26 microbial genetics
... 2. Transduction: transfer of bacterial DNA incident to viral infection. - could be generalized (host DNA accidentally, randomly packaged in capsid) - could be specialized (takes genes adjacent to a viral insertion site). ...
... 2. Transduction: transfer of bacterial DNA incident to viral infection. - could be generalized (host DNA accidentally, randomly packaged in capsid) - could be specialized (takes genes adjacent to a viral insertion site). ...
bacteria - Pleasantville High School
... and sniffling). •HIV specifically attacks white blood cells ...
... and sniffling). •HIV specifically attacks white blood cells ...
Essential Knowledge 3.C.3: Viral replication results in genetic
... variation and viral infection can introduce genetic variation into the hosts. A. Viral replication differs from other reproductive strategies and generates genetic variation via various mechanisms. B. The reproductive cycles of viruses facilitate transfer of genetic information. ...
... variation and viral infection can introduce genetic variation into the hosts. A. Viral replication differs from other reproductive strategies and generates genetic variation via various mechanisms. B. The reproductive cycles of viruses facilitate transfer of genetic information. ...
AP Biology - Naber Biology
... 20. What is a prophage? 21. Because cells that have incorporated phage DNA into their genome may continue to divide and propagate the viral genome, this might be considered somewhat like the Trojan horse. What might trigger the switchover from lysogenic to lytic mode? ...
... 20. What is a prophage? 21. Because cells that have incorporated phage DNA into their genome may continue to divide and propagate the viral genome, this might be considered somewhat like the Trojan horse. What might trigger the switchover from lysogenic to lytic mode? ...
Viral Structure and Life Cycles : Notes - Mr. Lesiuk
... -Composed of a core of ______________________________ surrounded by a _____________________________________ ______________________ -The Capsid ______________________ the nucleic acid core. -Nucleic Acid can be _____________________________ but never both. (retroviruses contain RNA) -The ____________ ...
... -Composed of a core of ______________________________ surrounded by a _____________________________________ ______________________ -The Capsid ______________________ the nucleic acid core. -Nucleic Acid can be _____________________________ but never both. (retroviruses contain RNA) -The ____________ ...
Virology study guide for mid
... acidification within the vesicles 1. lead to degradation of viral structures ...
... acidification within the vesicles 1. lead to degradation of viral structures ...
Viruses: viruses are not considered to be living organisms do not
... characteristics of living things ...
... characteristics of living things ...
Chapter 5: Viruses and Monerans
... 2. Would you classify viruses as living or nonliving? Explain. Arguments can be made for both sides. Because viruses are not cells, they cannot perform all the functions of living cells. For example, they cannot take in food or get rid of wastes. This is support to classify them as nonliving. Howeve ...
... 2. Would you classify viruses as living or nonliving? Explain. Arguments can be made for both sides. Because viruses are not cells, they cannot perform all the functions of living cells. For example, they cannot take in food or get rid of wastes. This is support to classify them as nonliving. Howeve ...
virus
... Viruses are simple, acellular entities consisting of one or more molecules of either DNA or RNA enclosed in a coat of protein Either single-stranded or double-stranded DNA or RNA - linear, closed circle, or able to assume either shape. Reproduce only within living cells Virion All viruses have a nuc ...
... Viruses are simple, acellular entities consisting of one or more molecules of either DNA or RNA enclosed in a coat of protein Either single-stranded or double-stranded DNA or RNA - linear, closed circle, or able to assume either shape. Reproduce only within living cells Virion All viruses have a nuc ...
Slide ()
... A) The linearized double-stranded DNA genome of KS virus showing important genes of the lytic cycle. The genome contains 87 open reading frames (ORFs) coding for latent proteins, reactivation proteins, and structural proteins. Host genes that help the virus evade immune surveillance and inhibit apop ...
... A) The linearized double-stranded DNA genome of KS virus showing important genes of the lytic cycle. The genome contains 87 open reading frames (ORFs) coding for latent proteins, reactivation proteins, and structural proteins. Host genes that help the virus evade immune surveillance and inhibit apop ...
Gene Therapy - MsSunderlandsBiologyClasses
... • Adeno-associated viruses - A class of small, single-stranded DNA viruses that can insert their genetic material at a specific site on chromosome ...
