The Civil War - Social Circle City Schools
... last few in Union hands by the time Lincoln took office. Confederate forces were now demanding that they either surrender or face an attack. With supplies running low Major Anderson wrote to Lincoln for help. What should Lincoln do? ...
... last few in Union hands by the time Lincoln took office. Confederate forces were now demanding that they either surrender or face an attack. With supplies running low Major Anderson wrote to Lincoln for help. What should Lincoln do? ...
our past we leave behind at Sumter" PowerPoint Presentation!
... SLAVE STATES THAT STAY WITH THE UNION LINCOLN SENDS UNION TROOPS INTO BORDER STATES TO PREVENT THEM FROM LEAVING THE UNION. LINCOLN BREAKS THE CONSTITUTION IN ORDER TO SAVE IT – EXCEEDS HIS POWERS MARYLAND VERY STRATEGIC – WASH. D.C ...
... SLAVE STATES THAT STAY WITH THE UNION LINCOLN SENDS UNION TROOPS INTO BORDER STATES TO PREVENT THEM FROM LEAVING THE UNION. LINCOLN BREAKS THE CONSTITUTION IN ORDER TO SAVE IT – EXCEEDS HIS POWERS MARYLAND VERY STRATEGIC – WASH. D.C ...
Reconstruction
... On March 4, 1865, President Lincoln addressed the American public in his second inaugural address. He hoped to reunite the nation and it’s people. He believed that the War was now over, and that the North and South needed to embrace one another. ...
... On March 4, 1865, President Lincoln addressed the American public in his second inaugural address. He hoped to reunite the nation and it’s people. He believed that the War was now over, and that the North and South needed to embrace one another. ...
Civil War 09 ppt
... – Issued the Emancipation Proclamation (January 1, 1863) -had little effect on slavery -slaves would be free in the southern states, when North won the war ...
... – Issued the Emancipation Proclamation (January 1, 1863) -had little effect on slavery -slaves would be free in the southern states, when North won the war ...
File
... “If I could save the Union without freeing any slave I would do it, and if I could save it by freeing all the slaves I would do it; and if I could save it by freeing some and leaving others alone I would also do that.” ~President Abraham Lincoln 1862~ ...
... “If I could save the Union without freeing any slave I would do it, and if I could save it by freeing all the slaves I would do it; and if I could save it by freeing some and leaving others alone I would also do that.” ~President Abraham Lincoln 1862~ ...
Why did Southerners dislike Abraham Lincoln?
... – Richmond replaces Montgomery as capital of Confederacy ...
... – Richmond replaces Montgomery as capital of Confederacy ...
Slavery Divides the Nation, 1820–1861
... territories. • He demanded that fugitive, or runaway, slaves be returned to their owners as lost “property.” • He said that if the North did not agree to these demands, the South would use force to leave the Union. ...
... territories. • He demanded that fugitive, or runaway, slaves be returned to their owners as lost “property.” • He said that if the North did not agree to these demands, the South would use force to leave the Union. ...
Battles of the Civil War PPT
... Declares that all slaves in the rebelling states are to be set free Has little immediate effect on slavery – slaves were freed as the North took back each southern enslaved area [email protected] ...
... Declares that all slaves in the rebelling states are to be set free Has little immediate effect on slavery – slaves were freed as the North took back each southern enslaved area [email protected] ...
secession
... government cannot endure, permanently, half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved — I do not expect the house to fall — but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing or all the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread ...
... government cannot endure, permanently, half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved — I do not expect the house to fall — but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing or all the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread ...
The Politics of Slavery
... The states break apart A month after Lincoln’s election, South Carolina became the first state to secede Within months by Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. ...
... The states break apart A month after Lincoln’s election, South Carolina became the first state to secede Within months by Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. ...
On the Eve of the Civil War
... Harriet Tubman operated the “railroad” for 10 years. 48. Why would enslaved Africans travel north to freedom? How do you know? The slaves wanted their freedom, and the northern states as well as Canada offered it to many of them. Paragraph 5 ...
... Harriet Tubman operated the “railroad” for 10 years. 48. Why would enslaved Africans travel north to freedom? How do you know? The slaves wanted their freedom, and the northern states as well as Canada offered it to many of them. Paragraph 5 ...
Civil War Exam Review: Most Southerners did not own slaves, and
... The battle of Gettysburg took place in Pennsylvania, and was a confederate attack on the Union; the confederates lost and were not able to attack again. It was the turning point. The Confederacy lost Vicksburg and control of the Mississippi River the next day. Lincoln’s number one goal during the Ci ...
... The battle of Gettysburg took place in Pennsylvania, and was a confederate attack on the Union; the confederates lost and were not able to attack again. It was the turning point. The Confederacy lost Vicksburg and control of the Mississippi River the next day. Lincoln’s number one goal during the Ci ...
