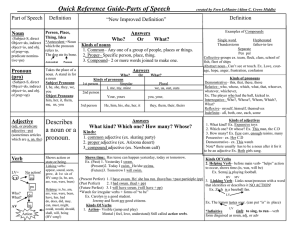
How to determine the part of speech of a word
... that, if, whether These introduce subordinate clauses (sentences inside sentences). Examples: She said that she was going, I wonder if you are going, I wonder whether you are going. Pronouns Nominative I you he she it we they ...
... that, if, whether These introduce subordinate clauses (sentences inside sentences). Examples: She said that she was going, I wonder if you are going, I wonder whether you are going. Pronouns Nominative I you he she it we they ...
Year 3 - Crossley Fields
... modal verbs, they are often used to avoid being too definite when making a point. They help to ‘cover’ the speaker/writer by suggesting that you cannot be sure of a fact, or there may be some exceptions to the point being made. For example: ‘CO2 emissions are probably a major cause of global warming ...
... modal verbs, they are often used to avoid being too definite when making a point. They help to ‘cover’ the speaker/writer by suggesting that you cannot be sure of a fact, or there may be some exceptions to the point being made. For example: ‘CO2 emissions are probably a major cause of global warming ...
Describes a noun or a pronoun.
... A. Begin at once. (a command subject is always You) B. Will Drew start soon? Drew will start soon. (change so it’s not a question) C. There is my book. My book is there. (flip it!) Direct Object—noun or pronoun (do): Find AV (transitive verb) and ask Who? Or What? Ex. Molly and Melanie asked a quest ...
... A. Begin at once. (a command subject is always You) B. Will Drew start soon? Drew will start soon. (change so it’s not a question) C. There is my book. My book is there. (flip it!) Direct Object—noun or pronoun (do): Find AV (transitive verb) and ask Who? Or What? Ex. Molly and Melanie asked a quest ...
Information for parents: Grammar and punctuation in the new
... A prefix is added at the beginning of a word in order to turn it into another word. A preposition links a following noun, pronoun or noun phrase to some other word in the sentence. Prepositions often describe locations or directions, but can describe other things, such as relations of time. Words li ...
... A prefix is added at the beginning of a word in order to turn it into another word. A preposition links a following noun, pronoun or noun phrase to some other word in the sentence. Prepositions often describe locations or directions, but can describe other things, such as relations of time. Words li ...
Parts of Speech - Moore Middle School
... between two (or more) things in a sentence. Prepositions can show where things are in relationship to each other, or how two things are related to each other. HINT: Prepositions are usually found hiding between nouns in a sentence. Examples: There is a treasure under the bridge. You should eat a ...
... between two (or more) things in a sentence. Prepositions can show where things are in relationship to each other, or how two things are related to each other. HINT: Prepositions are usually found hiding between nouns in a sentence. Examples: There is a treasure under the bridge. You should eat a ...
Grammar – A unit
... This ice cream is for you and I This homework is for she and him. I went swimming with you and they. Possessive Pronouns – a pronoun that shows possession (duh!), used as both a pronoun and an adjective – my, your, his, her, its, our their ...
... This ice cream is for you and I This homework is for she and him. I went swimming with you and they. Possessive Pronouns – a pronoun that shows possession (duh!), used as both a pronoun and an adjective – my, your, his, her, its, our their ...
KEY P. 1
... b. 440.1: the genitive / ‘s structure is used to talk about possessions, relationships etc. when the first noun refers to a person 495.2: the relative clause follows immediately after the noun it modifies 495.1: we use a non-restrictive / non-identifying relative clause when we simply give more info ...
... b. 440.1: the genitive / ‘s structure is used to talk about possessions, relationships etc. when the first noun refers to a person 495.2: the relative clause follows immediately after the noun it modifies 495.1: we use a non-restrictive / non-identifying relative clause when we simply give more info ...
the basics
... Verb phrase- a main verb and its helping verbs The snow has been falling for three days. Gerund phraseGerund-verb ending in –ing; acts as subject, DO, OP, and PN The boy escaped his brother by hiding under his bed. Infinitive phraseInfinitive-verb form that begins with the word to and functions as a ...
... Verb phrase- a main verb and its helping verbs The snow has been falling for three days. Gerund phraseGerund-verb ending in –ing; acts as subject, DO, OP, and PN The boy escaped his brother by hiding under his bed. Infinitive phraseInfinitive-verb form that begins with the word to and functions as a ...
-ing forms in English
... I am talking to you right now. (present progressive or present continuous) I have been thinking a lot about this decision. (present perfect progressive or present perfect continuous) You were already sleeping. (past progressive or past continuous) I will be taking my friend to the airport. (future p ...
