Unit II Review
... Ablative Various Uses - Most Prepositions (you know ablative of means) NOTE – look at page 62 for a discussion of ways to make sense of –ae endings! ...
... Ablative Various Uses - Most Prepositions (you know ablative of means) NOTE – look at page 62 for a discussion of ways to make sense of –ae endings! ...
Document
... 7. To find the Pr Nom, find the S and LV and find a noun or pronoun after the verb which is a “synonym” for the S. 8. To find the Pr Adj, find the S and LV and find an adjective after the LV which describes the S. ...
... 7. To find the Pr Nom, find the S and LV and find a noun or pronoun after the verb which is a “synonym” for the S. 8. To find the Pr Adj, find the S and LV and find an adjective after the LV which describes the S. ...
Grammar Review
... Write a sentence with a collective noun. Write a sentence with a compound noun. Write a sentence with an abstract noun. Write a sentence that uses a common noun and a proper noun. Write a sentence using at least three different types of nouns. ...
... Write a sentence with a collective noun. Write a sentence with a compound noun. Write a sentence with an abstract noun. Write a sentence that uses a common noun and a proper noun. Write a sentence using at least three different types of nouns. ...
The Most Common Writing Errors
... • There are no such words as: theirself, hisself, alright. Write themselves, himself, all right. • Do not capitalize subjects like biology, math, science, history. • Use the word “finish” instead of “done” • Use “who” when referring to people. • The party would (of, have) made me happy. ...
... • There are no such words as: theirself, hisself, alright. Write themselves, himself, all right. • Do not capitalize subjects like biology, math, science, history. • Use the word “finish” instead of “done” • Use “who” when referring to people. • The party would (of, have) made me happy. ...
The dreaded grammar cards
... Nouns as objects of prepositions Paws, my bird, ate bones from a bowl. (Bowl is the object of the preposition from.) ...
... Nouns as objects of prepositions Paws, my bird, ate bones from a bowl. (Bowl is the object of the preposition from.) ...
Prepositional Phrase: A preposition plus its object and modifiers
... Prepositional Phrase: A preposition plus its object and modifiers. Prepositions To, around, under, over, like, as, behind, with, outside, etc. Prepositional phrases may function as adjectives or as adverbs. Adjective prepositional phrases tell which one, what kind, how many, and how much, or give ot ...
... Prepositional Phrase: A preposition plus its object and modifiers. Prepositions To, around, under, over, like, as, behind, with, outside, etc. Prepositional phrases may function as adjectives or as adverbs. Adjective prepositional phrases tell which one, what kind, how many, and how much, or give ot ...
prepositions
... perfect tense, the main clause verb will be in the perfect conditional tense. (Would + have + V3). Eg :1.If the earthquake had occurred, the people would have left the place. 2. If you had asked me, I would have given the book to you. PARTS OF SPEECH Generally we express our feeling through the sent ...
... perfect tense, the main clause verb will be in the perfect conditional tense. (Would + have + V3). Eg :1.If the earthquake had occurred, the people would have left the place. 2. If you had asked me, I would have given the book to you. PARTS OF SPEECH Generally we express our feeling through the sent ...
GSP – Grammar 3 person singular with regular verbs
... Nouns are singular or plural and so to are verbs – this means they have to match when a verb is used alongside a noun. ...
... Nouns are singular or plural and so to are verbs – this means they have to match when a verb is used alongside a noun. ...
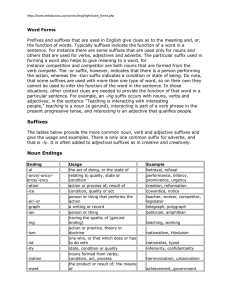
Word Forms - Professor Catherine Hatzakos
... Prefixes and suffixes that are used in English give clues as to the meaning and, or, the function of words. Typically suffixes indicate the function of a word in a sentence. For instance there are some suffixes that are used only for nouns and others that are used for verbs, adjectives and adverbs. ...
... Prefixes and suffixes that are used in English give clues as to the meaning and, or, the function of words. Typically suffixes indicate the function of a word in a sentence. For instance there are some suffixes that are used only for nouns and others that are used for verbs, adjectives and adverbs. ...
Seventh Grade English Memorization Lists
... A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun or a pronoun and another word in the sentence. Megan walked beside the lake. Megan walked to the lake. Memorize the prepositions, below. “The Preposition Song,” sung to the tune of “Yankee Doodle,” includes many, but not all, of the ...
... A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun or a pronoun and another word in the sentence. Megan walked beside the lake. Megan walked to the lake. Memorize the prepositions, below. “The Preposition Song,” sung to the tune of “Yankee Doodle,” includes many, but not all, of the ...
Non-Fiction Study Guide
... “Autumn leads into the hibernation of winter, setting the perfect mood for us quiet types.” *If you need additional practice in preparation for this quiz, you should refer to the following pages in your Writing and Grammar books. Nouns pp. 1, 5 (people, places, things, common and proper) Verbs pp. 1 ...