The Civil War
... • War of attrition: A battle strategy in which one side attempts to win a war by wearing down its enemy to the point of collapse through continuous losses in soldiers and materials. – The war will usually be won by the side with greater resources. – Example: Union victory at Cold Harbor (1864) - Th ...
... • War of attrition: A battle strategy in which one side attempts to win a war by wearing down its enemy to the point of collapse through continuous losses in soldiers and materials. – The war will usually be won by the side with greater resources. – Example: Union victory at Cold Harbor (1864) - Th ...
Standard VUS.7
... he urged Southerners to accept defeat and unite as Americans again, though some wanted to fight on. he engaged in fraudulent negotiations with Grant at Appomattox. he was defiant while being jailed for war crimes before later leaving to live in Canada. ...
... he urged Southerners to accept defeat and unite as Americans again, though some wanted to fight on. he engaged in fraudulent negotiations with Grant at Appomattox. he was defiant while being jailed for war crimes before later leaving to live in Canada. ...
The Furnace of Civil War
... gone far enough – Many Northerners (especially working class and from regions in North close to Mississippi River or Border States) believed he had gone too far – Fall 1862 elections went against Republicans (although they kept control of Congress) – Desertions in Union army increased; soldiers (esp ...
... gone far enough – Many Northerners (especially working class and from regions in North close to Mississippi River or Border States) believed he had gone too far – Fall 1862 elections went against Republicans (although they kept control of Congress) – Desertions in Union army increased; soldiers (esp ...
The Civil War (1861
... • North had economic advantages – Union controlled Treasury & had revenue from tariffs – Many people withdrew silver & gold from banks • Banks could not buy government bonds so they could not pay suppliers or soldiers • Legal Tender Act – created greenbacks ...
... • North had economic advantages – Union controlled Treasury & had revenue from tariffs – Many people withdrew silver & gold from banks • Banks could not buy government bonds so they could not pay suppliers or soldiers • Legal Tender Act – created greenbacks ...
reasons for the civil war
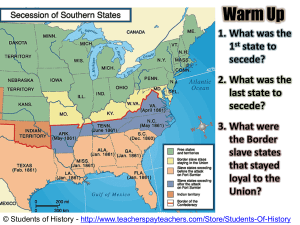
... 1. How were future new states to decide if they entered the Union as a free or slave state? 2. What was the Fugitive Slave Law? 3. How many slave states are there in 1850? 4. How many free states are there in 1850? 5. What evidence is there on the map to show a past compromise? DOCUMENT 2 - Civil Wa ...
... 1. How were future new states to decide if they entered the Union as a free or slave state? 2. What was the Fugitive Slave Law? 3. How many slave states are there in 1850? 4. How many free states are there in 1850? 5. What evidence is there on the map to show a past compromise? DOCUMENT 2 - Civil Wa ...
Gettysburg to Appomattox Presentation
... was all over in 30 minutes with a Confederate retreat back to their hill. • This was the bloodiest battle of the Civil War…Union (23,000) and the Confederates (28,000). • The Confederates made their retreat back to Virginia the very next day. ...
... was all over in 30 minutes with a Confederate retreat back to their hill. • This was the bloodiest battle of the Civil War…Union (23,000) and the Confederates (28,000). • The Confederates made their retreat back to Virginia the very next day. ...
Steps to the Civil War
... of speech by Charles Sumner on floor of Congress. Sir, speaking in an age of light, and in a land of constitutional liberty, where the safeguards of elections are justly placed among the highest triumphs of civilization, I fearlessly assert that the wrongs of much-abused Sicily, thus memorable in hi ...
... of speech by Charles Sumner on floor of Congress. Sir, speaking in an age of light, and in a land of constitutional liberty, where the safeguards of elections are justly placed among the highest triumphs of civilization, I fearlessly assert that the wrongs of much-abused Sicily, thus memorable in hi ...
Issues of the American Civil War

Issues of the American Civil War include questions about the name of the war, the tariff, states' rights and the nature of Abraham Lincoln's war goals. For more on naming, see Naming the American Civil War.The question of how important the tariff was in causing the war stems from the Nullification Crisis, which was South Carolina's attempt to nullify a tariff and lasted from 1828 to 1832. The tariff was low after 1846, and the tariff issue faded into the background by 1860 when secession began. States' rights was the justification for nullification and later secession. The most controversial right claimed by Southern states was the alleged right of Southerners to spread slavery into territories owned by the United States.As to the question of the relation of Lincoln's war goals to causes, goals evolved as the war progressed in response to political and military issues, and can't be used as a direct explanation of causes of the war. Lincoln needed to find an issue that would unite a large but divided North to save the Union, and then found that circumstances beyond his control made emancipation possible, which was in line with his ""personal wish that all men everywhere could be free"".