... • Adeno-associated viruses - A class of small, single-stranded DNA viruses that can insert their genetic material at a specific site on chromosome ...
General Virology - California State University, Fullerton
... • Tobacco mosaic virus is a ssRNA virus composed of 6000 nucleotides. The capsid is made of 2100 copies of a single protein subunit that contain 158 amino acids. Calculate the percentage of the genome that is used for structure. ...
... • Tobacco mosaic virus is a ssRNA virus composed of 6000 nucleotides. The capsid is made of 2100 copies of a single protein subunit that contain 158 amino acids. Calculate the percentage of the genome that is used for structure. ...
Coevolution --- viruses may have evolved along with cells
... Infectious Units, look for the effects of the virus on host cells --- mix dilutions of the virus with cells (animal, plant or bacterial), plate, and look for infected cells ...
... Infectious Units, look for the effects of the virus on host cells --- mix dilutions of the virus with cells (animal, plant or bacterial), plate, and look for infected cells ...
Viruses - saddlespace.org
... •Ultramicroscopic infectious agents that replicates within cells of living hosts. •Many are pathogenic; •Composed of a piece of nucleic acid wrapped in a thin coat of protein. ...
... •Ultramicroscopic infectious agents that replicates within cells of living hosts. •Many are pathogenic; •Composed of a piece of nucleic acid wrapped in a thin coat of protein. ...
Intro to Virology
... a. Obligate intracellular parasites (selfishly uses at its own benefit) b. Do not possess ribosomes – no translation c. Uses the hosts replication machinery 2. Define how the terms virion and virus differ a. Virion is the infectious particle b. Serves to transfer the viral genome 3. Identify the com ...
... a. Obligate intracellular parasites (selfishly uses at its own benefit) b. Do not possess ribosomes – no translation c. Uses the hosts replication machinery 2. Define how the terms virion and virus differ a. Virion is the infectious particle b. Serves to transfer the viral genome 3. Identify the com ...
Viruses & Prions
... When a virus has infected an organisms, there are two processes that can occur: ...
... When a virus has infected an organisms, there are two processes that can occur: ...
What is a virus
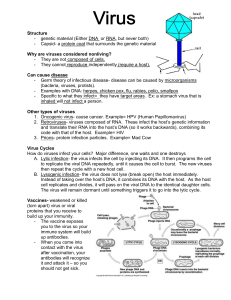
... - genetic material (Either DNA or RNA, but never both) - Capsid- a protein coat that surrounds the genetic material Why are viruses considered nonliving? - They are not composed of cells. - They cannot reproduce independently (require a host). Can cause disease - Germ theory of infectious disease- d ...
... - genetic material (Either DNA or RNA, but never both) - Capsid- a protein coat that surrounds the genetic material Why are viruses considered nonliving? - They are not composed of cells. - They cannot reproduce independently (require a host). Can cause disease - Germ theory of infectious disease- d ...
Understanding Viruses Video Questions
... 12. How much a virus can change (mutate) depends on how it is made. If its genetic material is DNA it is pretty ________________ . RNA viruses are ______________ . 13. This explains why the vaccine for a DNA virus like smallpox _____________ while RNA viruses like influenza _________________________ ...
... 12. How much a virus can change (mutate) depends on how it is made. If its genetic material is DNA it is pretty ________________ . RNA viruses are ______________ . 13. This explains why the vaccine for a DNA virus like smallpox _____________ while RNA viruses like influenza _________________________ ...
Viruses - Elgin Local Schools
... Viruses: Nucleic Acids: -DNA or RNA -single strand or double strand Capsid: proteins coat that enables infection of cell ...
... Viruses: Nucleic Acids: -DNA or RNA -single strand or double strand Capsid: proteins coat that enables infection of cell ...
DNA virus

A DNA virus is a virus that has DNA as its genetic material and replicates using a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase. The nucleic acid is usually double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) but may also be single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). DNA viruses belong to either Group I or Group II of the Baltimore classification system for viruses. Single-stranded DNA is usually expanded to double-stranded in infected cells. Although Group VII viruses such as hepatitis B contain a DNA genome, they are not considered DNA viruses according to the Baltimore classification, but rather reverse transcribing viruses because they replicate through an RNA intermediate. Notable diseases like smallpox, herpes, and chickenpox are caused by such DNA viruses.