... “Autumn leads into the hibernation of winter, setting the perfect mood for us quiet types.” *If you need additional practice in preparation for this quiz, you should refer to the following pages in your Writing and Grammar books. Nouns pp. 1, 5 (people, places, things, common and proper) Verbs pp. 1 ...
Grammar Notes: ”Parts of Speech”
... person), the one spoken to (second person), or the one spoken about (third person). – FIRST PERSON: • I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours ...
... person), the one spoken to (second person), or the one spoken about (third person). – FIRST PERSON: • I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours ...
WORD CLASSES, SENTENCE STRUCTURE and TERMINOLOGY
... A Phrase ~ does not have a verb watching the sun burn in the sky when I actually got there ...
... A Phrase ~ does not have a verb watching the sun burn in the sky when I actually got there ...
Parts of Speech - St. John's High School
... Takes the place of one or more nouns or pronouns; should agree in number and in gender with its antecedent. antecedent – the word or word group that a pronoun stands for. Types of pronouns - personal pronoun – refers to the one(s) speaking (first person), the one(s) spoken to (second person), ...
... Takes the place of one or more nouns or pronouns; should agree in number and in gender with its antecedent. antecedent – the word or word group that a pronoun stands for. Types of pronouns - personal pronoun – refers to the one(s) speaking (first person), the one(s) spoken to (second person), ...
A Brief Summary of the Latin Noun as Presented in Unit 1 of the
... At this point in your study, you have learned three different cases: the nominative, the accusative, and the dative. These three cases play the grammatical roles outlined below. NOMINATIVE Case: indicates either the Subject or the Subjective Complement of the Verb. The Subjective Complement may be e ...
... At this point in your study, you have learned three different cases: the nominative, the accusative, and the dative. These three cases play the grammatical roles outlined below. NOMINATIVE Case: indicates either the Subject or the Subjective Complement of the Verb. The Subjective Complement may be e ...
The Parts of Speech in English
... The Parts of Speech in English English grammar books usually refer to the 8 Parts of Speech: Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Adverbs, Verbs, Conjunctions, Prepositions, and Interjections. Why do YOU need to know the parts of speech? If you do not know what part of speech a word is, you are more likely ...
... The Parts of Speech in English English grammar books usually refer to the 8 Parts of Speech: Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Adverbs, Verbs, Conjunctions, Prepositions, and Interjections. Why do YOU need to know the parts of speech? If you do not know what part of speech a word is, you are more likely ...
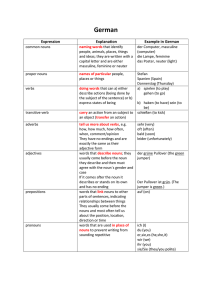
German - Crofton School
... tell us more about verbs, e.g. how, how much, how often, when, comment/opinion They have no endings and are exactly the same as their adjective form words that describe nouns; they usually come before the noun they describe and then must agree with the noun´s gender and case If it comes after the no ...
... tell us more about verbs, e.g. how, how much, how often, when, comment/opinion They have no endings and are exactly the same as their adjective form words that describe nouns; they usually come before the noun they describe and then must agree with the noun´s gender and case If it comes after the no ...
Nouns
... Prepositions formed from more than one word Examples: according to, in place of, because of, and instead of, ...
... Prepositions formed from more than one word Examples: according to, in place of, because of, and instead of, ...
Parts of Speech
... Parts of speech are the basic categories of words or word “families” that exist in the English language. ...
... Parts of speech are the basic categories of words or word “families” that exist in the English language. ...
Parts of Speech
... (near in space or time) that, those (distant in space or time) A relative pronoun introduces a subordinate clause. Ex: who, whom, which, what, that ...
... (near in space or time) that, those (distant in space or time) A relative pronoun introduces a subordinate clause. Ex: who, whom, which, what, that ...
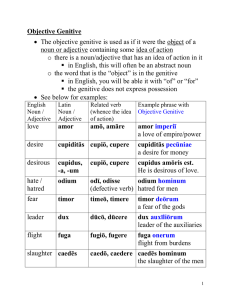
Objective Genitive + Ablative Separation
... Objective Genitive The objective genitive is used as if it were the object of a noun or adjective containing some idea of action o there is a noun/adjective that has an idea of action in it in English, this will often be an abstract noun o the word that is the “object” is in the genitive in En ...
... Objective Genitive The objective genitive is used as if it were the object of a noun or adjective containing some idea of action o there is a noun/adjective that has an idea of action in it in English, this will often be an abstract noun o the word that is the “object” is in the genitive in En ...
Nothing but Nouns
... They take the place of nouns. *See what I did there? They takes place of the noun pronoun. ...
... They take the place of nouns. *See what I did there? They takes place of the noun pronoun. ...