* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viruses
Viral phylodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Social history of viruses wikipedia , lookup
Oncolytic virus wikipedia , lookup
Bacteriophage wikipedia , lookup
Virus quantification wikipedia , lookup
Plant virus wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to viruses wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
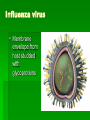
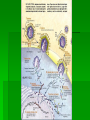
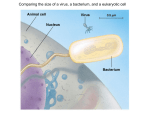
Viruses Chapter 10.17 What you need to know! The components of a virus. The differences between lytic and lysogenic cycles. What’s a Virus? Not a living cell but an infectious particle Obligate intracellular parasite Contains: 1. nucleic acids 2. protein coat Viruses are Tiny Protein Coats-Capsids Capsids are made from proteins called capsomeres Capsids have many different shapes depending on the virus: Rod shape, Helical, Polyhedral, Icosahedral Some viruses will have membrane left from the host cell Tabacco Mosaic Virus Helical capsid with RNA Adenovirus Respiratory virus in animal Polyhedral capsid with glycoprotein spikes Influenza virus Membrane envelope from host studded with glycoproteins Bacteriophages Viruses that infect bacteria icosahedral shape of a phage resembles a lunar landing probe Viral Genome DNA double helix Single stranded DNA Double stranded RNA Single stranded RNA Viral Reproduction Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites Isolated viruses cannot reproduce They lack the ribosomes and enzymes for making proteins Viruses can only infect limited range of host Lytic Cycle Virus infects host cell Cell constructs virus Cell dies and releases the virus Lysogenic Cycle Virus infects host cell Virus nucleic acid hides inside host DNA A stimulus triggers the virus into the Lytic Cycle RNA as genetic material Either used directly as mRNA Or retroviruses deliver an enzyme called “Reverse Transcriptase” that converts RNA into DNA HIV Due to their single strand, RNA viruses mutate a lot HIV – enveloped RNA Virus Attaches only to T-cells (WBC) Translates RNA into DNA, integration into cellular DNA called provirus Provirus DNA is transcribed to make new HIV viruses that leave cell Provirus never leaves cell Immune Response and Vaccinations Body produces antibodies that fit specific virus structure Vaccination are treated versions of the virus that don’t infect and allow the immune system to develop antibodies Example: measles , small pox, Hep B, polio