BACTERIA - Virus and Bacteria worksheet
... 3. ________________________ Viruses that contain RNA are called: 4. ________________________ Name of virus that attack bacteria? 5. ________________________ Made up of only protein only; cause of “Mad Cow disease” ...
... 3. ________________________ Viruses that contain RNA are called: 4. ________________________ Name of virus that attack bacteria? 5. ________________________ Made up of only protein only; cause of “Mad Cow disease” ...
Name - Southington Public Schools
... Textbook reference: L2 Biology section 16.5, L3 Biology section 19-3. Viruses are particles that enter living cells and use the cell’s machinery to produce more virus particles. Some viruses destroy the host cell immediately after they infect it. Others incorporate their genetic material into the ho ...
... Textbook reference: L2 Biology section 16.5, L3 Biology section 19-3. Viruses are particles that enter living cells and use the cell’s machinery to produce more virus particles. Some viruses destroy the host cell immediately after they infect it. Others incorporate their genetic material into the ho ...
Section 18.1 Summary – pages 475-483
... Discuss with the people around you the difference between these three words: ...
... Discuss with the people around you the difference between these three words: ...
virus - BiG.NeT
... What is a Virus? How is it different from Bacteria? For one thing, they differ greatly in size. The biggest viruses are only as large as the tiniest bacteria. Another difference is their structure. Bacteria are complex compared to viruses. ...
... What is a Virus? How is it different from Bacteria? For one thing, they differ greatly in size. The biggest viruses are only as large as the tiniest bacteria. Another difference is their structure. Bacteria are complex compared to viruses. ...
Characteristics
... DNA into the cell. B The viral DNA attaches to the host DNA. C DNA replication takes place (Interphase) D The cell undergoes mitosis E Stress causes the viral DNA to create the “weird” protein thus creating an outbreak! ...
... DNA into the cell. B The viral DNA attaches to the host DNA. C DNA replication takes place (Interphase) D The cell undergoes mitosis E Stress causes the viral DNA to create the “weird” protein thus creating an outbreak! ...
Biological Properties of Tomato apex necrosis virus (ToANV)
... Not all genera are within assigned families at this time, and some new genera and families are not shown at right. According to Hull, (page 87) he says there are 977 species of plant viruses as of 2002, more are being identified all the time. Within the genus Potyvirus, there are more than 100 defin ...
... Not all genera are within assigned families at this time, and some new genera and families are not shown at right. According to Hull, (page 87) he says there are 977 species of plant viruses as of 2002, more are being identified all the time. Within the genus Potyvirus, there are more than 100 defin ...
Discovery of DNA
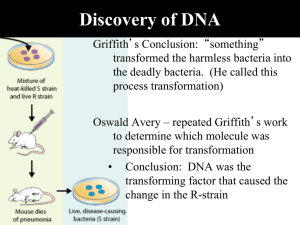
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
Virus - Homework Market
... http://higheredbcs.wiley.com/legacy/college/black/0471420840/animations/ch10/ch10_Viruses/ind ex.html ...
... http://higheredbcs.wiley.com/legacy/college/black/0471420840/animations/ch10/ch10_Viruses/ind ex.html ...
notes chap. 24 virsuses - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 2. Lytic Cycle – immediate taking over of a host cell. a. Attachment – virus attaches tail fibers down onto host cell membrane. b. Entry – DNA/RNA is injected into cell. c. Replication – viral DNA/RNA tells host cell to make more viruses d. Assembly – making of more viruses e. Lysis (release) – hos ...
... 2. Lytic Cycle – immediate taking over of a host cell. a. Attachment – virus attaches tail fibers down onto host cell membrane. b. Entry – DNA/RNA is injected into cell. c. Replication – viral DNA/RNA tells host cell to make more viruses d. Assembly – making of more viruses e. Lysis (release) – hos ...
1406 final exam guide.doc
... Sex linked genes are more likely to be inherited by males or females What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy What is a linked gene What is Nondisjunction, at what stage of meiosis does this occurs? Types of changes in chromosome structure.( deletion, duplication invertion, reciprocal translocation What ...
... Sex linked genes are more likely to be inherited by males or females What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy What is a linked gene What is Nondisjunction, at what stage of meiosis does this occurs? Types of changes in chromosome structure.( deletion, duplication invertion, reciprocal translocation What ...
