* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of Speech
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kagoshima verb conjugations wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
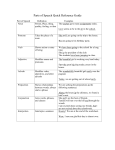
Parts of Speech Noun: a word that represents person, place, or thing. Inside of a sentence, a noun can serve as a subject, an object, or a part of a phrase. Some nouns are harder-to-define objects such as emotions, countries, and ideals (justice, for instance). For instance, patriotism, or love of one’s country, is a noun. The –ism ending on “patriotism” shows that the word is a noun. Subjects in sentences can be difficult to locate under certain conditions. The following link may provide some helpful tips to understand and locate the subject of a sentence: http://grammar.ccc.commnet.edu/grammar/subjects.htm To open the link, hold down the CTRL key and click on the link at the same time. If this method (CTRL + click) doesn’t work, copy and paste the link directly into your internet search browser. Pronoun: a “replacement” noun, a word that serves as an ambassador for a noun. There are many different types of pronouns; the most common pronouns are “I”, “he”, or “she” (subject pronouns) and “me”, “him”, or “her” (object pronouns). Adjective: a word that modifies—describes or limits—a noun or pronoun (Example: “That was an “excellent” paragraph.” The adjective “excellent” modifies the noun paragraph.) Adverb: a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. (Example: “You have done “ well” on the test.” The adverb “well” modifies the verb have done.) Verb: a word that shows action or a state of being (forms of “to be” used as linking verbs). For example, read the following sentence: “Jim and Brady practice football and watch games on the weekends.” Both “practice” and “watch” are verbs. Another example of a verb is a linking verb. You can test whether a verb is a linking verb by substituting the word for an = sign. Other verbs are helping verbs (or auxiliary verbs); helping verbs occur in sentences with other verbs, combining to create verb tenses. Linking verb example: “Jaleesa is adventurous.” Using the linking verb test, “Jaleesa = adventurous”, as a formula, is logical. Therefore, the “is” in this sentence is a linking verb. Helping verb example: “Jaleesa is practicing for her debate.” Here, the “is” does not function the same way. Preposition: a word that states a relationship between one noun and another. In Real Writing, there is a good definition of this term with examples in Chapter 21. Article: a word that behaves like a descriptive word and helps define a noun. There are different types of articles. Interjection: this part of speech acts to express surprise or strong emotion. The following sentence begins with an interjection: “Alas, the store is out of marzipan.” The interjection “alas” shows the emotion of regret in a way that is mild. Regard the following sentences for a stronger emotional interjection example: “The store is out of marzipan. Alas!” Notice that the interjection “alas” is set as a complete thought.