Viruses - Humble ISD
... 1. Virus _____________ to the cell ____________________ of the host cell 2. Trick cell into allowing it inside 3. Virus releases its __________________________ (DNA or RNA) into the host cell - ____________________ – Viral DNA is ____________ - Transcription – Viral _______ is converted into _______ ...
... 1. Virus _____________ to the cell ____________________ of the host cell 2. Trick cell into allowing it inside 3. Virus releases its __________________________ (DNA or RNA) into the host cell - ____________________ – Viral DNA is ____________ - Transcription – Viral _______ is converted into _______ ...
MCDB 1030
... 3. Describe the principle events that occur in the life cycle of a + strand RNA virus. ...
... 3. Describe the principle events that occur in the life cycle of a + strand RNA virus. ...
Topic 15 - FSU Biology
... Virus- RNA or DNA accompanied by protein which have the capacity to harness the machinery of cells for replication; they are not living per se since they cannot replicate themselves Viruses- common features (fig. 18.2)- genome (consisting of DNA or RNA); capsid (protein coat); viral envelope (membra ...
... Virus- RNA or DNA accompanied by protein which have the capacity to harness the machinery of cells for replication; they are not living per se since they cannot replicate themselves Viruses- common features (fig. 18.2)- genome (consisting of DNA or RNA); capsid (protein coat); viral envelope (membra ...
Sequences vs Viruses: Producer vs Product, Cause and
... simply replicate in them and be shed in their urine but when they infect humans they may cause fatal illnesses of the kidneys or respiratory tract; viruses that are pathogenic for humans may replicate only in humans and other primates; viruses may not replicate in mosquito cells or may replicate to ...
... simply replicate in them and be shed in their urine but when they infect humans they may cause fatal illnesses of the kidneys or respiratory tract; viruses that are pathogenic for humans may replicate only in humans and other primates; viruses may not replicate in mosquito cells or may replicate to ...
No Slide Title
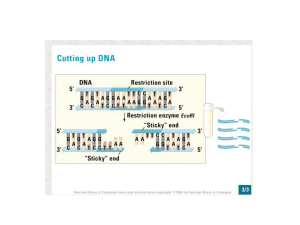
... Restriction Enzymes • Restriction enzymes cut DNA from any source into fragments • Sticky ends can pair up with complementary DNA with the help of ligase producing recombinant DNA • Example: EcoRI, HindII ...
... Restriction Enzymes • Restriction enzymes cut DNA from any source into fragments • Sticky ends can pair up with complementary DNA with the help of ligase producing recombinant DNA • Example: EcoRI, HindII ...
Viruses
... • Nucleid acid (genom) • Capsid • Envelope (only enveloped viruses ) Nucleocapsid –virion, or capsid and genomu for coated viruses ...
... • Nucleid acid (genom) • Capsid • Envelope (only enveloped viruses ) Nucleocapsid –virion, or capsid and genomu for coated viruses ...
Viruses + Bacteria
... • Do not undergo lytic or lysogenic phases. • Not all harmful. May cause striking color patterns in flowers. ...
... • Do not undergo lytic or lysogenic phases. • Not all harmful. May cause striking color patterns in flowers. ...
Intro to Virology
... May be either RNA or DNA, single- or double-stranded, linear or circular May have the common bases that occur in RNA or DNA, or genome may have one or more unusual bases (e.g., hydroxymethylcytosine instead of ...
... May be either RNA or DNA, single- or double-stranded, linear or circular May have the common bases that occur in RNA or DNA, or genome may have one or more unusual bases (e.g., hydroxymethylcytosine instead of ...
Lecture 16: Spherical Virus Structures
... Triangulation numbers, T There are constraints preserving specificity of interactions within an icosahedron -Caspar and Klug (1962) Showed that only certain multiples (1,3,4,7) of 60 subunits are likely to occur The more subunits used to build the virus the larger the volume it ...
... Triangulation numbers, T There are constraints preserving specificity of interactions within an icosahedron -Caspar and Klug (1962) Showed that only certain multiples (1,3,4,7) of 60 subunits are likely to occur The more subunits used to build the virus the larger the volume it ...
Ch 19 Viruses
... Components = nucleic acid + capsid ◦ Nucleic acid: DNA or RNA (double or single-stranded) ◦ Capsid: protein shell Accessory Structure: Some viruses also have viral envelopes that surround capsid ...
... Components = nucleic acid + capsid ◦ Nucleic acid: DNA or RNA (double or single-stranded) ◦ Capsid: protein shell Accessory Structure: Some viruses also have viral envelopes that surround capsid ...
Viruses Are Viruses Living Things? ______ Why? Viruses, can all
... viral DNA is injected into the host cell viral DNA is __________________ into the host ___________________ host cell divides with the ____________________ as a part of it eventually the viral DNA can be triggered to separate from the host cell DNA and pick up with the lytic cycle at step 2. ...