... I am talking to you right now. (present progressive or present continuous) I have been thinking a lot about this decision. (present perfect progressive or present perfect continuous) You were already sleeping. (past progressive or past continuous) I will be taking my friend to the airport. (future p ...
The Phrase - Net Start Class
... Notes on Phrases A phrase is a group of words that functions as a single part of speech. A phrase does not have a subject and a verb (BK book page L173). Why don’t you go with Jennifer? ( with Jennifer is a phrase because it does not have a subject and a verb). Prepositional Phrases : A prepositiona ...
... Notes on Phrases A phrase is a group of words that functions as a single part of speech. A phrase does not have a subject and a verb (BK book page L173). Why don’t you go with Jennifer? ( with Jennifer is a phrase because it does not have a subject and a verb). Prepositional Phrases : A prepositiona ...
A - Parts of Sentence Intro 11
... Follow the chart on the second page of the DGP notes for help APPOSITIVE - noun or pronoun that follows or renames another noun/pronoun. Ex. My son Beck likes trains. (place an = sign) ...
... Follow the chart on the second page of the DGP notes for help APPOSITIVE - noun or pronoun that follows or renames another noun/pronoun. Ex. My son Beck likes trains. (place an = sign) ...
Glossary of Grammatical Terms
... Tim, who always washes his hands before he eats, knows cleanliness is good for him. ...
... Tim, who always washes his hands before he eats, knows cleanliness is good for him. ...
Lect. 7 The Syntax of English
... Information is useful. The information is useful. An information is useful(wrong) ...
... Information is useful. The information is useful. An information is useful(wrong) ...
Grammar wrap-up — Verbs, Adverbs, and Prepositions I realized
... Irish has only four tenses, one “mood” and one “voice”, those being: Present Habitual, Simple Past, Past Habitual, and Future tenses; Conditional Mood (if-then / would), and Subjunctive Voice (hope / curse). In our western dialect we only have a few personal pronoun endings to worry about when conju ...
... Irish has only four tenses, one “mood” and one “voice”, those being: Present Habitual, Simple Past, Past Habitual, and Future tenses; Conditional Mood (if-then / would), and Subjunctive Voice (hope / curse). In our western dialect we only have a few personal pronoun endings to worry about when conju ...
Verbals
... Shelly needs someone to advise her. (“to advise” is an adjective modifying “someone”) Greg is afraid to talk to Jessica (“to talk” is an adverb modifying “afraid”) ...
... Shelly needs someone to advise her. (“to advise” is an adjective modifying “someone”) Greg is afraid to talk to Jessica (“to talk” is an adverb modifying “afraid”) ...
GrammarNotes
... • Adverbs – tell us how, where, or when something happens. – Ex: The hockey season starts soon (when). – Later, I will take the class outside (where) for ice cream. • Comparative form – compares two actions, add the ending –er or use the word more. – Ex: Professional artists draw better than the maj ...
... • Adverbs – tell us how, where, or when something happens. – Ex: The hockey season starts soon (when). – Later, I will take the class outside (where) for ice cream. • Comparative form – compares two actions, add the ending –er or use the word more. – Ex: Professional artists draw better than the maj ...
Parts of Speech
... Noun: a word that represents person, place, or thing. Inside of a sentence, a noun can serve as a subject, an object, or a part of a phrase. Some nouns are harder-to-define objects such as emotions, countries, and ideals (justice, for instance). For instance, patriotism, or love of one’s country, is ...
... Noun: a word that represents person, place, or thing. Inside of a sentence, a noun can serve as a subject, an object, or a part of a phrase. Some nouns are harder-to-define objects such as emotions, countries, and ideals (justice, for instance). For instance, patriotism, or love of one’s country, is ...
Verbals Handout
... Traveling might satisfy your desire for new experiences. (subject) They do not appreciate my singing. (direct object) Birds can escape from dangers by flying. (object of the preposition) ...
... Traveling might satisfy your desire for new experiences. (subject) They do not appreciate my singing. (direct object) Birds can escape from dangers by flying. (object of the preposition) ...
phrases - Thought
... • Few of the villagers had ever been there before. • The girl with the trumpet in the next house keeps us awake. ...
... • Few of the villagers had ever been there before. • The girl with the trumpet in the next house keeps us awake. ...
nouns, pronouns, and adjectives
... 3. As an appositive. An appositive is a word or phrase that identifies, explains, or gives information about the sentence. It is set off from the rest of the sentence by commas. An appositive is not needed to make the sentence complete. Ex: Tokyo, the capital of Japan, is a crowded city. 4. To show ...
... 3. As an appositive. An appositive is a word or phrase that identifies, explains, or gives information about the sentence. It is set off from the rest of the sentence by commas. An appositive is not needed to make the sentence complete. Ex: Tokyo, the capital of Japan, is a crowded city. 4. To show ...