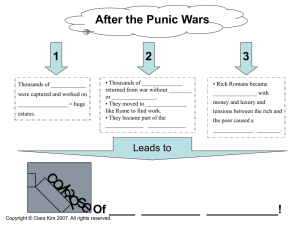
After the Punic Wars
... Senators didn't trust anyone who wanted to be a dictator and take their power. They thought he was trying to end the Republic. Caesar tried to get control of the senate by adding more senators who were loyal to him. Therefore, the senators felt their power was slipping even further. He granted citiz ...
... Senators didn't trust anyone who wanted to be a dictator and take their power. They thought he was trying to end the Republic. Caesar tried to get control of the senate by adding more senators who were loyal to him. Therefore, the senators felt their power was slipping even further. He granted citiz ...
Punic Wars
... – Finally turned tables on Carthage by changing rules of naval warfare • Equipped ships with huge hooks and • Stationed soldiers on ships • Would hook enemy ship, pull nearby, board it with soldiers – Converted naval warfare into mini-land battles • Something Rome was very good at • Won First Punic ...
... – Finally turned tables on Carthage by changing rules of naval warfare • Equipped ships with huge hooks and • Stationed soldiers on ships • Would hook enemy ship, pull nearby, board it with soldiers – Converted naval warfare into mini-land battles • Something Rome was very good at • Won First Punic ...
The Late Empire
... The emperor Commodus (the son of Marcus Aurelius) was probably insane. He claimed at various times to be the reincarnation of Hercules and Jupiter. He order the months of the Roman year to be named after him and changed the name of Rome to Colonia Commodiana. He was eventually strangled in his bath. ...
... The emperor Commodus (the son of Marcus Aurelius) was probably insane. He claimed at various times to be the reincarnation of Hercules and Jupiter. He order the months of the Roman year to be named after him and changed the name of Rome to Colonia Commodiana. He was eventually strangled in his bath. ...
Roman History - Rossview Latin
... D. M. Atilius Regulus 2. “The gods are with you”, “Remember Rome!”, “Curiatii forever!” These are some of the words shouted out by two opposing armies as six of their comrades, three from each side, prepared to fight during the reign of A. Servius Tullius B. Tarquinius Superbus C. Ancus Marcius D. T ...
... D. M. Atilius Regulus 2. “The gods are with you”, “Remember Rome!”, “Curiatii forever!” These are some of the words shouted out by two opposing armies as six of their comrades, three from each side, prepared to fight during the reign of A. Servius Tullius B. Tarquinius Superbus C. Ancus Marcius D. T ...
roman republic - my social studies class
... By 500 BC, the now independent city-state of Rome ruled only the small area within ten to fifteen miles of the city itself, and was part of an alliance of Latin city-states in the Tiber valley. Rome’s key geographic position at the best crossing of the Tiber River, with its relative size and militar ...
... By 500 BC, the now independent city-state of Rome ruled only the small area within ten to fifteen miles of the city itself, and was part of an alliance of Latin city-states in the Tiber valley. Rome’s key geographic position at the best crossing of the Tiber River, with its relative size and militar ...
Lesson 4
... husbands were away. Still, Roman women had little power outside the home and could not vote. ...
... husbands were away. Still, Roman women had little power outside the home and could not vote. ...
What the Romans Brought to Britain
... • The chiefs were also required to turn over hostages to the Romans, often members of their own families, in order to insure that they would not break the peace treaty. ...
... • The chiefs were also required to turn over hostages to the Romans, often members of their own families, in order to insure that they would not break the peace treaty. ...
Identify at least two of the big trends leading to WWI.
... Pursuit of excellence, virtue, use of persuasion over force ...
... Pursuit of excellence, virtue, use of persuasion over force ...
The True Cause of the Punic Wars
... The goal of this research was to study the politics that lead up to the three Punic Wars. This study is best facilitated by the examination of the treaties between Rome and Carthage, especially the treaty in the History of Philinus of Agrigentum. Philinus was a Greek historian from a southern Sicili ...
... The goal of this research was to study the politics that lead up to the three Punic Wars. This study is best facilitated by the examination of the treaties between Rome and Carthage, especially the treaty in the History of Philinus of Agrigentum. Philinus was a Greek historian from a southern Sicili ...
I. Rome`s Creation of a Mediterranean Empire, 753 b.c.e.–330 c.e. 1
... emerged between the patrician elite and the plebeian majority. 5. Roman women had relatively more freedom than Greek women, but their legal status was still that of a child, subordinate to the paterfamilias of their own or their husband’s family. Eventually procedures evolved that made it possible f ...
... emerged between the patrician elite and the plebeian majority. 5. Roman women had relatively more freedom than Greek women, but their legal status was still that of a child, subordinate to the paterfamilias of their own or their husband’s family. Eventually procedures evolved that made it possible f ...
