* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria and Viruses
Social history of viruses wikipedia , lookup
Oncolytic virus wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Virus quantification wikipedia , lookup
Bacteriophage wikipedia , lookup
Plant virus wikipedia , lookup
Negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to viruses wikipedia , lookup
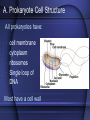
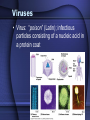
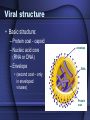
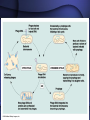
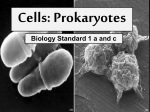
Bacteria and Viruses Bacteria are prokaryotes • Pro – before • Karyon – nucleus • The simplest forms of life • Earth’s first cells Prokaryote Review • Single-celled • No nucleus • No membrane bound organelles • Divided into 2 kingdoms – Archaebacteria – Eubacteria A. Prokaryote Cell Structure All prokaryotes have: • • • • cell membrane cytoplasm ribosomes Single loop of DNA Most have a cell wall Some prokaryotes have: • plasmids • pili • flagella Some prokaryotes form endospores that enable them to survive harsh conditions. Bacteria Shape • Cocci (ball-shaped) • Bacillus (rod-shaped) • Spirilli (spiral-shaped) Bacteria & Disease • Pathogen – a disease causing agent • Bacteria are harmful because they damage their host’s tissues by – A direct attack on the host’s tissue – By releasing poisonous toxins Controlling Bacteria • Pasteurization – heating product to a temperature that will kill most bacteria • Sanitation • Vaccines – a preparation of killed or weakened pathogens introduced into the body to produce immunity • Antibiotics – chemical that destroys or inhibits the growth of bacteria Viruses • Virus: “poison” (Latin); infectious particles consisting of a nucleic acid in a protein coat Viruses • • • • Viruses are not cells. They are not alive Reproduce only within a host cell. They do not have – Enzymes for metabolism – Do not have ribosomes – Do not have the equipment to make proteins Viral structure • Basic structure: – Protein coat - capsid – Nucleic acid core (RNA or DNA) – Envelope envelope RNA • (second coat – only in enveloped viruses) Protein coat Lytic Cycle • Virus attaches to host cell’s membrane and injects its nucleic acid into the host cell. • The viral nucleic acid takes over protein synthesis, creating new viruses. • The host cell bursts, lyses, releasing the newly formed viruses. The Lysogenic Cycle • • • • Replication of the viral genome without destroying the host cell. Virus DNA enters host, becomes part of Hosts DNA. Host Cell copies its DNA and Virus DNA and reproduces normally but passes on Virus DNA to all its offspring. Cell with Virus DNA but not active is called a prophage. Prophage can become active and become lytic at anytime Controlling Viruses • Antibiotics don’t work against viruses – Antibiotics work by interfering with cellular processes such as protein synthesis • Vaccinations – Help build up your immune system – Work well against viruses that don’t mutate