious Beliefs Etruscans had many gods – much like the Greek gods. At first, they worshipped outside on stone platforms or earth and later they built temples. They believed the universe was divided into provinces, each with its own gods. Humans lived in the middle of the universe. To the left lay the east, which was ruled by the gods of the heavens – this is why they built their temples to face east. The Etruscans went to soothsayers – people who can predict events – to find out about the future. Soothsayers would read omens – signs that explained what is to happen or the will of the gods. Tombs of Gold The Etruscans built catacombs which were underground tombs for the dead. Outside each Etruscan city was a necropolis – a cemetery made up of acres of Etruscan catacombs. Section 3 Etruscans and Romans 616 B.C. : Lucius Taruinius became the first Etruscan ruler of Rome. The Etruscans made many contributions to Roman civilization: Architecture: an arch for building bridges, Rome’s first sewer system, drained the swamp at the bottom of the Palantine – this is where the Forum, or public square would later be built. Customs: fights of enslaved people at Etruscan funerals – these were models for the gladiatorial games which were fights between armed men, men and animals, women and dwarfs, between animals. Another custom was the triumph: a parade-like welcome given to a Roman hero returning from battle. Symbols: fasces: bundle of rods bound around an ax. IT BECAME Rome’s symbol of a Roman ruler’s power to beat or execute other people. Religious beliefs: soothsayers, gods with human forms, etc. o Etruscans built first temple on the Capitoline – one of the seven hills of Rome. Today it is the center of Rome’s municipal, or city, government o The Romans thought that the worlds of the living and the dead came together at the mundus, or meeting point of the worlds of the living and the dead. MAIN IDEAS In Italy, the Etruscans dominated Etruria and eventually all of northern Italy, including the Latin village on the Palantine. A few wealthy families owned most of the land on Etruria. The Etruscans built their temples to face east because they thought the east and the left were lucky. Experts learned much of what they know about Etruscan life from Etruscan catacombs. Lucius Tarquinius was the first Etruscan ruler of Rome. Romans borrowed several customs from the Etruscans: gladiatorial games, the triumph, and the fasces The Etruscans introduced the Romans to soothsayers and gods with human forms. Romans learned many things from the Etruscans: use of the arch in building, an alphabet, and a ritual for establishing cities.