File - Mr. Sager World History
... 1. Which region located on the North African coast was offering competition to Rome for power? 2. Which group of people settled Carthage? 3. Carthage had become a great ____________________ competition and led the area in _________________________. 4. Where else did Carthage have settlements? 5. The ...
... 1. Which region located on the North African coast was offering competition to Rome for power? 2. Which group of people settled Carthage? 3. Carthage had become a great ____________________ competition and led the area in _________________________. 4. Where else did Carthage have settlements? 5. The ...
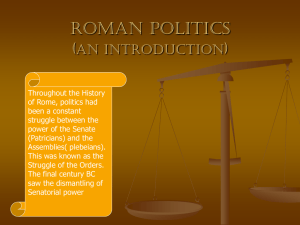
An Introduction to Roman Politics
... After which it would be back to the provinces but this time one could expect to hold a more influential post in command of a sizeable force. ...
... After which it would be back to the provinces but this time one could expect to hold a more influential post in command of a sizeable force. ...
Rome and Early Christianity Section 1
... • Successful expansion not possible without powerful army ...
... • Successful expansion not possible without powerful army ...
How To Write a DBQ
... With the start of the Roman Classical Age came a new type of government in Rome, as well as increased trade and heightened Roman influence throughout Europe. As the term “Empire” suggests, Rome as ruled by an emperor – the first being Augustus – who was backed by the Senate, a group of very wealthy ...
... With the start of the Roman Classical Age came a new type of government in Rome, as well as increased trade and heightened Roman influence throughout Europe. As the term “Empire” suggests, Rome as ruled by an emperor – the first being Augustus – who was backed by the Senate, a group of very wealthy ...
9th Grade World History Overview
... 13) Chapter 16 Web Activity - “The Christian Catacombs of Rome”. 14) View Presentation on Aqueduct Construction, weigh pros/cons, and write an opinion paragraph detailing and supporting your position. 15) Complete Ancient Rome and Roman Heritage Search a Word puzzles. 16) Play Roman Jeopardy. 17) Re ...
... 13) Chapter 16 Web Activity - “The Christian Catacombs of Rome”. 14) View Presentation on Aqueduct Construction, weigh pros/cons, and write an opinion paragraph detailing and supporting your position. 15) Complete Ancient Rome and Roman Heritage Search a Word puzzles. 16) Play Roman Jeopardy. 17) Re ...
Unit Test - Greece and Rome Instructions : Do NOT write on this test
... 3. philosopher who taught that the aim of life is to seek pleasure and avoid pain 4. great teacher who was sentenced to death for criticizing Greek leaders and democracy 5. philosopher who wrote about government, justice, and the nature of physical and spiritual things 6. thinker who developed appro ...
... 3. philosopher who taught that the aim of life is to seek pleasure and avoid pain 4. great teacher who was sentenced to death for criticizing Greek leaders and democracy 5. philosopher who wrote about government, justice, and the nature of physical and spiritual things 6. thinker who developed appro ...
File
... 16. By 45 BCE Caesar was the undisputed master of Rome and he pursued reforms that strengthened his own power. He provided land ___________ for his soldiers, restructured the ___________ of a huge percentage of Rome’s debtors, and also changed the ___________ to make it look more like the one we us ...
... 16. By 45 BCE Caesar was the undisputed master of Rome and he pursued reforms that strengthened his own power. He provided land ___________ for his soldiers, restructured the ___________ of a huge percentage of Rome’s debtors, and also changed the ___________ to make it look more like the one we us ...
Unit 1 PowerPoint Presentation
... • This new government was called a Republic which means “Thing of the People” • A senate of 300 members ruled Rome • The senators were all patricians, or landholding upper class ...
... • This new government was called a Republic which means “Thing of the People” • A senate of 300 members ruled Rome • The senators were all patricians, or landholding upper class ...
This list begins with the founding of the village of Rome around
... Tiberius, the first senator to advocate land reform, was assassinated in 133BC by land-owners. The "Social War" (revolt by Roman allies in Italy) First Mithridatic War (Black Sea region) Sulla became the first Roman general to seize power Civil war in Rome Second Mithridatic War Sulla returned power ...
... Tiberius, the first senator to advocate land reform, was assassinated in 133BC by land-owners. The "Social War" (revolt by Roman allies in Italy) First Mithridatic War (Black Sea region) Sulla became the first Roman general to seize power Civil war in Rome Second Mithridatic War Sulla returned power ...
#10—Crash Course World History The Roman Empire or Republic
... 16. By 45 BCE Caesar was the undisputed master of Rome and he pursued reforms that strengthened his own power. He provided land ___________ for his soldiers, restructured the ___________ of a huge percentage of Rome’s debtors, and also changed the ___________ to make it look more like the one we us ...
... 16. By 45 BCE Caesar was the undisputed master of Rome and he pursued reforms that strengthened his own power. He provided land ___________ for his soldiers, restructured the ___________ of a huge percentage of Rome’s debtors, and also changed the ___________ to make it look more like the one we us ...