Ch. 18 – Microbial Models of DNA
... Control of Viral Genes • Bacteria posses restriction endonucleases, which are enzymes that degrade viral DNA as it enters • Go lysogenic instead – if phage is added to a specific site within bacterial DNA then it’s a prophage and it codes for a protein that represses the other phage genes. • Some b ...
... Control of Viral Genes • Bacteria posses restriction endonucleases, which are enzymes that degrade viral DNA as it enters • Go lysogenic instead – if phage is added to a specific site within bacterial DNA then it’s a prophage and it codes for a protein that represses the other phage genes. • Some b ...
BTY328: Viruses
... plasma membrane, and only their nucleic acids are injected into the cytoplasm. Many enveloped viruses enter cells through engulfment by receptor-mediated endocytosis to form coated vesicles. These vesicles fuse with lysosomes where viral uncoating is completed. The envelope of paramyxoviruses, membr ...
... plasma membrane, and only their nucleic acids are injected into the cytoplasm. Many enveloped viruses enter cells through engulfment by receptor-mediated endocytosis to form coated vesicles. These vesicles fuse with lysosomes where viral uncoating is completed. The envelope of paramyxoviruses, membr ...
Chapter 14: Viruses, Prions, and Viroids
... 8. What is a benefit of infection with a lysogenic phage? What change may occur with the bacterial cell? 9. Understand how filamentous phage (M13 and fd) replicate in host cells. What is unique to replication of a ssDNA molecule? 10. What are three mechanisms that reduce infection by phage? 11. Unde ...
... 8. What is a benefit of infection with a lysogenic phage? What change may occur with the bacterial cell? 9. Understand how filamentous phage (M13 and fd) replicate in host cells. What is unique to replication of a ssDNA molecule? 10. What are three mechanisms that reduce infection by phage? 11. Unde ...
Chapter 25 Notes Viruses
... could infect the leaves of healthy plants Dr. Wendell Stanley – (1935) the first to isolate the tobacco mosaic virus and show that it could be crystallized ...
... could infect the leaves of healthy plants Dr. Wendell Stanley – (1935) the first to isolate the tobacco mosaic virus and show that it could be crystallized ...
Virus (Latin: slimy toxin, venom) English viruses plural but actually
... other conserved nerve proteins, most warm blooded animals, nerve cells ...
... other conserved nerve proteins, most warm blooded animals, nerve cells ...
Plate 32 - Viral Replication
... used to make the bacterial DNA • Capsids begin to be assembled around the viral DNA ...
... used to make the bacterial DNA • Capsids begin to be assembled around the viral DNA ...
Document
... As parasites they cause many diseases in humans, domestic animals and crop plants. ...
... As parasites they cause many diseases in humans, domestic animals and crop plants. ...
3.5.4 Viruses - Spanish Point Biology
... As parasites they cause many diseases in humans, domestic animals and crop plants. ...
... As parasites they cause many diseases in humans, domestic animals and crop plants. ...
Ch. 16 - Harford Community College
... • Most are single-stranded RNA viruses. They enter plant cells through damaged cell walls or are inherited from a parent. ...
... • Most are single-stranded RNA viruses. They enter plant cells through damaged cell walls or are inherited from a parent. ...
Viruses - SaddleSpace/Haiku
... Make a virus less harmful (virulent): a. Grow in different host cell, e.g. flu vaccines are grown in chicken eggs so the flu virus will look for chicken cells instead of human cells. b. Find a less harmful, but similar looking virus, e.g. cow pox vs small pox. c. Chemically alter or destroy the n ...
... Make a virus less harmful (virulent): a. Grow in different host cell, e.g. flu vaccines are grown in chicken eggs so the flu virus will look for chicken cells instead of human cells. b. Find a less harmful, but similar looking virus, e.g. cow pox vs small pox. c. Chemically alter or destroy the n ...
Lecture 3 Virus
... - Reproduce only within a living host cell (obligate parasitism )تطفل إبجااري. - Each type of a virus infects a limited range of host cells (host range )مدى اإلصااة Viruses are host specific ...
... - Reproduce only within a living host cell (obligate parasitism )تطفل إبجااري. - Each type of a virus infects a limited range of host cells (host range )مدى اإلصااة Viruses are host specific ...
Viruses Virus • Microscopic particle that invades and
... Classifying Viruses All viruses contain nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat Classified by shape o Crystals o Spheres o Cylinders o Spacecraft Cycles of viruses Lysogenic Cycle – the virus goes into a host cell but remains inactive; when the host cell divides, copies o ...
... Classifying Viruses All viruses contain nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat Classified by shape o Crystals o Spheres o Cylinders o Spacecraft Cycles of viruses Lysogenic Cycle – the virus goes into a host cell but remains inactive; when the host cell divides, copies o ...