Unit 4: Viruses Intro Video Anatomy of a Virus
... Double stranded DNA Single stranded DNA Double stranded RNA Single stranded RNA ...
... Double stranded DNA Single stranded DNA Double stranded RNA Single stranded RNA ...
Capsid
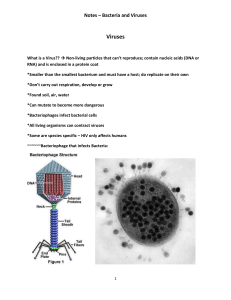
... plant, animal, bacterial = bacteriophages • virion = nucleic acid + protein coat (capsid) and another envelope similar to membrane (enveloped viruses) ...
... plant, animal, bacterial = bacteriophages • virion = nucleic acid + protein coat (capsid) and another envelope similar to membrane (enveloped viruses) ...
Bacteria and Viruses – Comparison Chart
... Put an X in the box if the statement corresponds to bacteria. Put an X in the box if the statement corresponds to Viruses. Mark both boxes if the statement applies to both. Bacteria Virus Incapable of metabolism Can not reproduce outside of another living organism Contains genetic material Contains ...
... Put an X in the box if the statement corresponds to bacteria. Put an X in the box if the statement corresponds to Viruses. Mark both boxes if the statement applies to both. Bacteria Virus Incapable of metabolism Can not reproduce outside of another living organism Contains genetic material Contains ...
Viruses Quiz Answer Key
... 8. What does it mean for a virus to “infect” a cell? a) The virus lands on the outside of the cell then completely enters the cell. b) The virus lands on the outside of the cell and injects its genetic material into the cell. c) The virus lands on the outside of the cell and injects its proteins int ...
... 8. What does it mean for a virus to “infect” a cell? a) The virus lands on the outside of the cell then completely enters the cell. b) The virus lands on the outside of the cell and injects its genetic material into the cell. c) The virus lands on the outside of the cell and injects its proteins int ...
Notes: Viruses
... Viruses do not use energy Viruses do not grow & develop Viruses can only reproduce when they are inside of a living host cell Viruses can form crystals and remain viable for a long time ...
... Viruses do not use energy Viruses do not grow & develop Viruses can only reproduce when they are inside of a living host cell Viruses can form crystals and remain viable for a long time ...
“Ancient” Viruses
... Could be any gene-but loss of function abolishes the ability to infect. A virus with a loss-of-function mutation in an essential gene is defective. How can you propagate a defective mutant virus? ...
... Could be any gene-but loss of function abolishes the ability to infect. A virus with a loss-of-function mutation in an essential gene is defective. How can you propagate a defective mutant virus? ...
Viruses_Summary (1)
... Many have geometric shapes, like cut diamonds. Others are shaped like spiky eggs, skinny sticks or pieces of looped string. Some are more complicated and look like tiny spaceship landing pods. Viruses don’t have a nucleus. Their DNA (genes) just floats around inside them. They aren’t really even pro ...
... Many have geometric shapes, like cut diamonds. Others are shaped like spiky eggs, skinny sticks or pieces of looped string. Some are more complicated and look like tiny spaceship landing pods. Viruses don’t have a nucleus. Their DNA (genes) just floats around inside them. They aren’t really even pro ...
Viruses
... Only 3 characteristics of life: reproduction, evolution, and genetic code (DNA/RNA) Can only reproduce inside a host cell! Process or reproduction = lytic cycle ...
... Only 3 characteristics of life: reproduction, evolution, and genetic code (DNA/RNA) Can only reproduce inside a host cell! Process or reproduction = lytic cycle ...
Viruses
... Viruses • Use infected cell to produce more viruses • Capsid: protein coat surrounding DNA/RNA core • bacteriophage – virus that infects bacteria ...
... Viruses • Use infected cell to produce more viruses • Capsid: protein coat surrounding DNA/RNA core • bacteriophage – virus that infects bacteria ...
DNA virus

A DNA virus is a virus that has DNA as its genetic material and replicates using a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase. The nucleic acid is usually double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) but may also be single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). DNA viruses belong to either Group I or Group II of the Baltimore classification system for viruses. Single-stranded DNA is usually expanded to double-stranded in infected cells. Although Group VII viruses such as hepatitis B contain a DNA genome, they are not considered DNA viruses according to the Baltimore classification, but rather reverse transcribing viruses because they replicate through an RNA intermediate. Notable diseases like smallpox, herpes, and chickenpox are caused by such DNA viruses.