... viral DNA is injected into the host cell viral DNA is __________________ into the host ___________________ host cell divides with the ____________________ as a part of it eventually the viral DNA can be triggered to separate from the host cell DNA and pick up with the lytic cycle at step 2. ...
Contagion Worksheet
... 2. What U.S. government agency tracks diseases here in the U.S. (and monitors world diseases as well)? ...
... 2. What U.S. government agency tracks diseases here in the U.S. (and monitors world diseases as well)? ...
Summaries II
... • The attachment of a virion to a host cell is a highly specific process involving complementary receptors on the surface of a susceptible host cell and its infecting virus. • Resistance of the host to infection by the virus can involve restrictionmodification systems that recognize and destroy dou ...
... • The attachment of a virion to a host cell is a highly specific process involving complementary receptors on the surface of a susceptible host cell and its infecting virus. • Resistance of the host to infection by the virus can involve restrictionmodification systems that recognize and destroy dou ...
Viruses - North Mac Schools
... Virion- virus outside of cell • Capsid-protein coat surrounding nucleic acid • Genetic material- DNA or RNA ...
... Virion- virus outside of cell • Capsid-protein coat surrounding nucleic acid • Genetic material- DNA or RNA ...
Viruses
... 2. Viruses require a host organism, or living cell, to reproduce. 3. Viruses are parasites because they harm living cells. A virus has two basic parts: 1. a core of hereditary material 2. an outer coat of protein Viral Host Cell Infection 1. After a cell attaches to its host cell, it injects its her ...
... 2. Viruses require a host organism, or living cell, to reproduce. 3. Viruses are parasites because they harm living cells. A virus has two basic parts: 1. a core of hereditary material 2. an outer coat of protein Viral Host Cell Infection 1. After a cell attaches to its host cell, it injects its her ...
viruses and bacteria
... 7. Describe what a vaccine is. 8. Explain why the tobacco mosaic virus infects only a cell of a tobacco plant and not a human cell? 9. State at least 3 uses of bacteria. 10. Give 3 types of disease caused by bacteria and 3 by viruses ...
... 7. Describe what a vaccine is. 8. Explain why the tobacco mosaic virus infects only a cell of a tobacco plant and not a human cell? 9. State at least 3 uses of bacteria. 10. Give 3 types of disease caused by bacteria and 3 by viruses ...
How Biologists Classify Organisms... (pg 113
... This knowledge of viruses is used in recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology. We use empty virus capsids, put in the DNA / RNA we want to introduce into a cell, give this virus a supply of target cells, and let it do its thing. We have made cells that contain our “inserted gene”...they now make something ...
... This knowledge of viruses is used in recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology. We use empty virus capsids, put in the DNA / RNA we want to introduce into a cell, give this virus a supply of target cells, and let it do its thing. We have made cells that contain our “inserted gene”...they now make something ...
Life Under a Microscope: Viruses Questions
... Humans aren't the only ones who get sick from viruses. There are viruses that infect plants and viruses that infect animals. There are even viruses that infect bacteria! Would you believe that viruses aren't even alive? A virus is so small and so simple that it cannot even be considered a living thi ...
... Humans aren't the only ones who get sick from viruses. There are viruses that infect plants and viruses that infect animals. There are even viruses that infect bacteria! Would you believe that viruses aren't even alive? A virus is so small and so simple that it cannot even be considered a living thi ...
Section 19–2 Viruses
... This section describes the structure of a virus. It also explains how viruses cause infection. ...
... This section describes the structure of a virus. It also explains how viruses cause infection. ...
Viruses - Killeen ISD
... • Structure that contains genetic material (DNA or RNA) wrapped in protein • Does NOT have a cell • Does NOT breathe, eat, produce wastes • Can reproduce, but only if in a host cell ...
... • Structure that contains genetic material (DNA or RNA) wrapped in protein • Does NOT have a cell • Does NOT breathe, eat, produce wastes • Can reproduce, but only if in a host cell ...
Our selections for Fall 2005
... – Mixing of viruses that infect birds, pigs, produce new strains able to jump to humans. – New antigenic type leaves population unprotected – Numerous epidemics throughout history • Flu of 1918-1919 killed 20 million – Asia watched very carefully: bird flu? ...
... – Mixing of viruses that infect birds, pigs, produce new strains able to jump to humans. – New antigenic type leaves population unprotected – Numerous epidemics throughout history • Flu of 1918-1919 killed 20 million – Asia watched very carefully: bird flu? ...
DNA virus

A DNA virus is a virus that has DNA as its genetic material and replicates using a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase. The nucleic acid is usually double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) but may also be single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). DNA viruses belong to either Group I or Group II of the Baltimore classification system for viruses. Single-stranded DNA is usually expanded to double-stranded in infected cells. Although Group VII viruses such as hepatitis B contain a DNA genome, they are not considered DNA viruses according to the Baltimore classification, but rather reverse transcribing viruses because they replicate through an RNA intermediate. Notable diseases like smallpox, herpes, and chickenpox are caused by such DNA viruses.