Viruses
... Sometimes further wrapped يُغَلَّفin a membranous envelope (Viral envelope ) الغالف الفيروسي, eg. Influenza virus. ...
... Sometimes further wrapped يُغَلَّفin a membranous envelope (Viral envelope ) الغالف الفيروسي, eg. Influenza virus. ...
Unit 10 Simple Life Forms Chp 18: Viruses Module #3
... 4. Why are viruses not considered “living things” (organisms)? ...
... 4. Why are viruses not considered “living things” (organisms)? ...
File
... a) some may carry oncogenes- genes to send cell cycle out of control b) some viruses may turn on protooncogenes at inappropriate times ...
... a) some may carry oncogenes- genes to send cell cycle out of control b) some viruses may turn on protooncogenes at inappropriate times ...
Virus PowerPoint Notes
... Stanley (1935) isolated __________ of tobacco mosaic virus. Inferred viruses were not truly __________. ...
... Stanley (1935) isolated __________ of tobacco mosaic virus. Inferred viruses were not truly __________. ...
virus4
... 1. Lytic cycle-results in lysis of the cell 2. Lysogenic cycle-may result in lysis of the cell or the virus becomes a permanent part of the chromosome by integrating ...
... 1. Lytic cycle-results in lysis of the cell 2. Lysogenic cycle-may result in lysis of the cell or the virus becomes a permanent part of the chromosome by integrating ...
Viruses and Bacteria
... • Small packages of nucleic acids in a protein coat • Are NOT cells—no cytoplasm and do not perform metabolic reactions • Obligate intracellular parasites— dependent upon other cells for replication ...
... • Small packages of nucleic acids in a protein coat • Are NOT cells—no cytoplasm and do not perform metabolic reactions • Obligate intracellular parasites— dependent upon other cells for replication ...
Foundations in Microbiology
... Survey of DNA Viruses • Animal viruses are categorized according to nucleic acid, capsid, and presence or absence of envelope • 7 DNA viral families • DNA viruses causing human disease: – enveloped DNA viruses – nonenveloped DNA viruses – nonenveloped ssDNA viruses ...
... Survey of DNA Viruses • Animal viruses are categorized according to nucleic acid, capsid, and presence or absence of envelope • 7 DNA viral families • DNA viruses causing human disease: – enveloped DNA viruses – nonenveloped DNA viruses – nonenveloped ssDNA viruses ...
Name Khan academy viruses https://www.khanacademy.org/science
... Why don’t viruses fit into the standard definition of life? Describe several methods by which viruses can enter host cells. What happens when viruses get into a cell? What molecules enter the cells in particular? 5. Why does Sal Kahn say that viruses “hijack” the cell? Explain this hijacking mechani ...
... Why don’t viruses fit into the standard definition of life? Describe several methods by which viruses can enter host cells. What happens when viruses get into a cell? What molecules enter the cells in particular? 5. Why does Sal Kahn say that viruses “hijack” the cell? Explain this hijacking mechani ...
Viruses
... it in by using receptors that are meant to let in something else. (Nutrients, for example) ...
... it in by using receptors that are meant to let in something else. (Nutrients, for example) ...
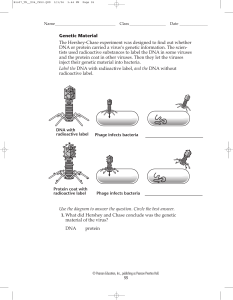
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... DNA or protein carried a virus’s genetic information. The scientists used radioactive substances to label the DNA in some viruses and the protein coat in other viruses. Then they let the viruses inject their genetic material into bacteria. Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without ra ...
... DNA or protein carried a virus’s genetic information. The scientists used radioactive substances to label the DNA in some viruses and the protein coat in other viruses. Then they let the viruses inject their genetic material into bacteria. Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without ra ...
CDC select agent survey form
... fragmented, in host chromosomes or in expression vectors) that have potential to encode infectious and/or replication competent forms of any of the select agent viruses. ____ 2. Nucleic Acids (synthetic or naturally derived, and that are in a vector or host chromosome; can be expressed in vivo or in ...
... fragmented, in host chromosomes or in expression vectors) that have potential to encode infectious and/or replication competent forms of any of the select agent viruses. ____ 2. Nucleic Acids (synthetic or naturally derived, and that are in a vector or host chromosome; can be expressed in vivo or in ...
DNA virus

A DNA virus is a virus that has DNA as its genetic material and replicates using a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase. The nucleic acid is usually double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) but may also be single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). DNA viruses belong to either Group I or Group II of the Baltimore classification system for viruses. Single-stranded DNA is usually expanded to double-stranded in infected cells. Although Group VII viruses such as hepatitis B contain a DNA genome, they are not considered DNA viruses according to the Baltimore classification, but rather reverse transcribing viruses because they replicate through an RNA intermediate. Notable diseases like smallpox, herpes, and chickenpox are caused by such DNA viruses.